Regional Sustainability ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 59-67.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2020.09.001cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2020.09.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Huihui Caoa, Guanghui Donga,b,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-03
Revised:2020-07-03
Accepted:2020-09-01
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2020-10-17
Contact:
Guanghui Dong
E-mail:ghdong@lzu.edu.cn
Huihui Cao, Guanghui Dong. Social development and living environment changes in the Northeast Tibetan Plateau and contiguous regions during the late prehistoric period[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 59-67.
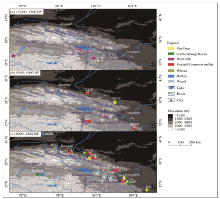
Fig. 2.
Spatiotemporal patterns of animal and plant assemblages (i.e., percentages number of identified specimens) from prehistoric sites in the NEPT and NETP-CR during ~15,000-5000 BP (a), 5500-4000 BP (b), and 4000-2200 BP (c). BP, years before present; YNG, Yeniugou; JXG, Jiangxigou; 151, Yaowuyao; LYH, Layihai; XCY, Xichengyi; MZZ, Mozuizi; SNSZ, Shannashuzha; ADQH, Andaqiha; ZR, Zongri; MZS, Mazongshan; HSG, Huoshaogou; GGY, Ganguya; DHS, Donghuishan; JCK, Jinchankou; DHZ, Dahezhuang; LJP, Lijiaping; QJP, Qijiaping; XS, Xishan; BY, Bayan; GG, Gagai; LS, Longshan; KLSSW, Kalashishuwan; TLTLH, Talitaliha; TWDLH, Tawendaliha; XRYMKB, Xiariyamakebu."

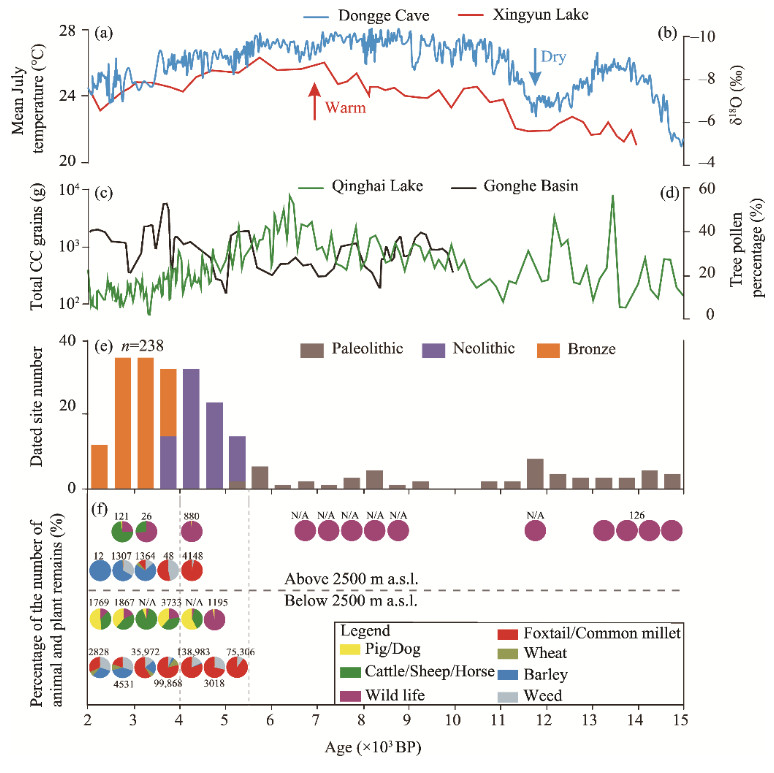
Fig. 3.
Assemblages of plant and animal remains unearthed from prehistoric sites and the number of dated sites in the NETP and NETP-CR compared to climate records. (a), pollen-based mean July temperature reconstruction from Xingyun Lake (Wu et al., 2018); (b), δ18O record of the Asian monsoon strength from Dongge Cave stalagmites (Dykoski et al., 2005); (c), total charcoal concentrations (CC) from the Gonghe Basin (Miao et al., 2017); (d), tree pollen percentage in the Qinghai Lake (Shen et al., 2005); (e), the number of dated sites every 500 yr in the NETP-CR during 15,000-2000 BP; (f), assemblages of animal and plant remains identified from prehistoric sites below and above 2500 m a.s.l. in the NETP-CR. The total number identified is marked at the top of each pie chart, N/A (not available) means there is only composition ratio and no specific number in the original literature."
| [1] |
Aldenderfer, M ., 2011. Peopling the Tibetan Plateau: insights from archaeology. High Alt. Med. Biol. 12(2), 141-147.
doi: 10.1089/ham.2010.1094 pmid: 21718162 |
| [2] | An, J.Y., Chen, H.H. , 2010. Report of the faunal remains from Zongri Culture sites. In: Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology (ed.). The first series of Chinese zooarchaeology. Beijing: Cultural Relics. 232-240. (in Chinese) |
| [3] |
Barton, L., Newsome, S.D., Chen, F.H ., et al., 2009. Agricultural origins and the isotopic identity of domestication in northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106(14), 5523-5528.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809960106 pmid: 19307567 |
| [4] | Brantingham, P.J., Gao, X., Olsen, J.W ., et al., 2007. A short chronology for the peopling of the Tibetan Plateau. Developments in Quaternary Sciences. 9, 129-150. |
| [5] | Brantingham, P.J., Gao, X., Madsen, D.B ., et al., 2013. Late occupation of the high-elevation northern Tibetan Plateau based on cosmogenic, luminescence, and radiocarbon ages. Geoarchaeology. 28(5), 413-431. |
| [6] | Bronk Ramsey, C ., 2017. OxCal version 4.3.2. https://c14.arch.ox.ac.uk/oxcal.html. |
| [7] | Bureau of National Cultural Relics, 1996. Atlas of Chinese Cultural Relics-Fascicule of Qinghai Province. Beijing: China Cartograghic Publishing House Press. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | Bureau of National Cultural Relics, 2011. Atlas of Chinese Cultural Relics-Fascicule of Gansu Province. Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press. (in Chinese) |
| [9] |
Chen, F.H., Dong, G.H., Zhang, D.J ., et al., 2015. Agriculture facilitated permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau after 3600 B.P. Science. 347(6219), 248-250.
doi: 10.1126/science.1259172 pmid: 25593179 |
| [10] | Chen, F.H., Fu, B.J., Xia, J ., et al., 2019a. Major advances in studies of the physical geography and living environment of China during the past 70 years and future prospects. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 62(11), 1665-1701. |
| [11] |
Chen, F.H., Welker, F., Shen, C.C ., et al., 2019b. A late Middle Pleistocene Denisovan mandible from the Tibetan Plateau. Nature. 569(7756), 409-412.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1139-x pmid: 31043746 |
| [12] | Chen, H.H., Ge, S.B., Li, G.L ., 1998. A tentative study of the cultural nature of Zongri Culture. Archaeology. ( 5), 15-26. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Chen, S.Q ., 2006. Adaptive changes of hunter-gatherers during the late Pleistocene-early Holocene transition in China. Acta Anthropologica Sinica. 25, 195-207. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | Cheng, Z.J., Weng, C.Y., Steinke, S ., et al., 2018. Anthropogenic modification of vegetated landscapes in southern China from 6,000 years ago. Nat. Geosci. 11(12), 939-943. |
| [15] | Cheung, C., Jing, Z.C., Tang, J.G ., et al., 2017. Examining social and cultural differentiation in early Bronze Age China using stable isotope analysis and mortuary patterning of human remains at Xin’anzhuang, Yinxu. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 9(5), 799-816. |
| [16] | Cui, Y.F., Yang, Y.S., Zhang, S.J ., et al., 2020. Discuss on the trade and motive force of Majiayao cultural painted pottery in Gansu-Qinghai region. Quaternary Sciences. 40(2), 538-546. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | Cui, Y.P., Hu, Y.W., Chen, H.H ., et al., 2006. Stable isotopic analysis on human bones from Zongri site. Quaternary Sciences. 26(4), 604-611. (in Chinese) |
| [18] |
d’Alpoim, Guedes , J.A., 2015. Rethinking the spread of agriculture to the Tibetan Plateau. Holocene. 25(9), 1498-1510.
doi: 10.1177/0959683615585835 |
| [19] |
d’Alpoim Guedes, J.A., Lu, H.L., Hein, A.M ., et al., 2015. Early evidence for the use of wheat and barley as staple crops on the margins of the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112(18), 5625-5630.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423708112 pmid: 25902511 |
| [20] | d’Alpoim, Guedes , J.A., 2018. Did foragers adopt farming? A perspective from the margins of the Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 489(S1), 91-100. |
| [21] | Dodson, J.R., Li, X.Q., Zhou, X.Y ., et al., 2013. Origin and spread of wheat in China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 72, 108-111. |
| [22] | Dong, G.H., Jia, X., An, C.B ., et al., 2012. Mid-Holocene climate change and its effect on prehistoric cultural evolution in eastern Qinghai Province, China. Quat. Res. 77(1), 23-30. |
| [23] | Dong, G.H., Jia, X., Elston, R ., et al., 2013a. Spatial and temporal variety of prehistoric sites and its influencing factors in the upper Yellow River valley, Qinghai Province, China. J. Archaeol. Sci. 40(5), 2538-2546. |
| [24] | Dong, G.H., Wang, L., Cui, Y.F ., et al., 2013b. The spatiotemporal pattern of the Majiayao cultural evolution and its relation to climate change and variety of subsistence strategy during late Neolithic period in Gansu and Qinghai Provinces, northwest China. Quat. Int. 316, 155-161. |
| [25] | Dong, G.H., Ren, L.L., Jia, X ., et al., 2016. Chronology and subsistence strategy of Nuomuhong culture in the Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 426, 42-49. |
| [26] | Dong, G.H., Liu, F.W., Chen, F.H ., 2017. Environmental and technological effects on ancient social evolution at different spatial scales. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 60(12), 2067-2077. |
| [27] | Dong, G.H ., 2018. Understanding past human-environment interaction from an interdisciplinary perspective. Sci. Bull. 63(16), 1023-1024. |
| [28] | Dong, G.H., Yang, Y.S., Liu, X.Y ., et al., 2018. Prehistoric trans-continental cultural exchange in the Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Holocene. 28(4), 621-628. |
| [29] | Dong, G.H., Li, R., Lu, M.X ., et al., 2020. Evolution of human-environmental interactions in China from the Late Paleolithic to the Bronze Age. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 44(2), 233-250. |
| [30] | Dykoski, C.A., Edwards, R.L., Cheng, H ., et al., 2005. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 233(1-2), 71-86. |
| [31] | Elston, R.G., Dong, G.H., Zhang, D.J ., 2011. Late Pleistocene intensification technologies in Northern China. Quat. Int. 242(2), 401-415. |
| [32] | Fiorentino, G., Caldara, M., De Santis, V ., et al., 2013. Climate changes and human-environment interactions in the Apulia region of southeastern Italy during the Neolithic period. Holocene. 23(9), 1297-1316. |
| [33] | Gai, P., Wang, G.D ., 1983. Excavation report on a Mesolithic site at Layihai, upper Yellow River. Acta Anthropologica Sinica. 2(1), 49-59, 116. (in Chinese) |
| [34] | Hou, G.L., Xu, C.J., Fan, Q.S ., 2010. Three expansions of prehistoric humans towards northeast margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and environmental change. Acta Geographica Sinica. 65(1), 65-72. (in Chinese) |
| [35] | Hou, G.L., Lai, Z.P., Sun, Y.J ., et al., 2013. Impact of the Holocene climatic optimum on human activities in the northeastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Arid Land Geography. 36(6), 971-978. (in Chinese) |
| [36] | Hou, G.L., Cao, G.C., E, C.Y ., et al., 2016. New evidence of human activities at an altitude of 4000 meters area of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geographica Sinica. 71(7), 1231-1240. (in Chinese) |
| [37] | Hou, J.Z., Huang, Y.S., Zhao, J.T ., et al., 2016. Large Holocene summer temperature oscillations and impact on the peopling of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43(3), 1323-1330. |
| [38] | Huang, W.W., Chen, K.Z., Yuan, B.Y. , 1987. Discovery of Paleolithic Artifacts in the Xiao Qaidam Lake Area, Qinghai Province. Beijing: Sciences Press. (in Chinese) |
| [39] | Huang, X.Z., Liu, S.S., Dong, G.H ., et al., 2017. Early human impacts on vegetation on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the middle to late Holocene. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 41(3), 286-301. |
| [40] | Hong, L.Y., Cui, J.F., Chen, H.H ., 2012. Migration, trade, imitation and innovation: analysis of the Late Neolithic pottery from the Zongri site. A Collection of Studies on Archaeology. 19, 325-345. (in Chinese) |
| [41] | Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, 2011. Science for Archaeology (3 rd album) . Beijing: Science press, 80-99. (in Chinese) |
| [42] | Jia, X., Dong, G.H., Li, H ., et al., 2013. The development of agriculture and its impact on cultural expansion during the late Neolithic in the Western Loess Plateau, China. Holocene. 23(1), 85-92. |
| [43] | Li, S.C ., 2005. Regional characteristics and interaction of early copper smelting between northwest and Central Plain of China. Acta Archaeologica Sinica.( 3), 239-275, 278. (in Chinese) |
| [44] | Li, X., Zhang, S.J., Lu, M.X ., et al., 2020. Dietary shift and social hierarchy from the Proto-Shang to Zhou Dynasty in the Central Plains of China. Environ. Res. Lett. 15(3), doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab6783 |
| [45] | Li, Y.C., Tian, J.Y., Liu, F.W ., et al., 2019. Neolithic millet farmers contributed to the permanent settlement of the Tibetan Plateau by adopting barley agriculture. Natl. Sci. Rev. 6(5), 1005-1013. |
| [46] | Liu, X.Y., Jones, P.J., Matuzeviciute, G.M ., et al., 2019. From ecological opportunism to multi-cropping: Mapping food globalisation in prehistory. Quat. Sci. Rev. 206, 21-28. |
| [47] | Ma, M.M., Dong, G.H., Jia, X ., et al., 2016. Dietary shift after 3600 cal yr BP and its influencing factors in northwestern China: evidence from stable isotopes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 145, 57-70. |
| [48] | Madsen, D.B., Ma, H.Z., Brantingham, P.J ., et al., 2006. The Late Upper Paleolithic occupation of the northern Tibetan Plateau margin. J. Archaeol. Sci. 33(10), 1433-1444. |
| [49] | Madsen, D.B., Perreault, C., Rhode, D ., et al., 2017. Early foraging settlement of the Tibetan Plateau highlands. Archaeological Research in Asia. 11, 15-26. |
| [50] | Marinova, E., Atanassova, J ., 2006. Anthropogenic impact on vegetation and environment during the Bronze Age in the area of Lake Durankulak, NE Bulgaria: pollen, microscopic charcoal, non-pollen palynomorphs and plant macrofossils. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynology. 141(1-2), 165-178. |
| [51] |
Marshall, F., Reid, R.E.B., Goldstein, S ., et al., 2018. Ancient herders enriched and restructured African grasslands. Nature. 561(7723), 387-390.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0456-9 pmid: 30158702 |
| [52] |
Meyer, M.C., Aldenderfer, M.S., Wang, Z ., et al., 2017. Permanent human occupation of the central Tibetan Plateau in the early Holocene. Science. 355(6320), 64-67.
doi: 10.1126/science.aag0357 pmid: 28059763 |
| [53] | Miao, Y.F., Zhang, D.J., Cai, X.M ., et al., 2017. Holocene fire on the northeast Tibetan Plateau in relation to climate change and human activity. Quat. Int. 443, 124-131. |
| [54] | Qiang, M.R., Song, L., Jin, Y.X ., et al., 2017. A 16-ka oxygen-isotope record from Genggahai Lake on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: hydroclimatic evolution and changes in atmospheric circulation. Quat. Sci. Rev. 162, 72-87. |
| [55] | Reimer, P.J., Bard, E., Bayliss, A ., et al., 2013. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0-50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon. 55(4), 1869-1887. |
| [56] | Ren, L.L ., 2017. A study on animal exploitation strategies from the late Neolithic to Bronze Age in northeastern Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding areas, China. PhD Dissertation. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese) |
| [57] |
Ren, L.L., Dong, G.H., Liu, F.W ., et al., 2020. Foraging and farming: archaeobotanical and zooarchaeological evidence for Neolithic exchange on the Tibetan Plateau. Antiquity. 94(375), 637-652.
doi: 10.15184/aqy.2020.35 |
| [58] |
Revelles, J., Burjachs, F., Palomo, A ., et al., 2018. Human-environment interaction during the Mesolithic- Neolithic transition in the NE Iberian Peninsula. Vegetation history, climate change and human impact during the Early-Middle Holocene in the Eastern Pre-Pyrenees. Quat. Sci. Rev. 184, 183-200.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.08.025 |
| [59] |
Rhode, D., Zhang, H.Y., Madsen, D.B ., et al., 2007. Epipaleolithic/early Neolithic settlements at Qinghai Lake, western China. J. Archaeol. Sci. 34(4), 600-612.
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2006.06.016 |
| [60] |
Rhode, D., Brantingham, P.J., Perreault, C ., et al., 2014. Mind the gaps: testing for hiatuses in regional radiocarbon date sequences. J. Archaeol. Sci. 52, 567-577.
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2014.02.022 |
| [61] |
Samuels, K.L ., 2016. The cadence of climate: heritage proxies and social change. J. Soc. Archaeol. 16(2), 142-163.
doi: 10.1177/1469605316639804 |
| [62] |
Shen, J., Liu, X.Q., Wang, S.M ., et al., 2005. Palaeoclimatic changes in the Qinghai Lake area during the last 18,000 years. Quat. Int. 136, 131-140.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2004.11.014 |
| [63] | Spengler, R., Frachetti, M., Doumani, P ., et al., 2014. Early agriculture and crop transmission among Bronze Age mobile pastoralists of Central Eurasia. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 281(1783), doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.3382 |
| [64] |
Sun, Y.J., Lai, Z.P., Long, H ., et al., 2010. Quartz OSL dating of archaeological sites in Xiao Qaidam Lake of the NE Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its implications for palaeoenvironmental changes. Quat. Geochronol. 5(2-3), 360-364.
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2009.02.013 |
| [65] |
Tallavaara, M., Eronen, J.T., Luoto, M ., 2018. Productivity, biodiversity, and pathogens influence the global hunter-gatherer population density. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115(6), 1232-1237.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715638115 pmid: 29282314 |
| [66] | Tang, H.S., Zhou, C.L., Li, Y.Q ., et al., 2013. A new discovery of microlithic information at the entrance to the Northern Qingzang Plateau of the Kunlun Mountains of Qinghai. Chinese Science Bulletin. 58(3), 247-253. (in Chinese) |
| [67] |
Wang, J., Xia, H., Yao, J.T ., et al., 2020. Subsistence strategies of prehistoric hunter-gatherers on the Tibetan Plateau during the Last Deglaciation. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 63(3), 395-404.
doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9519-8 |
| [68] |
Wang, L., Yang, Y.S., Jia, X ., 2016. Hydrogeomorphic settings of late Paleolithic and early-mid Neolithic sites in relation to subsistence variation in Gansu and Qinghai Provinces, northwest China. Quat. Int. 426, 18-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.03.017 |
| [69] | Wang, Y.R ., 2017. Identify the beginning of sheep husbandry in western China. PhD Dissertation. Cambridge: University of Cambridge. |
| [70] |
Wu, D., Chen, X.M., Lv, F.Y ., et al., 2018. Decoupled early Holocene summer temperature and monsoon precipitation in southwest China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 193, 54-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.05.038 |
| [71] | Xie, D.J. , 2002. Prehistoric Archaeology of Gansu Province and Qinghai Province. Beijing: Cultural Relics Press. (in Chinese) |
| [72] |
Yang, Y.S., Dong, G.H., Zhang, S.J ., et al., 2017. Copper content in anthropogenic sediments as a tracer for detecting smelting activities and its impact on environment during prehistoric period in Hexi Corridor, Northwest China. Holocene. 27(2), 282-291.
doi: 10.1177/0959683616658531 |
| [73] |
Yang, Y.S., Ren, L.L., Dong, G.H ., et al., 2019a. Economic change in the prehistoric Hexi Corridor (4800-2200 BP), north-west China. Archaeometry. 61(4), 957-976.
doi: 10.1111/arcm.v61.4 |
| [74] | Yang, Y.S., Zhang, S.J., Oldknow, C ., et al., 2019b. Refined chronology of prehistoric cultures and its implication for re-evaluating human-environment relations in the Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 62(10), 1578-1590. |
| [75] | Yi, M.J., Gao, X., Zhang, X.L ., et al., 2011. A preliminary report on investigations in 2009 of some prehistoric sites in the Tibetan Plateau marginal region. Acta Anthropologica Sinica. 30(2), 124-136. (in Chinese) |
| [76] |
Zhang, D.J., Dong, G.H., Wang, H ., et al., 2016. History and possible mechanisms of prehistoric human migration to the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 59(9), 1765-1778.
doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5482-x |
| [77] |
Zhang, J., Huang, X.Z., Wang, Z.L ., et al., 2018. A late-Holocene pollen record from the western Qilian Mountains and its implications for climate change and human activity along the Silk Road, Northwestern China. Holocene. 28(7), 1141-1150.
doi: 10.1177/0959683618761548 |
| [78] | Zhang, S.J., Dong, G.H ., 2017. Human adaptation strategies to different altitude environment during mid-late Bronze age in northeast Tibetan Plateau. Quaternary Sciences. 37(4), 696-708. (in Chinese) |
| [79] |
Zhang, S.J., Yang, Y.S., Storozum, M.J ., et al., 2017. Copper smelting and sediment pollution in Bronze Age China: a case study in the Hexi Corridor, Northwest China. Catena. 156, 92-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.04.001 |
| [80] | Zhang, X.H ., 2012. Plant archaeological survey and achievement in Guanting basin, Qinghai Province and related issues. Archaeology and Cultural Relics. ( 3), 26-33. (in Chinese) |
| [81] |
Zhang, X.L., Ha, B.B., Wang, S.J ., et al., 2018. The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago. Science. 362(6418), 1049-1051.
doi: 10.1126/science.aat8824 pmid: 30498126 |
| [82] |
Zhou, X.Y., Li, X.Q., Dodson, J ., et al., 2012. Land degradation during the Bronze Age in Hexi Corridor (Gansu, China). Quat. Int. 254, 42-48.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2011.06.046 |
| [83] |
Zhou, X.Y., Li, X.Q., Dodson, J ., et al., 2016. Rapid agricultural transformation in the prehistoric Hexi Corridor, China. Quat. Int. 426, 33-41.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.04.021 |
| [84] | Zhuang, Y.J., Kidder, TR ., 2014. Archaeology of the Anthropocene in the Yellow River region, China, 8000-2000 cal. BP. Holocene. 24(11), 1602-1623. |
| [1] | Issa NYASHILU, Robert KIUNSI, Alphonce KYESSI. Climate change vulnerability assessment in the new urban planning process in Tanzania [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100155-. |
| [2] | Homayoon RAOUFI, Hamidreza JAFARI, Wakil Ahmad SARHADI, Esmail SALEHI. Assessing the impact of climate change on agricultural production in central Afghanistan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100156-. |
| [3] | Frank BAFFOUR-ATA, Louisa BOAKYE, Moses Tilatob GADO, Ellen BOAKYE-YIADOM, Sylvia Cecilia MENSAH, Senyo Michael KWAKU KUMFO, Kofi Prempeh OSEI OWUSU, Emmanuel CARR, Emmanuel DZIKUNU, Patrick DAVIES. Climatic and non-climatic factors driving the livelihood vulnerability of smallholder farmers in Ahafo Ano North District, Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100157-. |
| [4] | SONG Boyi, ZHANG Shihang, LU Yongxing, GUO Hao, GUO Xing, WANG Mingming, ZHANG Yuanming, ZHOU Xiaobing, ZHUANG Weiwei. Characteristics and drivers of the soil multifunctionality under different land use and land cover types in the drylands of China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100162-. |
| [5] | Camillus Abawiera WONGNAA, Alex Amoah SEYRAM, Suresh BABU. A systematic review of climate change impacts, adaptation strategies, and policy development in West Africa [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100137-. |
| [6] | Suchitra PANDEY, Geetilaxmi MOHAPATRA, Rahul ARORA. Spatio-temporal variation of depth to groundwater level and its driving factors in arid and semi-arid regions of India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100143-. |
| [7] | Ramya Kundayi RAVI, Priya BABY, Nidhin ELIAS, Jisa George THOMAS, Kathyayani Bidadi VEERABHADRAIAH, Bharat PAREEK. Preparedness, knowledge, and perception of nursing students about climate change and its impact on human health in India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100116-. |
| [8] | Ashma SUBEDI, Nani RAUT, Smriti GURUNG. How Himalayan communities are changing cultivation practices in the context of climate change [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 378-389. |
| [9] | Liton Chandra VOUMIK, Md. Hasanur RAHMAN, Md. Maznur RAHMAN, Mohammad RIDWAN, Salma AKTER, Asif RAIHAN. Toward a sustainable future: Examining the interconnectedness among Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), urbanization, trade openness, economic growth, and energy usage in Australia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 405-415. |
| [10] | Rula AWAD, Hosam TITI, Aziza MOHAMED-BRAHMI, Mohamed JAOUAD, Aziza GASMI-BOUBAKER. Small ruminant value chain in Al-Ruwaished District, Jordan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 416-424. |
| [11] | WU Fan, LIANG Youjia, LIU Lijun, YIN Zhangcai, HUANG Jiejun. Identifying eco-functional zones on the Chinese Loess Plateau using ecosystem service bundles [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 425-440. |
| [12] | Arifah , Darmawan SALMAN, Amir YASSI, Eymal Bahsar DEMMALLINO. Knowledge flow analysis of knowledge co-production-based climate change adaptation for lowland rice farmers in Bulukumba Regency, Indonesia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 194-202. |
| [13] | Tobias ACKERL, Lemlem Fitwi WELDEMARIAM, Mary NYASIMI, Ayansina AYANLADE. Climate change risk, resilience, and adaptation among rural farmers in East Africa: A literature review [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 185-193. |
| [14] | Enoch YELELIERE, Philip ANTWI-AGYEI, Frank BAFFOUR-ATA. Impacts of climate change on the yields of leguminous crops in the Guinea Savanna agroecological zone of Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 139-149. |
| [15] | Girma TILAHUN, Amare BANTIDER, Desalegn YAYEH. Synergies and trade-offs of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practices selected by smallholder farmers in Geshy watershed, Southwest Ethiopia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 129-138. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号