Regional Sustainability ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (1): 73-82.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2021.01.005cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2021.01.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Shuhong Yanga,b, Tao Yanga,c,*( )
)
Received:2020-06-09
Revised:2021-01-12
Accepted:2021-01-28
Published:2021-01-20
Online:2021-03-11
Contact:
Tao Yang
E-mail:tao.yang@hhu.edu.cn
Shuhong Yang, Tao Yang. Exploration of the dynamic water resource carrying capacity of the Keriya River Basin on the southern margin of the Taklimakan Desert, China[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(1): 73-82.
Table 1
Partitioning of water resource region in the Keriya River Basin."
| Sub-region | Distribution | Area (×104 hm2) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| IV-1 | Middle and upper reaches of the Keriya River Basin | 83.82 | Areas above the Nunumaimaitilangan Hydrological Station |
| IV-2 | Irrigation area in the lower reach of the Keriya River Basin | 4.85 | Areas below the Nunumaimaitilangan Hydrological Station |
| IV-3 | Oasis area in the lower reach of the Keriya River Basin | 277.23 | Areas downstream of the Keriya River Basin entering deserts |
| IV-4 | River areas in the east of the Keriya River Basin | 17.71 | Aqiang River, Pishge River, and Tamiya River |
| Total | 383.61 | ||
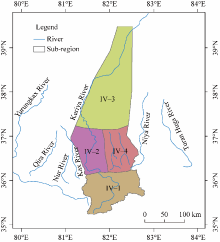
Fig. 1.
Location of the study area and distribution of water resource sub-region in the Keriya River Basin. IV-1, middle and upper reaches of the Keriya River Basin; IV-2, irrigation area in the lower reach of the Keriya River Basin; IV-3, oasis area in the lower reach of the Keriya River Basin; and IV-4, river areas in the east of the Keriya River Basin."
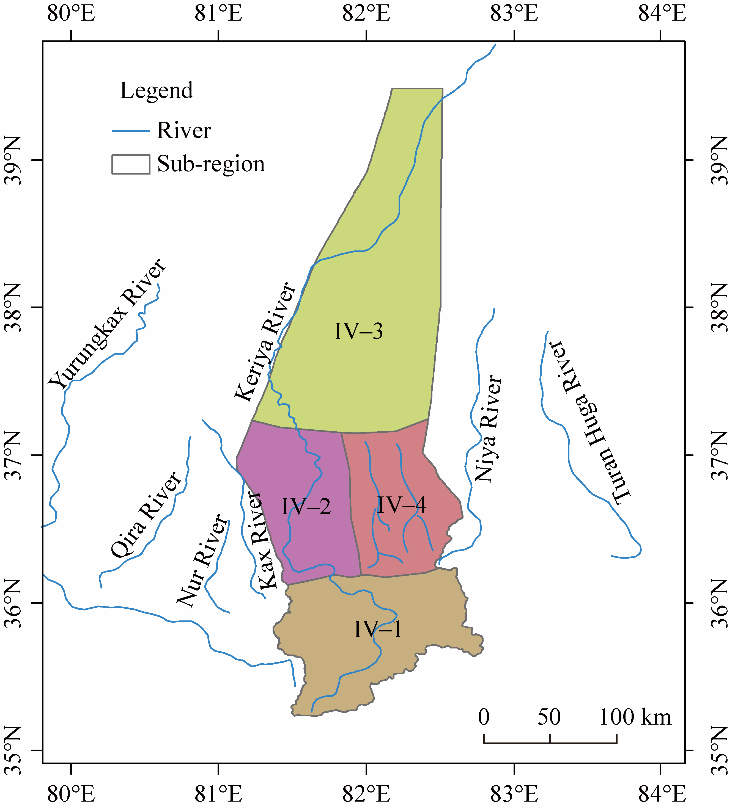
Table 2
Calculation results of the dynamic water resource carrying capacity in the current year (2015), the short term (2020), the middle term (2030), and the long term (2050)."
| Year | Scenario | Population (×105) | Cultivated land area (×104 hm2) | Industrial added value (×108 CNY) | Carrying capacity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual/Predicted | Bearable | Actual/Predicted | Bearable | Actual/Predicted | Bearable | |||
| 2015 | RCP2.6 | 2.82 | 3.32 | 3.36 | 3.99 | 5.52 | 6.52 | 0.85 |
| RCP4.5 | 2.82 | 3.32 | 3.36 | 3.97 | 5.52 | 6.41 | 0.85 | |
| RCP8.5 | 2.82 | 3.35 | 3.36 | 4.00 | 5.52 | 6.73 | 0.83 | |
| 2020 | RCP2.6 | 3.09 | 3.61 | 3.69 | 4.41 | 8.66 | 10.67 | 0.83 |
| RCP4.5 | 3.09 | 3.69 | 3.69 | 4.42 | 8.66 | 10.48 | 0.83 | |
| RCP8.5 | 3.09 | 3.65 | 3.69 | 4.42 | 8.66 | 10.39 | 0.84 | |
| 2030 | RCP2.6 | 3.80 | 5.12 | 4.54 | 6.19 | 30.19 | 42.13 | 0.73 |
| RCP4.5 | 3.80 | 5.19 | 4.54 | 6.20 | 30.19 | 42.66 | 0.72 | |
| RCP8.5 | 3.80 | 5.14 | 4.54 | 6.18 | 30.19 | 41.94 | 0.73 | |
| 2050 | RCP2.6 | 4.64 | 7.38 | 5.54 | 8.49 | 72.82 | 111.05 | 0.64 |
| RCP4.5 | 4.64 | 7.43 | 5.54 | 8.56 | 72.82 | 112.78 | 0.64 | |
| RCP8.5 | 4.64 | 7.40 | 5.54 | 8.47 | 72.82 | 111.29 | 0.64 | |
| [1] | Cheng, Q., Zuo, X., Zhong, F., 2019. Evaluation of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. In: AGU Fall Meeting. |
| [2] | Editing Commission of the Third National Report on Climate Change of China, 2011. The Second National Report on Climate Change. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese). |
| [3] | Gao, X.J., Shi, Y., Song, R.Y., et al., 2008. Reduction of future monsoon precipitation over China: Comparison between a high resolution RCM simulation and the driving GCM. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 100, 73-86. |
| [4] | Hariyanto, B., 2017. The carrying capacity ratio (CCR) analysis of meteoric water resources at the Middle East Java region. Adv. Sci. Lett. 23(12), 11678-11682. |
| [5] | IPCC, 2007. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I. Contribution to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [6] | IPCC, 2014. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I. Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [7] |
Jonathan, H.M., 1999. Carrying capacity in agriculture: globe and regional issue. Ecol. Econ. 29(3), 443-461.
doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(98)00089-5 |
| [8] | Kang, J., Zi, X., Wang, S., et al., 2019. Evaluation and optimization of agricultural water resources carrying capacity in Haihe River Basin, China. Water. 11(5), 999. |
| [9] | Li, S., Liu, B., 2019. Research on Water Resources Carrying Capacity Based on ET. In: Dong W., Lian Y., Zhang Y. (eds) Sustainable Development of Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering in China. Environ. Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61630-8_31 |
| [10] | Men, B., Liu, H., Tian, W., et al., 2019. The impact of reservoirs on runoff under climate change: a case of Nierji reservoir in China. Water. 11(5), 1005. |
| [11] | Ministry of Water Resource of Xinjiang, 2016. Hotan District Water Resources Bulletin, Hotan: Hotan District Press (in Chinese). |
| [12] | Nogueira, M., 2019. The sensitivity of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle to temperature fluctuations at synoptic to decadal time-scales in different satellite-and model-based products. Clim. Dyn. 52(1-2), 617-636. |
| [13] | Peng, T., Deng, H., 2020. Comprehensive evaluation on water resource carrying capacity based on DPESBR framework: A case study in Guiyang, southwest China. J. Clean Prod. 122235. |
| [14] |
Shi, Y., Gao, X.J., Wang, Y.G., et al., 2009. Simulation and projection of monsoon rainfall and rain patterns over eastern China under global warming by RegCM3. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters. 2(5), 308-313.
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2009.11446816 |
| [15] | Shi, Y., Gao, X.J., Filippo, G., et al., 2010. High resolution simulation of changes in different-intensity precipitation events over China under global warming. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 6(3), 164-169. |
| [16] | Song, F., Yang, X., Wu, F., 2018. Catastrophe progression method based on MK test and correlation analysis for assessing water resources carrying capacity in Hubei province. J. Water Clim. Chang. 11(2), 556-567. |
| [17] | Song, R.Y., Gao, X.J., Shi, Y., 2008. Simulation of changes in cold events in southern China under global warming. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 4(6), 352-3563. |
| [18] | Song, X., Kong, F., Zhan, C., 2011. Assessment of water resources carrying capacity in Tianjin City of China. Water Resour. Manag. 25(3), 857-873. |
| [19] | Tukimat, N.N.A., Harun, S., 2019. Comparative study on the reservoir operation planning with the climate change adaptation. SN Applied Sciences. 1(11), 1449. |
| [20] |
Wang, C., Hou, Y., Xue, Y., 2017. Water resources carrying capacity of wetlands in Beijing: Analysis of policy optimization for urban wetland water resources management. J. Clean Prod. 161, 1180-1191.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.204 |
| [21] | Wang, L., Wang, Z., Liu, X., 2018. Water resources carrying capacity analysis of YarLung Tsangpo River Basin (I). Water. 10(9), 1131. |
| [22] | Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Su, X., et al., 2019. Evaluation of the comprehensive carrying capacity of interprovincial water resources in China and the spatial effect. J. Hydrol. 575, 794-809. |
| [23] | Wang, Z., Luo, Y., Zhang, M., 2014. Quantitative evaluation of sustainable development and eco-environmental carrying capacity in water-deficient regions: a case study in the Haihe River Basin, China. J. Integr. Agric. 13(1), 195-206. |
| [24] | Wei, X., Wang, J., Wu, S., et al., 2019. Comprehensive evaluation model for water environment carrying capacity based on VPOSRM framework: A case study in Wuhan, China. Sust. Cities Soc. 50, 101640. |
| [25] | Wu, X., Hu, F., 2020. Analysis of ecological carrying capacity using a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. Ecol. Indic. 113, 106243. |
| [26] |
Yang, Z., Song, J., Cheng, D., et al., 2019. Comprehensive evaluation and scenario simulation for the water resources carrying capacity in Xi’an city, China. J. Environ. Manage. 230, 221-233.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.085 pmid: 30290309 |
| [27] | Yi, L., Yang, Y.Z., Yan, H.M., et al., 2018. Research methods of water resources carrying capacity: progress and prospects. Journal of Resources and Ecology. 9(5), 455-460 (in Chinese). |
| [28] | Yu, Y., Markus, D., Yu, R.D., et al., 2015. Large-scale hydrological modeling and decision-making for agricultural water consumption and allocation in the main stem Tarim River, China. Water. 7(6), 2821-2839 |
| [29] | Yu, Y., Chen, X., Yu, R.D., et al., 2017. Agricultural water allocation strategies along the oasis of Tarim River in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manage. 187, 24-36. |
| [30] | Zhang, X.Y., Zuo, Q.T., 2012. A study on concept of water resource carrying capacity under climate change and its computing methods. Yellow River. 34(10), 12-13 (in Chinese). |
| [31] | Zuo, Q.T., 2005. Urban Water Resources Carrying Capacity: Theory, Method and Application. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press (in Chinese). |
| [32] | Zuo, Q.T., 2017. Review of research methods of water resources carrying capacity. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources. 37(3), 1-6 (in Chinese). |
| [1] | Issa NYASHILU, Robert KIUNSI, Alphonce KYESSI. Climate change vulnerability assessment in the new urban planning process in Tanzania [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100155-. |
| [2] | Homayoon RAOUFI, Hamidreza JAFARI, Wakil Ahmad SARHADI, Esmail SALEHI. Assessing the impact of climate change on agricultural production in central Afghanistan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100156-. |
| [3] | Frank BAFFOUR-ATA, Louisa BOAKYE, Moses Tilatob GADO, Ellen BOAKYE-YIADOM, Sylvia Cecilia MENSAH, Senyo Michael KWAKU KUMFO, Kofi Prempeh OSEI OWUSU, Emmanuel CARR, Emmanuel DZIKUNU, Patrick DAVIES. Climatic and non-climatic factors driving the livelihood vulnerability of smallholder farmers in Ahafo Ano North District, Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100157-. |
| [4] | SONG Boyi, ZHANG Shihang, LU Yongxing, GUO Hao, GUO Xing, WANG Mingming, ZHANG Yuanming, ZHOU Xiaobing, ZHUANG Weiwei. Characteristics and drivers of the soil multifunctionality under different land use and land cover types in the drylands of China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100162-. |
| [5] | Camillus Abawiera WONGNAA, Alex Amoah SEYRAM, Suresh BABU. A systematic review of climate change impacts, adaptation strategies, and policy development in West Africa [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100137-. |
| [6] | Debanjan BASAK, Indrajit Roy CHOWDHURY. Role of self-help groups on socioeconomic development and the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) among rural women in Cooch Behar District, India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100140-. |
| [7] | Suchitra PANDEY, Geetilaxmi MOHAPATRA, Rahul ARORA. Spatio-temporal variation of depth to groundwater level and its driving factors in arid and semi-arid regions of India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100143-. |
| [8] | Ramya Kundayi RAVI, Priya BABY, Nidhin ELIAS, Jisa George THOMAS, Kathyayani Bidadi VEERABHADRAIAH, Bharat PAREEK. Preparedness, knowledge, and perception of nursing students about climate change and its impact on human health in India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100116-. |
| [9] | Ashma SUBEDI, Nani RAUT, Smriti GURUNG. How Himalayan communities are changing cultivation practices in the context of climate change [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 378-389. |
| [10] | Liton Chandra VOUMIK, Md. Hasanur RAHMAN, Md. Maznur RAHMAN, Mohammad RIDWAN, Salma AKTER, Asif RAIHAN. Toward a sustainable future: Examining the interconnectedness among Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), urbanization, trade openness, economic growth, and energy usage in Australia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 405-415. |
| [11] | Rula AWAD, Hosam TITI, Aziza MOHAMED-BRAHMI, Mohamed JAOUAD, Aziza GASMI-BOUBAKER. Small ruminant value chain in Al-Ruwaished District, Jordan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 416-424. |
| [12] | WU Fan, LIANG Youjia, LIU Lijun, YIN Zhangcai, HUANG Jiejun. Identifying eco-functional zones on the Chinese Loess Plateau using ecosystem service bundles [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 425-440. |
| [13] | Girma TILAHUN, Amare BANTIDER, Desalegn YAYEH. Synergies and trade-offs of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practices selected by smallholder farmers in Geshy watershed, Southwest Ethiopia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 129-138. |
| [14] | Kalamkas NURALINA, Raissa BAIZHOLOVA, Natalya ALEKSANDROVA, Viktor KONSTANTINOV, Alexander BIRYUKOV. Socio-economic development of countries based on the Composite Country Development Index (CCDI) [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 115-128. |
| [15] | Enoch YELELIERE, Philip ANTWI-AGYEI, Frank BAFFOUR-ATA. Impacts of climate change on the yields of leguminous crops in the Guinea Savanna agroecological zone of Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 139-149. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号