Regional Sustainability ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 31-36.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2020.07.001cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2020.07.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yupeng Liua,b, Jiajia Lia,b,c, Linlin Duana,b,c, Min Daid, Wei-qiang Chena,b,c,*( )
)
Received:2019-12-31
Revised:2020-06-02
Accepted:2020-06-28
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2020-09-30
Contact:
Wei-qiang Chen
E-mail:wqchen@iue.ac.cn
Yupeng Liu, Jiajia Li, Linlin Duan, Min Dai, Wei-qiang Chen. Material dependence of cities and implications for regional sustainability[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 31-36.
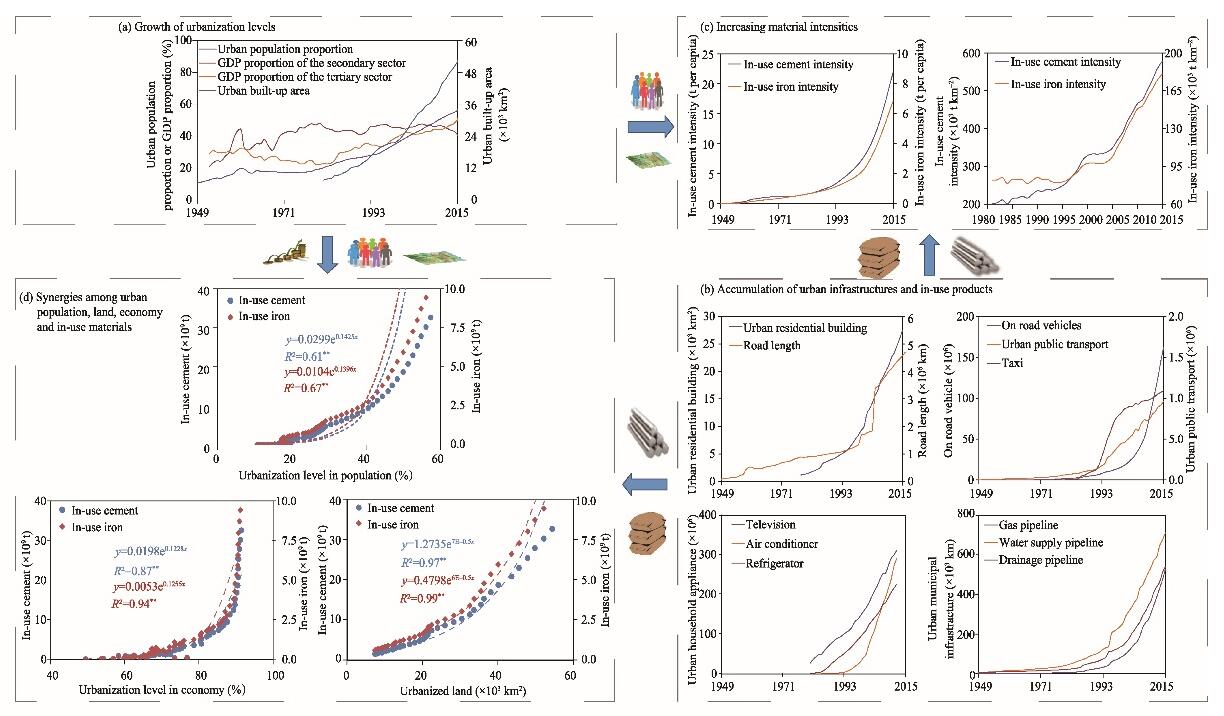
Fig. 3.
Relationships among urban population, built-up area, gross domestic product (GDP), and in-use material stocks from 1949 to 2015 in China. (a), dynamics of urban population, built-up area, and GDP of the secondary and the tertiary sectors; (b), accumulation of urban infrastructures and in-use products; (c), increasing material intensities; (d), relationships between in-use material stocks and urbanization levels from population, land, and economic perspectives.** denotes significant difference at P<0.01 level."
| [1] | Alberti, M ., 1996. Measuring urban sustainability. Environ. Impact. Asses. 16(4-6), 381-424. |
| [2] | Bai, X., Surveyer, A., Elmqvist, T ., et al., 2016. Defining and advancing a systems approach for sustainable cities. Curr. Opin. Env. Sust. 23, 69-78. |
| [3] | Braungart, M., McDonough, W. , 2002. Cradle to Cradle: Remaking the Way We Make Things. New York: North Point Press, 1-193. |
| [4] | Bren d’Amour, C., Reitsma, F., Baiocchi, G ., et al., 2017. Future urban land expansion and implications for global croplands. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 114(34), 8939-8944. |
| [5] | Canning, D ., 1998. A database of world stocks of infrastructure, 1950-95. The World Bank Economic Review. 12(3), 529-547. |
| [6] | Chen, W.Q., Graedel, T.E ., 2015. In-use product stocks link manufactured capital to natural capital. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 112(20), 6265-6270. |
| [7] | Chini, C.M., Stillwell, A.S ., 2019. The metabolism of U.S. cities 2.0. J. Ind. Ecol. 23(6), 1353-1362. |
| [8] | Costanza, R., d’Arge, R., de Groot, R ., et al., 1997. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Ecol. Econ. 387(15), 253-260. |
| [9] | Forman, R.T.T ., 2008. The urban region: natural systems in our place, our nourishment, our home range, our future. Landscape Ecol. 23, 251-253. |
| [10] | Gong, P., Liang, S., Carlton, E.J ., et al., 2012. Urbanisation and health in China. The Lancet. 379(9818), 843-852. |
| [11] |
Grimm, N.B., Faeth, S.H., Golubiewski, N.E ., et al., 2008. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science. 319(5864), 756-760.
doi: 10.1126/science.1150195 pmid: 18258902 |
| [12] | Haberl, H., Wiedenhofer, D., Pauliuk, S ., et al., 2019. Contributions of sociometabolic research to sustainability science. Nat. Sustain. 2, 173-184. |
| [13] | Jacobs, J ., 1969. The Economy of Cities. New York: Random House, 1-288. |
| [14] |
Kates, R.W., Clark, W.C., Corell, R ., et al., 2001. Sustainability science. Science. 292, 641-642.
pmid: 11330321 |
| [15] | Krausmann, F., Wiedenhofer, D., Lauk, C ., et al., 2017. Global socioeconomic material stocks rise 23-fold over the 20 th century and require half of annual resource use. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 114(8), 1880-1885. |
| [16] | Leon, D.A ., 2008. Cities, urbanization and health. Int. J. of Epidemiol. 37(1), 4-8. |
| [17] | Li, J.J., Liu, Y.P., Han, J ., et al., 2018. Creating land by materials? An important feature of China’s urbanization. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 39, 9246-9256. (in Chinese) |
| [18] |
Liu, Y.P., Wu, J.G., Yu, D.Y ., 2018a. Disentangling the complex effects of socioeconomic, climatic, and urban form factors on air pollution: a case study of China. Sustainability. 10(3), 776.
doi: 10.3390/su10030776 |
| [19] | Liu, Y.P., Wu, J.G., Yu, D.Y ., et al., 2018b. The relationship between urban form and air pollution depends on seasonality and city size. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 25(16), 15554-15567. |
| [20] | Liu, Z.F., He, C.Y., Zhou, Y.Y ., et al., 2014. How much of the world’s land has been urbanized, really? A hierarchical framework for avoiding confusion. Landscape Ecol. 29, 763-771. |
| [21] | Ma, Q., Wu, J.G., He, C.Y ., 2016. A hierarchical analysis of the relationship between urban impervious surfaces and land surface temperatures: spatial scale dependence, temporal variations, and bioclimatic modulation. Landscape Ecol. 31, 1139-1153. |
| [22] | Maslow, A ., 1954. Motivation and Personality. New York: Harper and Row, 1-336. |
| [23] | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). 2005. Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Synthesis. Washington DC: Island Press, 1-160. |
| [24] |
Montgomery, M.R ., 2008. The urban transformation of the developing world. Science. 319(5864), 761-764.
pmid: 18258903 |
| [25] | Moran, D., Kanemoto, K., Jiborn, M ., et al., 2018. Carbon footprints of 13,000 cities. Environ. Res. Lett. 13(6), 064041. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aac72a. |
| [26] | Pauliuk, S., Wang, T., Müller, D.B ., 2013. Steel all over the world: Estimating in-use stocks of iron for 200 countries. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 71, 22-30. |
| [27] | Pauliuk, S., Müller, D.B ., 2014. The role of in-use stocks in the social metabolism and in climate change mitigation. Global Environ. Change. 24, 132-142. |
| [28] |
Pickett, S.T.A., Cadenasso, M.L., Grove, J.M ., et al., 2011. Urban ecological systems: Scientific foundations and a decade of progress. J. Environ. Manage. 92, 331-362.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.08.022 pmid: 20965643 |
| [29] | Ramaswami, A., Weible, C., Main, D ., et al., 2012. A social-ecological-infrastructural systems framework for interdisciplinary study of sustainable city systems. J. Ind. Ecol. 16, 801-813. |
| [30] | Rao, N.D., Baer, P ., 2012. “Decent living” emissions: A conceptual framework. Sustainability. 4(4), 656-681. |
| [31] | Rauch, J.N ., 2009. Global mapping of Al, Cu, Fe, and Zn in-use stocks and in-ground resources. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106(45), 18920-18925. |
| [32] | Schneider, A., Friedl, M.A., Potere, D ., 2010. Mapping global urban areas using MODIS 500-m data: New methods and datasets based on ‘urban ecoregions’. Remote Sens. Environ. 114(8), 1733-1746. |
| [33] | Seto, K.C., Sánchez-Rodríguez, R., Fragkias, M ., 2010. The new geography of contemporary urbanization and the environment. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 35, 167-194. |
| [34] | Seto, K.C., Güneralp, B., Hutyra, L.R ., 2012. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 109(40), 16083-16088. |
| [35] | Solecki, W., Seto, K.C., Marcotullio, P.J ., 2013. It’s time for an urbanization science. Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development. 55(1), 12-17. |
| [36] | Tanikawa, H., Hashimoto, S ., 2009. Urban stock over time: spatial material stock analysis using 4d-GIS. Build. Res. Informat. 37(5-6), 483-502. |
| [37] |
Tanikawa, H., Fishman, T., Okuoka, K ., et al., 2015. The weight of society over time and space: A comprehensive account of the construction material stock of Japan, 1945-2010. J. Ind. Ecol. 19(5), 778-791.
doi: 10.1111/jiec.12284 |
| [38] | Thacker, S., Adshead, D., Fay, M ., et al., 2019. Infrastructure for sustainable development. Nat. Sustain. 2, 324-331. |
| [39] | Verburg, P.H., Overmars, K.P ., 2009. Combining top-down and bottom-up dynamics in land use modeling: exploring the future of abandoned farmlands in Europe with the Dyna-CLUE model. Landscape Ecol. 24, 1167. doi: 10.1007/s10980-009-9355-7. |
| [40] | Wiedenhofer, D., Steinberger, J.K., Eisenmenger, N ., et al., 2015. Maintenance and expansion: Modeling material stocks and flows for residential buildings and transportation networks in the EU25. J. Ind. Ecol. 19(5), 538-551. |
| [41] | Wu, J.G., Xiang, W.N., Zhao, J.Z ., 2014. Urban ecology in China: Historical developments and future directions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 125, 222-233. |
| [42] | Yang, Y., Heijungs, R ., 2018. On the use of different models for consequential life cycle assessment. Int. J. of Life Cycle Assess. 23, 751-758. |
| [43] | Ye, J.A., Xu, J., Yi, H ., 2006. The fourth wave of urbanization in China. City Planning Reviews. 30, 13-18. (in Chinese) |
| [44] | Yu, D., Shao, H.B., Shi, P.J ., et al., 2009. How does the conversion of land cover to urban use affect net primary productivity? A case study in Shenzhen City, China. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 149(11), 2054-2060. |
| [45] | Zhang, Q., Seto, K.C ., 2013. Can night-time light data identify typologies of urbanization? a global assessment of successes and failures. Remote Sens. 5, 3476-3494. |
| [46] | Zhao, J.Z., Liu, X., Dong, R.C ., et al., 2016. Landsenses ecology and ecological planning toward sustainable development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 23(4), 293-297. |
| [47] | Zhou, L., Dickinson, R.E., Tian, Y ., et al., 2004. Evidence for a significant urbanization effect on climate in China. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 101(26), 9540-9544. |
| [48] |
Zhu, Y.G., Ioannidis, J.P., Li, H ., et al., 2011. Understanding and harnessing the health effects of rapid urbanization in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(12), 5099-5104.
doi: 10.1021/es2004254 pmid: 21542627 |
| [49] |
Zhu, Y.G., Gillings, M., Simonet, P ., et al., 2017. Microbial mass movements. Science. 357, 1099.
doi: 10.1126/science.aao3007 pmid: 28912233 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号