Regional Sustainability ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (2): 109-115.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2021.03.001cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2021.03.001
• Short Communication • Next Articles
Honghu MENGa,b, Xiaoyang GAOc, Yigang SAONGd, Guanlong CAOa,e, Jie LIa,*( )
)
Received:2020-12-21
Revised:2021-01-28
Accepted:2021-03-25
Published:2021-04-20
Online:2021-08-13
Contact:
Jie LI
E-mail:jieli@xtbg.ac.cn
Honghu MENG, Xiaoyang GAO, Yigang SAONG, Guanlong CAO, Jie LI. Biodiversity arks in the Anthropocene[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(2): 109-115.
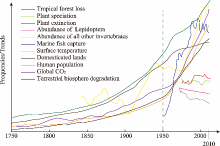
Fig. 1.
Selected characteristics of biodiversity-associated factors trends from 1750 to the “Great Acceleration” period that human activity is accelerating. The figure used the following sources: the frequency of tropical forest loss, marine fish capture, surface temperature, domesticated lands, human population, global CO2, and terrestrial biosphere degradation (adopted after Steffen et al. (2015)); the frequency of global index of invertebrate abundance: Lepidoptera and all other invertebrates from 1970 (adopted after Dirzo et al. (2014)); and the frequency of plant speciation and extinction from 1980 (adopted after Gao et al. (2020))."


Fig. 2.
Biodiversity arks should be the key areas where the vulnerable biodiversity is sheltered to alleviate human activity and buffered the climate change under the anthropogenic disturbance. For example, human activity and climate warming are impacting on the biodiversity, even in regions of the Indochina Peninsula, which are considered as the global biodiversity hotspot, e.g., the slash-and-burn cultivation in Laos (a) and the cold-adapted plants at high elevation (mountaintop) of Victoria Hills, Arakan Yoma, Myanmar (b)."

| [1] |
Adams W.M., Aveling R., Brockington D., et al., 2004. Biodiversity conservation and the eradication of poverty. Science. 306(5699), 1146-1149.
doi: 10.1126/science.1097920 |
| [2] |
Alexander J.M., Chalmandrier L., Lenoir J., et al., 2018. Lags in the response of mountain plant communities to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 24(2), 563-579.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.2018.24.issue-2 |
| [3] |
Arneth A., Shin Y.J., Leadleyd P., et al., 2020. Post-2020 biodiversity targets need to embrace climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117(49), 30882-30891.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009584117 |
| [4] |
Braje T.J., Erlandson J.M., 2013. Human acceleration of animal and plant extinctions: A Late Pleistocene, Holocene, and Anthropocene continuum. Anthropocene. 4, 14-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.ancene.2013.08.003 |
| [5] |
Dirzo R., Young H.S., Galetti M., et al., 2014. Defaunation in the Anthropocene. Science. 345(6195), 401-406.
doi: 10.1126/science.1251817 |
| [6] |
Gao J.G., Liu H., Wang N., et al., 2020. Plant extinction excels plant speciation in the Anthropocene. BMC Plant Biol. 20, 430.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02646-3 |
| [7] |
Harrison S., 2020. Plant community diversity will decline more than increase under climatic warming. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 375(1794), 20190106.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0106 |
| [8] | IPBES Report,2019. Transforming changes are necessary to restore and protect nature. [2021-01-28]. https://www.ipbes.net/. |
| [9] | IPCC,2019. The IPCC and the Sixth Assessment Cycle. [2021-01-28]. http://www.ipcc.ch/. |
| [10] |
Isbel F., Gonzalez A., Loreau M., et al., 2017. Linking the influence and dependence of people on biodiversity across scales. Nature. 546, 65-72.
doi: 10.1038/nature22899 |
| [11] |
Johnson C.N., Balmford A., Brook B.W., et al., 2017. Biodiversity losses and conservation responses in the Anthropocene. Science. 356(6335), 270-275.
doi: 10.1126/science.aam9317 |
| [12] |
Kennedy C.M., Oakleaf J.R., Theobald D.M., et al., 2019. Managing the middle: A shift in conservation priorities based on the global human modification gradient. Glob. Change Biol. 25(3), 811-826.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.2019.25.issue-3 |
| [13] |
Locke F., Ellis E.C., Venter O., et al., 2019. Three global conditions for biodiversity conservation and sustainable use: an implementation framework. Natl. Sci. Rev. 6(6), 1080-1082.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz136 |
| [14] |
Mamalakis A., Randerson J.T., Yu J.Y., et al., 2021. Zonally contrasting shifts of the tropical rain belt in response to climate change. Nat. Clim. Change. 11, 143-151.
doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-00963-x |
| [15] |
Maslin M.A., Lewis S.L., 2015. Define the Anthropocene. Nature. 519, 171-180.
doi: 10.1038/nature14258 |
| [16] |
Meng H.H., Zhou S.S., Li L., et al., 2019a.Conflict between biodiversity conservation and economic growth: Insight into rare plants in tropical China. Biodivers. Conserv. 28(2), 523-537.
doi: 10.1007/s10531-018-1661-4 |
| [17] |
Meng H.H., Zhou S.S., Jiang X.L., et al., 2019b.Are Mountaintops climate refugia for plants under global warming? A lesson from high-mountain oaks in tropical rainforest. Alp. Bot. 129(2), 175-183.
doi: 10.1007/s00035-019-00226-2 |
| [18] | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment,2005. Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Synthesis.Washington DC:Island Press. |
| [19] |
Myers N., Mittermeier R.A., Mittermeier C.G., et al., 2000. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature. 403, 853-858.
doi: 10.1038/35002501 |
| [20] |
Ordonez A., Williams J.W., Svenning J.C., 2016. Mapping climatic mechanisms likely to favour the emergence of novel communities. Nat. Clim. Change. 6, 1104-1109.
doi: 10.1038/nclimate3127 |
| [21] |
Otto S.P., 2018. Adaptation, speciation and extinction in the Anthropocene. Proc. R. Soc. B. 285(1891), 20182047.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.2047 |
| [22] | Panetta A.M., Stanton M.L., Harte J., 2018. Climate warming drives local extinction: Evidence from observation and experimentation. Sci. Adv. 4(2), eaaq1819. |
| [23] |
Raftery A.E., Zimmer A., Frierson D.M.W., et al., 2017. Less than 2°C warming by 2100 unlikely. Nat. Clim. Change. 7, 637-641.
doi: 10.1038/nclimate3352 pmid: 30079118 |
| [24] |
Rands M.R.W., Adams W.M., Bennun L., et al., 2010. Biodiversity conservation: Challenges beyond 2010. Science. 329(5997), 1298-1303.
doi: 10.1126/science.1189138 |
| [25] |
Steffen W., Broadgate W., Deutsch L., et al., 2015. The trajectory of the Anthropocene: the Great Acceleration. Anthropocene Rev. 2(1), 81-98.
doi: 10.1177/2053019614564785 |
| [26] |
Suggitt A.J., Wilson R.J., Isaac N.J.B., et al., 2018. Extinction risk from climate change is reduced by microclimatic buffering. Nat. Clim. Change. 8, 713-717.
doi: 10.1038/s41558-018-0231-9 |
| [27] |
Sutherland W.J., Atkinson P.W., Broad S., et al., 2021. A 2021 Horizon scan of emerging global biological conservation issues. Trend. Ecol. Evol. 36(1), 87-97.
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2020.10.014 |
| [28] |
Tang C.Q., Yang Y.C., Ohsawa M., et al., 2013. Survival of a tertiary relict species, Liriodendron chinense (Magnoliaceae), in southern China, with special reference to village fengshui forests. Am. J. Bot. 100(10), 2112-2119.
doi: 10.3732/ajb.1300057 |
| [29] |
Thomas C.D., Franco A.M.A., Hill J.K., 2006. Range retractions and extinction in the face of climate warming. Trends Ecol. Evol. 21(8), 415-416.
pmid: 16757062 |
| [30] |
Vellend M., Baeten L., Becker-Scarpitta A., et al., 2017. Plant biodiversity change across scales during the Anthropocene. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 68, 563-586.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042916-040949 pmid: 28125286 |
| [31] |
Vellend M., Baeten L., Myers-Smith I.H., et al., 2013. Global meta-analysis reveals no net change in local-scale plant biodiversity over time. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(48), 19456-19459.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312779110 pmid: 24167259 |
| [32] |
Zalasiewicz J., Waters C.N., Wolf A.P., et al., 2017. Making the case for a formal Anthropocene Epoch: an analysis of ongoing critiques. Newsl. Stratigr. 50(2), 205-226.
doi: 10.1127/nos/2017/0385 |
| [1] | Issa NYASHILU, Robert KIUNSI, Alphonce KYESSI. Climate change vulnerability assessment in the new urban planning process in Tanzania [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100155-. |
| [2] | Homayoon RAOUFI, Hamidreza JAFARI, Wakil Ahmad SARHADI, Esmail SALEHI. Assessing the impact of climate change on agricultural production in central Afghanistan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100156-. |
| [3] | Frank BAFFOUR-ATA, Louisa BOAKYE, Moses Tilatob GADO, Ellen BOAKYE-YIADOM, Sylvia Cecilia MENSAH, Senyo Michael KWAKU KUMFO, Kofi Prempeh OSEI OWUSU, Emmanuel CARR, Emmanuel DZIKUNU, Patrick DAVIES. Climatic and non-climatic factors driving the livelihood vulnerability of smallholder farmers in Ahafo Ano North District, Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100157-. |
| [4] | SONG Boyi, ZHANG Shihang, LU Yongxing, GUO Hao, GUO Xing, WANG Mingming, ZHANG Yuanming, ZHOU Xiaobing, ZHUANG Weiwei. Characteristics and drivers of the soil multifunctionality under different land use and land cover types in the drylands of China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100162-. |
| [5] | Camillus Abawiera WONGNAA, Alex Amoah SEYRAM, Suresh BABU. A systematic review of climate change impacts, adaptation strategies, and policy development in West Africa [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100137-. |
| [6] | Suchitra PANDEY, Geetilaxmi MOHAPATRA, Rahul ARORA. Spatio-temporal variation of depth to groundwater level and its driving factors in arid and semi-arid regions of India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100143-. |
| [7] | Ramya Kundayi RAVI, Priya BABY, Nidhin ELIAS, Jisa George THOMAS, Kathyayani Bidadi VEERABHADRAIAH, Bharat PAREEK. Preparedness, knowledge, and perception of nursing students about climate change and its impact on human health in India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100116-. |
| [8] | Setyardi Pratika MULYA, Delik HUDALAH. Agricultural intensity for sustainable regional development: A case study in peri-urban areas of Karawang Regency, Indonesia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100117-. |
| [9] | Ashma SUBEDI, Nani RAUT, Smriti GURUNG. How Himalayan communities are changing cultivation practices in the context of climate change [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 378-389. |
| [10] | LIU Binsheng, ZHANG Xiaohui, TIAN Junfeng, CAO Ruimin, SUN Xinzhang, XUE Bin. Rural sustainable development: A case study of the Zaozhuang Innovation Demonstration Zone in China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 390-404. |
| [11] | Liton Chandra VOUMIK, Md. Hasanur RAHMAN, Md. Maznur RAHMAN, Mohammad RIDWAN, Salma AKTER, Asif RAIHAN. Toward a sustainable future: Examining the interconnectedness among Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), urbanization, trade openness, economic growth, and energy usage in Australia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 405-415. |
| [12] | Rula AWAD, Hosam TITI, Aziza MOHAMED-BRAHMI, Mohamed JAOUAD, Aziza GASMI-BOUBAKER. Small ruminant value chain in Al-Ruwaished District, Jordan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 416-424. |
| [13] | WU Fan, LIANG Youjia, LIU Lijun, YIN Zhangcai, HUANG Jiejun. Identifying eco-functional zones on the Chinese Loess Plateau using ecosystem service bundles [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 425-440. |
| [14] | Surendra Singh JATAV, Kalu NAIK. Measuring the agricultural sustainability of India: An application of Pressure-State-Response (PSR) model [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(3): 218-234. |
| [15] | HAO Yun, WU Miao, ZHANG Xiaoyun, WANG Lixian, HE Jingjing. Research on the implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity among the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation countries [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(3): 322-331. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号