Regional Sustainability ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 100247.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2025.100247cstr: 32279.14.REGSUS.2025027
• Full Length Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Olani Bekele SAKILUa,b, CHEN Haiboa,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-17
Accepted:2025-08-13
Published:2025-08-30
Online:2025-09-15
Contact:
CHEN Haibo
E-mail:hbchen@ujs.edu.cn
Olani Bekele SAKILU, CHEN Haibo. Exploring the influence of trade openness, energy consumption, natural resource rents, and human capital in achieving carbon neutrality[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(4): 100247.
Table 1
Descriptions of the variables and data sources."
| Variable | Abbreviation | Description | Unit | Supporting literature | Data sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 emissions | CO2 | t | Huang et al. ( | World Development Indicators ( | |
| Export | EXP | Percentage of export of goods and services in the gross domestic product (GDP) | % | Mahmood ( | World Development Indicators ( |
| Import | IMP | Percentage of import of goods and services in the GDP | % | Mukhtarov et al. ( | World Development Indicators ( |
| Renewable energy consumption | RNE | Percentage of renewable energy consumption in the total energy consumption | % | Amin and Song ( | World Development Indicators ( |
| Fossil fuel consumption | FEC | Percentage of fossil fuel consumption in the total energy consumption | % | Raghutla and Chittedi ( | World Development Indicators ( |
| Natural resource rents | NR | Percentage of the total natural resource rents in GDP | % | Zhang et al. ( | World Development Indicators ( |
| Human capital | HC | Years of education received | a | Jahanger et al. ( | Penn World Table (PWT) ( |
Table 2
Descriptive statistic results of the variables."
| Variable | Mean | Standard deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnCO2 | 12.119 | 1.576 | 7.962 | 16.208 | 0.027 | 3.162 |
| lnEXP | 3.265 | 0.539 | 1.907 | 4.798 | 0.301 | 3.218 |
| lnIMP | 3.300 | 0.487 | 1.940 | 4.611 | 0.399 | 3.201 |
| lnRNE | 2.455 | 1.850 | -4.605 | 4.329 | -2.413 | 9.154 |
| lnFEC | 4.330 | 0.235 | 3.289 | 4.605 | -0.966 | 3.851 |
| NR | 0.805 | 1.181 | 0.000 | 8.809 | 2.695 | 14.146 |
| HC | 2.301 | 0.437 | 1.327 | 3.434 | 0.084 | 2.656 |
Table 3
Results of correlation test for the variables."
| Variable | lnCO2 | lnEXP | lnIMP | lnRNE | lnFEC | NR | HC | VIF | Tolerance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnCO2 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| lnEXP | -0.172 | 1.000 | 1.27 | 0.79 | |||||
| lnIMP | -0.357 | 0.900 | 1.000 | 1.01 | 0.99 | ||||
| lnRNE | -0.237 | -0.312 | -0.115 | 1.000 | 1.91 | 0.52 | |||
| lnFEC | 0.357 | 0.232 | 0.133 | -0.646 | 1.000 | 1.75 | 0.57 | ||
| NR | 0.025 | 0.280 | 0.170 | -0.307 | 0.168 | 1.000 | 1.24 | 0.81 | |
| HC | 0.231 | 0.372 | 0.220 | -0.171 | 0.187 | 0.335 | 1.000 | 1.25 | 0.80 |
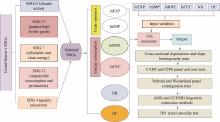
Fig. 2.
Conceptual framework of this study. SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; EXP, export; IMP, import; RNE, renewable energy consumption; FEC, fossil fuel consumption; NR, natural resource rents; HC, human capital; CIPS, Cross-Sectional Im, Pesaran, and Shin; CADF, Cross-Sectional Augmented Dickey-Fuller; AMG, augmented mean group; CCEMG, common correlated effects mean group; DH, Dumitrescu and Hurlin."
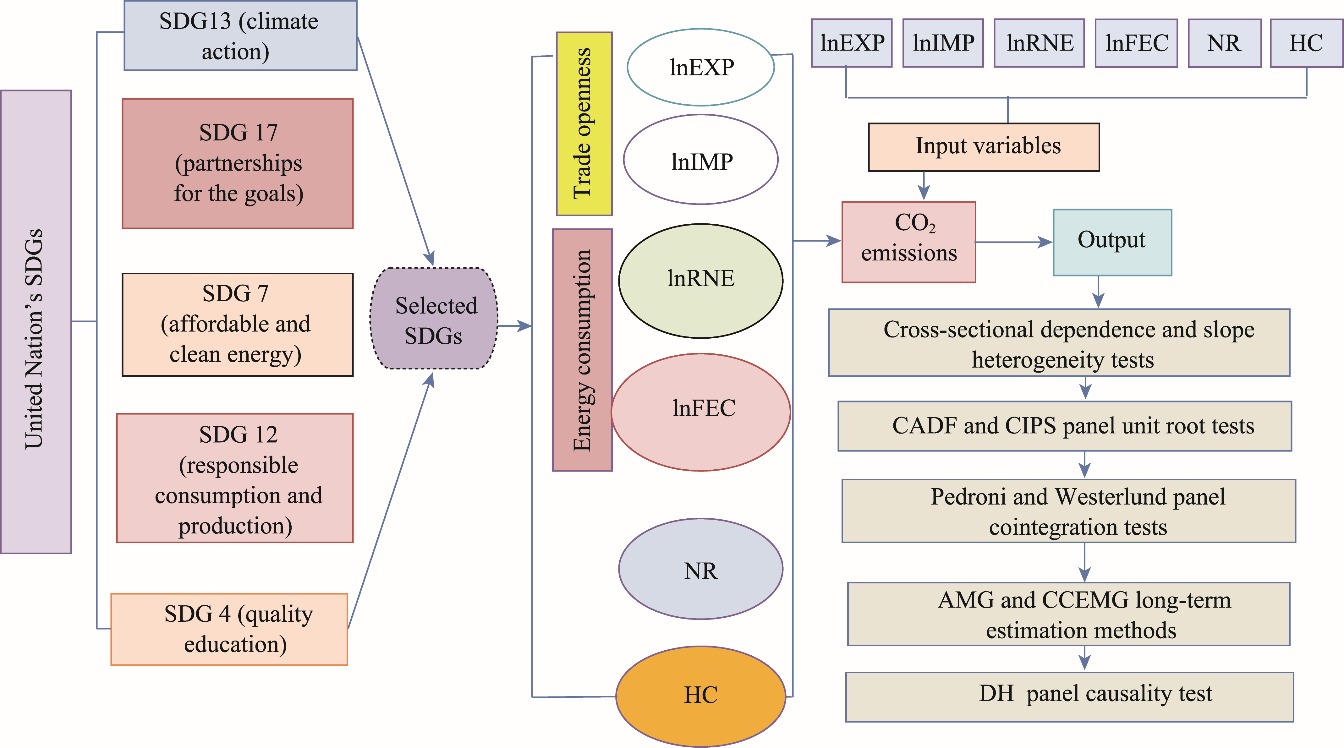
Table 4
Results of the cross-sectional dependence and slope heterogeneity tests of the variables."
| Test | Variable | Statistic value | P-value | Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-sectional dependence test | lnCO2 | 63.34*** | 0.000 | 0.80 |
| lnEXP | 16.83*** | 0.000 | 0.21 | |
| lnIMP | 10.92*** | 0.000 | 0.14 | |
| lnRNE | 35.84*** | 0.000 | 0.45 | |
| lnFEC | 23.93*** | 0.000 | 0.30 | |
| NR | 29.14*** | 0.000 | 0.37 | |
| HC | 75.63*** | 0.000 | 0.96 | |
| Slope heterogeneity test | $\bar{\Delta}$ | 27.69*** | 0.000 | - |
| $\bar{\Delta}_{a d j}$ | 31.82*** | 0.000 | - |
Table 5
Results of the Cross-Sectional Augmented Dickey-Fuller (CADF) and Cross-Sectional Im, Pesaran, and Shin (CIPS) panel unit root tests of the variables."
| Variable | CADF | CIPS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At the level | At the first difference | At the level | At the first difference | |
| lnCO2 | -2.396 | -3.623*** | -2.131 | -4.980*** |
| lnEXP | -2.599 | -3.876*** | -1.625 | -5.155*** |
| lnIMP | -2.702** | -3.967*** | -1.938 | -4.782*** |
| lnRNE | -2.267 | -4.010*** | -1.929 | -5.212*** |
| lnFEC | -2.096 | -4.506*** | -2.391 | -5.555*** |
| NR | -2.407 | -3.859*** | -1.757 | -3.730*** |
| HC | -2.011 | -3.619*** | -1.538 | -5.268*** |
Table 6
Results of the Pedroni and Westerlund cointegration tests of the variables."
| Pedroni test | Statistic value | P-value | Westerlund test | Statistic value | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Phillips-Perron test | 3.5139*** | 0.000 | Variance ratio | 2.0147** | 0.022 |
| Phillips-Perron test | -3.3336*** | 0.000 | |||
| Augmented Dickey-Fuller test | -2.5613*** | 0.005 |
Table 7
Results of augmented mean group (AMG) and common correlated effects mean group (CCEMG) estimation on the impacts of driving factors on CO2 emissions in 20 developing countries."
| Variable | AMG | CCEMG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | P-value | Coefficient | P-value | |
| lnEXP | -0.051** (0.023) | 0.025 | -0.096* (0.057) | 0.092 |
| lnIMP | 0.080*** (0.027) | 0.003 | 0.100* (0.052) | 0.057 |
| lnRNE | -0.062* (0.032) | 0.054 | -0.203*** (0.055) | 0.000 |
| lnFEC | 1.230*** (0.252) | 0.000 | 0.524* (0.312) | 0.093 |
| NR | 0.007 (0.027) | 0.798 | 0.043 (0.058) | 0.461 |
| HC | -0.093*** (0.023) | 0.000 | -0.385*** (0.146) | 0.008 |
| Constant | 0.316* (0.164) | 0.054 | 1.097 (2.077) | 0.597 |
| RMSE | 0.0322 | 0.0286 | ||
| Wald Chi | 58.52*** | 30.18*** | ||
| Probability>Chi | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Observation | 640 | 640 | ||
Table 8
Mean Group (MG) and Fully Modified Ordinary Least Squares (FMOLS) estimation results."
| Variable | MG | FMOLS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | P-value | Coefficient | P-value | |
| lnEXP | -0.048* (0.028) | 0.088 | -0.206* (0.116) | 0.076 |
| lnIMP | 0.081*** (0.030) | 0.008 | 0.429*** (0.138) | 0.002 |
| lnRNE | -0.089*** (0.030) | 0.003 | -0.508*** (0.067) | 0.000 |
| lnFEC | 1.290*** (0.230) | 0.000 | 1.884*** (0.196) | 0.000 |
| NR | 0.031 (0.029) | 0.279 | 0.020 (0.037) | 0.595 |
| HC | -0.089*** (0.029) | 0.002 | -0.041** (0.018) | 0.021 |
| Constant | 0.375*** (0.138) | 0.007 | - | - |
| RMSE | 0.0367 | |||
| Wald Chi | 60.47*** | |||
| Probability>Chi | 0.000 | |||
| Observations | 640 | |||
Table 9
Results of panel causality tests."
| Null hypothesis | W-statistic value | Zbar-statistic value | P-value | Direction of causality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnEXP≠lnCO2 | 4.933*** | 5.252 | 0.000 | lnEXP↔lnCO2 |
| lnCO2≠lnEXP | 3.561*** | 2.648 | 0.000 | lnEXP↔lnCO2 |
| lnIMP≠lnCO2 | 3.797*** | 3.096 | 0.002 | lnIMP↔lnCO2 |
| lnCO2≠lnIMP | 5.088*** | 5.547 | 0.000 | lnIMP↔lnCO2 |
| lnRNE≠lnCO2 | 4.031*** | 3.539 | 0.000 | lnRNE↔lnCO2 |
| lnCO2≠lnRNE | 4.393*** | 4.227 | 0.000 | lnRNE↔lnCO2 |
| lnFEC≠lnCO2 | 2.014*** | 2.614 | 0.008 | lnFEC↔lnCO2 |
| lnCO2≠lnFEC | 3.333** | 2.214 | 0.026 | lnFEC↔lnCO2 |
| NR≠lnCO2 | 2.362 | 0.369 | 0.711 | - |
| lnCO2≠NR | 2.992 | 1.568 | 0.117 | - |
| HC≠lnCO2 | 2.889 | 1.371 | 0.170 | - |
| lnCO2≠HC | 5.728*** | 6.762 | 0.000 | lnCO2→HC |
| [1] | Adanu K., Adams S., 2023. Carbon-dioxide emissions management in Sub-Saharan Africa—the irrelevance of natural resource rent as a corrective policy tool. J. Environ. Econ. Policy. 12(4), 455-472. |
| [2] | Adikari A.P., Liu H.Y., Dissanayake D., et al., 2023. Human capital and carbon emissions: The way forward reducing environmental degradation. Sustainability. 15(4), 2926, doi: 10.3390/su15042926. |
| [3] | Aldegheishem A., 2024. The impact of air transportation, trade openness, and economic growth on CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1366054, doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1366054. |
| [4] | Ali A., Radulescu M., Balsalobre-Lorente D., 2023. A dynamic relationship between renewable energy consumption, nonrenewable energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emissions: Evidence from Asian emerging economies. Energy Environ. 34(8), 3529-3552. |
| [5] | AlNemer H.A., Hkiri B., Tissaoui K., 2023. Dynamic impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on CO2 emission and economic growth in Saudi Arabia: Fresh evidence from wavelet coherence analysis. Renew. Energy. 209, 340-356. |
| [6] | Amin A., Bte Mohamed Yusoff N.Y., Yousaf H., et al., 2023. The influence of renewable and non-renewable energy on carbon emissions in Pakistan: Evidence from stochastic impacts by regression on population, affluence, and technology model. Front. Environ. Sci. 11, 1182055, doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2023.1182055. |
| [7] | Amin N., Song H.M., 2023. The role of renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, trade, economic growth, and urbanization in achieving carbon neutrality: A comparative study for South and East Asian countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(5), 12798-12812. |
| [8] | Balsalobre-Lorente D., Shahbaz M., Roubaud D., et al., 2018. How economic growth, renewable electricity, and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy. 113, 356-367. |
| [9] | Baz K., Zhu Z., 2025. Life cycle analysis of green technologies: Assessing the impact of environmental policies on carbon emissions and energy efficiency. Geosci. Front. 16(2), 102004, doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2025.102004. |
| [10] | Behera P., Haldar A., Sethi N., 2023. Achieving carbon neutrality target in the emerging economies: Role of renewable energy and green technology. Gondwana Res. 121, 16-32. |
| [11] | Bilgili F., Kuşkaya S., Ünlü F., et al., 2022. Export quality, economic growth, and renewable-nonrenewable energy use: Non-linear evidence through regime shifts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29(24), 36189-36207. |
| [12] | Bilgili F., Alsanusi M., Kabir M.M., et al., 2024. Quantile dynamics of control of corruption, political stability, and renewable energy on environmental quality in the MENA region. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 27, 14001-14021. |
| [13] | Çakar N.D., Gedikli A., Erdoğan S., et al., 2021. Exploring the nexus between human capital and environmental degradation: The case of EU countries. J. Environ. Manage. 295, 113057, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113057. |
| [14] | Chen H.B., Lu J.W., Obobisa E.S., 2023. Striving towards 2050 net zero CO2 emissions: How critical are clean energy and financial sectors? Heliyon. 9(12), e22705, doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22705. |
| [15] | Chhabra M., Giri A.K., Kumar A., 2023. Do trade openness and institutional quality contribute to carbon emission reduction? Evidence from BRICS countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(17), 1-17. |
| [16] | Chondrogianni A., Tsalaporta P., 2023. Reversing environmental deterioration: The role of human capital in developing countries. Econ. Chang. Restruct. 56(3), 1585-1599. |
| [17] | Churchill S.A., Inekwe J., Ivanovski K., et al., 2023. Corrigendum to “The environmental Kuznets curve in the OECD: 1870-2014” [Energy Economics 75 (2018) 389-399]. Energy Econ. 124, 106885, doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106885. |
| [18] | Dada J.T., Adeiza A., Ismail N.A., et al., 2022. Investigating the link between economic growth, financial development, urbanization, natural resources, human capital, trade openness and ecological footprint: evidence from Nigeria. Journal of Bioeconomics. 24(2), 153-179. |
| [19] | Deka A., Ozdeser H., Seraj M., 2023. The effect of GDP, renewable energy and total energy supply on carbon emissions in the EU-27: new evidence from panel GMM. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(10), 28206-28216. |
| [20] | Dumitrescu E.I., Hurlin C., 2012. Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ. Model. 29(4), 1450-1460. |
| [21] | Eberhardt M., Teal F., 2010. Productivity Analysis in Global Manufacturing Production. Oxford: Department of Economics of University of Oxford. |
| [22] | Energy Institute, 2024. Energy Institute Statistical Review of World Energy 2024. [2024-07-21]. https://doi.org/https://www.energyinst.org/statistical-review. |
| [23] | Gershon O., Asafo J.K., Nyarko-Asomani A., et al., 2024. Investigating the nexus of energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon emissions in selected African countries. Energy Strateg. Rev. 51, 101269, doi: 10.1016/j.esr.2023.101269. |
| [24] | Ghazouani T., Maktouf S., 2024. Impact of natural resources, trade openness, and economic growth on CO2 emissions in oil-exporting countries: A panel autoregressive distributed lag analysis. Nat. Resour. Forum. 48(1), 211-231. |
| [25] | Goswami A., Kapoor H.S., Jangir R.K., et al., 2023. Impact of economic growth, trade openness, urbanization and energy consumption on carbon emissions: A study of India. Sustainability. 15(11), 9025, doi: 10.3390/su15119025. |
| [26] | Habiba U., Cao X.B., Anwar A., 2022. Do green technology innovations, financial development, and renewable energy use help to curb carbon emissions? Renew. Energy. 193, 1082-1093. |
| [27] | Hassan T., Song H.M., Kirikkaleli D., 2022. International trade and consumption-based carbon emissions: evaluating the role of composite risk for RCEP economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 3417-3437. |
| [28] | Huang Y.M., Kuldasheva Z., Bobojanov S., et al., 2023. Exploring the links between fossil fuel energy consumption, industrial value-added, and carbon emissions in G20 countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(4), 10854-10866. |
| [29] | Idroes G.M., Hardi I., Rahman M.H., et al., 2024. The dynamic impact of non-renewable and renewable energy on carbon dioxide emissions and ecological footprint in Indonesia. Carbon Research. 3(1), 35, doi: 10.1007/s44246-024-00117-0. |
| [30] | IEA(International Energy Agency) , 2023. World Energy Investment. [2024-07-20]. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2023. |
| [31] | IEA, 2024. World Energy Investment. [2024-07-21]. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2024. |
| [32] | Işık C., Bulut U., Ongan S., et al., 2024a. Exploring how economic growth, renewable energy, internet usage, and mineral rents influence CO2 emissions: a panel quantile regression analysis for 27 OECD countries. Resour. Policy. 92, 105025, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2024.105025. |
| [33] | Işık C., Kuziboev B., Ongan S., 2024b. The volatility of global energy uncertainty: Renewable alternatives. Energy. 297, 131250, doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.131250. |
| [34] | Işık C., Ongan S., Islam H., 2024c. Global environmental sustainability: the role of economic, social, governance (ECON-SG) factors, climate policy uncertainty (EPU) and carbon emissions. Air Qual. Atmos. Health. 18(3), 851-866. |
| [35] | Işık C., Ongan S., Islam H., et al., 2024d. Navigating sustainability: Unveiling the interconnected dynamics of ESG factors and SDGs in BRICS-11. Sustain. Dev. 32(5), 5437-5451. |
| [36] | Jahanger A., Usman M., Ahmad P., 2023. Investigating the effects of natural resources and institutional quality on CO2 emissions during globalization mode in developing countries. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20(9), 9663-9682. |
| [37] | Jayasooria D., Yi I., 2023. Chapter 40:The sustainable development goals. In: Yi, I., (ed.). Encyclopedia of the Social and Solidarity Economy. Genève: United Nations Inter-Agency Task Force on SSE (UNTFSSE), 310-320. |
| [38] | Jiang S., Chishti M.Z., Rjoub H., et al., 2022. Environmental R&D and trade-adjusted carbon emissions: Evaluating the role of international trade. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29(42), 63155-63170. |
| [39] | Karedla Y., Mishra R., Patel N., 2021. The impact of economic growth, trade openness and manufacturing on CO2 emissions in India: An autoregressive distributive lag (ARDL) bounds test approach. J. Econ. Financ. Adm. Sci. 26(52), 376-389. |
| [40] | Liu Y.X., Lei P., Zhao Z.H., et al., 2023. Influence of green financing, technology innovation, and trade openness on consumption-based carbon emissions in BRICS countries. Ekon. Istraz. 36(2), 2142262, doi: 10.1080/1331677x.2022.2142262. |
| [41] | Mahmood H., 2023. Trade, FDI, and CO2 emissions nexus in Latin America: The spatial analysis in testing the pollution haven and the EKC hypotheses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(6), 14439-14454. |
| [42] | Millimet D.L., Roy J., 2016. Empirical tests of the pollution haven hypothesis when environmental regulation is endogenous. J. Appl. Econom. 31(4), 652-677. |
| [43] | Mukhtarov S., Aliyev F., Aliyev J., et al., 2022. Renewable energy consumption and carbon emissions: evidence from an oil-rich economy. Sustainability. 15(1), 134, doi: 10.3390/su15010134. |
| [44] | Nwani C., Adams S., 2021. Environmental cost of natural resource rents based on production and consumption inventories of carbon emissions: assessing the role of institutional quality. Resour. Policy. 74, 102282, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102282. |
| [45] | Obobisa E.S., Chen H.B., Mensah I.A., 2022. The impact of green technological innovation and institutional quality on CO2 emissions in African countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 180, 121670, doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121670. |
| [46] | Obobisa E.S., 2024. An econometric study of eco-innovation, clean energy, and trade openness toward carbon neutrality and sustainable development in OECD countries. Sustain. Dev. 32(4), 3075-3099. |
| [47] | Obobisa E.S., Ahakwa I., 2024. Stimulating the adoption of green technology innovation, clean energy resources, green finance, and environmental taxes: The way to achieve net zero CO2 emissions in Europe? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 205, 123489, doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123489. |
| [48] | Payab A.H., Kautish P., Sharma R., et al., 2023. Does human capital complement sustainable development goals? Evidence from leading carbon emitter countries. Util. Policy. 81, 101509, doi: 10.1016/j.jup.2023.101509. |
| [49] | Pedroni P., 2004. Panel cointegration: Asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economt. Theory. 20(3), 597-625. |
| [50] | Peng L., Li Y.C., Raza S.A., et al., 2023. Natural resources and environmental sustainability: COP 26 targets from resources-based perspective. Resour. Policy. 83, 103623, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103623. |
| [51] | Pesaran M.H., 2004. General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. Empir. Econ. 60, 13-50. |
| [52] | Pesaran M.H., 2006. Estimation and inference in large heterogeneous panels with a multifactor error structure. Econometrica. 74(4), 967-1012. |
| [53] | Pesaran M.H., 2007. A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J. Appl. Econom. 22(2), 265-312. |
| [54] | Pesaran M.H., Yamagata T., 2008. Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J. Econom. 142(1), 50-93. |
| [55] | Raghutla C., Chittedi K.R., 2023. The effect of technological innovation and clean energy consumption on carbon neutrality in top clean energy-consuming countries: A panel estimation. Energy Strateg. Rev. 47, 101091, doi: 10.1016/j.esr.2023.101091. |
| [56] | Raihan A., 2024. The interrelationship amid carbon emissions, tourism, economy, and energy use in Brazil. Carbon Research. 3(1), 11, doi: 10.1007/s44246-023-00084-y. |
| [57] | Roy A., 2023. The impact of foreign direct investment, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, and natural resources on ecological footprint: an Indian perspective. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 18(1), 141-161. |
| [58] | Safi A., Chen Y.Y., Wahab S., et al., 2021. Does environmental taxes achieve the carbon neutrality target of G 7 economies? Evaluating the importance of environmental R&D. J. Environ. Manage. 293, 112908, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112908. |
| [59] | Safi N., Rashid M., Shakoor U., et al., 2023. Understanding the role of energy productivity, eco-innovation and international trade in shaping consumption-based carbon emissions: A study of BRICS nations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(43), 98338-98350. |
| [60] | Sakilu O.B., Chen H., 2024. Realizing carbon neutrality in top-emitter countries: Do green technology innovation, renewable energy, financial development, and environmental tax matters? Sustainability. 17(1), 37, doi: 10.3390/su17010037. |
| [61] | Sakilu O.B., Chen H., 2025. Carbon dioxide emissions prediction of selected developing countries using artificial neural network. J. Knowl. Econ. 1-31. |
| [62] | Su C.W., Umar M., Kirikkaleli D., et al., 2023. Testing the asymmetric effect of financial stability towards carbon neutrality target: The case of Iceland and global comparison. Gondwana Res. 116, 125-135. |
| [63] | Sun J., Qamruzzaman M., 2025. Technological innovation, trade openness, natural resources, clean energy on environmental sustainably: A competitive assessment between CO2 emission, ecological footprint, load capacity factor and inverted load capacity factor in BRICS+T. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1520562, doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1520562. |
| [64] | Tenaw D., Hawitibo A.L., 2021. Carbon decoupling and economic growth in Africa: Evidence from production and consumption-based carbon emissions. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 6, 100040, doi: 10.1016/j.resenv.2021.100040. |
| [65] | Umar M., Mirza N., Hasnaoui J.A., et al., 2022. The nexus of carbon emissions, oil price volatility, and human capital efficiency. Resour. Policy. 78, 102876, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102876. |
| [66] | Wang J., Li J., 2024. Carbon emissions, import, and export: A spatial econometric analysis of the Chinese cities. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 26(6), 16057-16072. |
| [67] | Wang K., Rehman M.A., Fahad S., et al., 2023. Unleashing the influence of natural resources, sustainable energy, and human capital on consumption-based carbon emissions in G-7 countries. Resour. Policy. 81, 103384, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103384. |
| [68] | Wang Q., Li Y.F., Li R.G., 2024a. Ecological footprints, carbon emissions, and energy transitions: The impact of artificial intelligence (AI). Hum. Soc. Sci. Commun. 11(1), 1-18. |
| [69] | Wang Q., Wang L.L., Li R.R., 2024b. Trade openness helps move towards carbon neutrality—insight from 114 countries. Sustain. Dev. 32(1), 1081-1095. |
| [70] | Wang Q., Zhang F.Y., Li R.G., 2024c. Free trade and carbon emissions revisited: The asymmetric impacts of trade diversification and trade openness. Sustain. Dev. 32(1), 876-901. |
| [71] | Wang Q., Zhang F.Y., Li R.R., et al., 2024d. Does artificial intelligence promote energy transition and curb carbon emissions? The role of trade openness. J. Clean Prod. 447, 141298, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141298. |
| [72] | Westerlund J., 2007. Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 69(6), 709-748. |
| [73] | World Development Indicators, 2024. World Development Indicators. [2024-8-24]. https://doi.org/databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators. |
| [74] | Yameogo C.E.W., Mushtaq R., Zafar M.W., et al., 2024. Impact of globalisation, remittances, and human capital on environmental quality: Evidence from landlocked African countries. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 29(3), 3469-3486. |
| [75] | Yi Y.C., Geng Y.X., Yang M.X., 2023. Has China-ASEAN trade opening increased China’s carbon emissions? Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 21(2), 52-59. |
| [76] | You Z., Li L., Waqas M., 2024. How do information and communication technology, human capital, and renewable energy affect CO2 emission; new insights from BRI countries. Heliyon. 10(4), e26481, doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26481. |
| [77] | Zafar M.W., Zaidi S.A.H., Khan N.R., et al., 2019. The impact of natural resources, human capital, and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: The case of the United States. Resour. Policy. 63, 101428, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101428. |
| [78] | Zhang X.Q., Shi X.D., Khan Y., et al., 2023. The impact of energy intensity, energy productivity, and natural resource rents on carbon emissions in Morocco. Sustainability. 15(8), 6720, doi: 10.3390/su15086720. |
| [79] | Zhou D.J., Obobisa E.S., Ayamba E.C., 2024. Achieving carbon neutrality goal in European countries: The role of green technology innovation, renewable energy, and financial development. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 1-31. |
| [80] | Zhou H., Awosusi A.A., Dagar V., et al., 2023. Unleashing the asymmetric effect of natural resources abundance on carbon emissions in regional comprehensive economic partnership: What role do economic globalization and disaggregating energy play? Resour. Policy. 85, 103914, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103914. |
| [1] | Saira SHAFIQ, Muhammad ZIA UL HAQ, Syed Abbas RAZA NAQVI, Wardha SARFARAZ, Hina ALI, Muhammad Majid ISLAM, Gul Zaib HASSAN, Muhammad NAWAZ, Tasawer ABBAS. Integrating neglected and underutilized crops (NUCs) in South Asian cropping systems and diets: Challenges and prospects [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(4): 100242-. |
| [2] | Md Maruf BILLAH, Mohammad Mahmudur RAHMAN, Santiago MAHIMAIRAJA, Alvin LAL, Asadi SRINIVASULU, Ravi NAIDU. Enhancing climate-smart coastal farming system through agriculture extension and advisory services towards the avenues of farm sustainability [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(4): 100243-. |
| [3] | Syed Masiur RAHMAN, Asif RAIHAN, Md Shafiul ALAM, Shakhawat CHOWDHURY. Greenhouse gas emission dynamics and climate change mitigation efforts toward sustainability in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(4): 100246-. |
| [4] | Mohammad Reza PAKRAVAN-CHARVADEH, Jeyran CHAMCHAM, Rahim MALEKNIA. How climate change adaptation strategies and climate migration interact to control food insecurity? [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(3): 100229-. |
| [5] | Saul NGARAVA, Alois Aldridge MUGADZA. Renewable energy and its impact on agricultural and economic development in the Netherlands and South Africa [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(2): 100209-. |
| [6] | Ivette Gnitedem KEUBENG, George Achu MULUH, Vatis Christian KEMEZANG. Controlling agricultural product price volatility: An empirical analysis from Cameroon [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(2): 100215-. |
| [7] | Osama AHMED, Mourad FAIZ, Laamari ABDELALI, Safwa KHOALI, Cataldo PULVENT, Sameh MOHAMED, Mame Samba MBAYE, Thomas GLAUBEN. Unlocking climate change resilience: Socioeconomic factors shaping smallholder farmers’ perceptions and adaptation strategies in Mediterranean and Sub-Saharan Africa regions [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(1): 100195-. |
| [8] | Felix KPENEKUU, Philip ANTWI-AGYEI, Fred NIMOH, Andrew DOUGILL, Albert BANUNLE, Jonathan ATTA-AIDOO, Frank BAFFOUR-ATA, Thomas Peprah AGYEKUM, Godfred ADDAI, Lawrence GUODAAR. Cost and benefit analysis of Climate-Smart Agriculture interventions in the dryland farming systems of northern Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2025, 6(1): 100196-. |
| [9] | MA Xing, QIANG Wenli, WANG Shijin, LIU Jiayi, Arunima MALIK, LI Mengyu, WANG Xiang. Evolutionary characteristics of export trade network in the Arctic region [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(4): 100176-. |
| [10] | Septri WIDIONO, Ekawati Sri WAHYUNI, Lala M. KOLOPAKING, Arif SATRIA. Livelihood vulnerability of indigenous people to climate change around the Kerinci Seblat National Park in Bengkulu, Indonesia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(4): 100181-. |
| [11] | Issa NYASHILU, Robert KIUNSI, Alphonce KYESSI. Climate change vulnerability assessment in the new urban planning process in Tanzania [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100155-. |
| [12] | Homayoon RAOUFI, Hamidreza JAFARI, Wakil Ahmad SARHADI, Esmail SALEHI. Assessing the impact of climate change on agricultural production in central Afghanistan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100156-. |
| [13] | Frank BAFFOUR-ATA, Louisa BOAKYE, Moses Tilatob GADO, Ellen BOAKYE-YIADOM, Sylvia Cecilia MENSAH, Senyo Michael KWAKU KUMFO, Kofi Prempeh OSEI OWUSU, Emmanuel CARR, Emmanuel DZIKUNU, Patrick DAVIES. Climatic and non-climatic factors driving the livelihood vulnerability of smallholder farmers in Ahafo Ano North District, Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100157-. |
| [14] | SONG Boyi, ZHANG Shihang, LU Yongxing, GUO Hao, GUO Xing, WANG Mingming, ZHANG Yuanming, ZHOU Xiaobing, ZHUANG Weiwei. Characteristics and drivers of the soil multifunctionality under different land use and land cover types in the drylands of China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100162-. |
| [15] | Camillus Abawiera WONGNAA, Alex Amoah SEYRAM, Suresh BABU. A systematic review of climate change impacts, adaptation strategies, and policy development in West Africa [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100137-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号