Regional Sustainability ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 100162.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2024.100162cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2024.100162
• Full Length Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Boyia,b,c,d, ZHANG Shihangb,c,d,e, LU Yongxingb,c,d, GUO Haob,c,d, GUO Xingb,c,d,e, WANG Mingmingb,c,d, ZHANG Yuanmingb,c,d, ZHOU Xiaobingb,c,d, ZHUANG Weiweia,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-28
Revised:2024-06-16
Accepted:2024-08-23
Published:2024-09-30
Online:2024-09-25
Contact:
ZHUANG Weiwei
E-mail:zww8611@sina.com
SONG Boyi, ZHANG Shihang, LU Yongxing, GUO Hao, GUO Xing, WANG Mingming, ZHANG Yuanming, ZHOU Xiaobing, ZHUANG Weiwei. Characteristics and drivers of the soil multifunctionality under different land use and land cover types in the drylands of China[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100162.
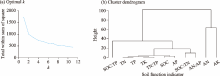
Fig. 1.
Clustering diagram of soil function indicators. (a), determining the optimal number of clusters (k); (b), a dendrogram of soil function indicators showing four main clusters. SOC, soil organic carbon; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; TK, total potassium; AN, available nitrogen; AP, available phosphorus; AK, available potassium."
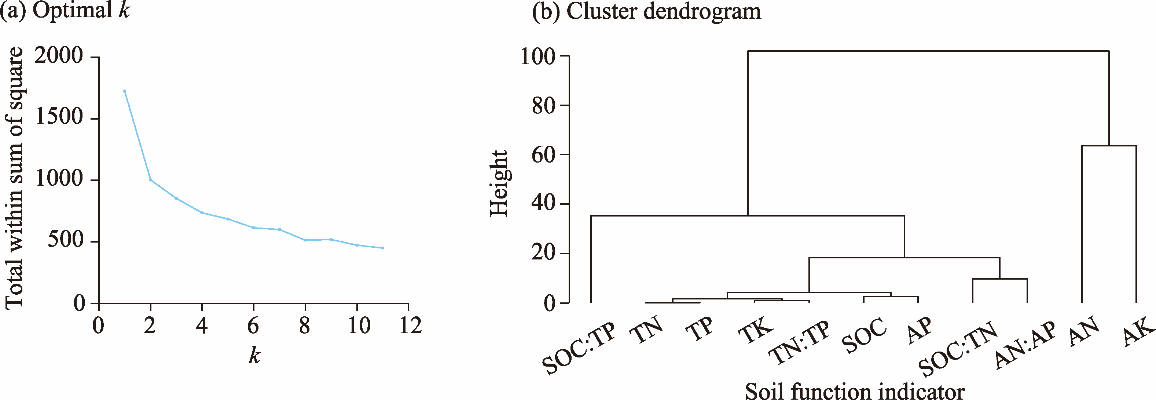
Table 1
Correlations between soil function indicators and the soil multifunctionality (SMF)."
| Soil organic carbon (SOC) | Total nitrogen (TN) | Total phosphorus (TP) | Total potassium (TK) | SOC:TN | SOC:TP | TN: TP | Available nitrogen (AN) | Available phosphorus (AP) | Available potassium (AK) | AN:AP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF1 | 0.82** | 0.96** | 0.56** | 0.69** | 0.91** | 0.43* | 0.53** | 0.78** | 0.57** | 0.59** | 0.77** |
| MF2 | 0.77** | 0.83** | 0.61** | 0.75** | 0.84** | 0.51** | 0.55** | 0.66** | 0.76** | 0.62** | 0.90** |
Table 2
Descriptive statistics of soil factors, vegetation, and climate factors in the drylands of China under different LULC types."
| LULC type | Parameter | SOC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | TK (g/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | pH | NDVI | MAP (mm) | MAT (°C) | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Mean | 8.12 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 2.01 | 190.16 | 8.53 | 157.41 | 6.71 | 0.36 | 550.12 | 7.09 | 0.41 |
| Min | 5.53 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 1.72 | 83.34 | 4.59 | 49.36 | 4.41 | 0.31 | 125.16 | -4.33 | 0.28 | |
| Max | 27.27 | 1.08 | 0.69 | 2.65 | 518.69 | 15.01 | 277.13 | 8.51 | 0.41 | 985.71 | 15.33 | 0.65 | |
| SD | 5.99 | 1.12 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 143.29 | 4.13 | 69.89 | 0.92 | 0.11 | 238.84 | 5.99 | 0.11 | |
| CV | 0.74 | 2.73 | 0.79 | 0.12 | 0.75 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.43 | 0.84 | 0.27 | |
| Grassland | Mean | 8.05 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 2.12 | 188.72 | 8.72 | 147.39 | 6.06 | 0.28 | 514.77 | 6.44 | 0.33 |
| Min | 4.98 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 1.17 | 79.88 | 5.51 | 54.12 | 3.70 | 0.22 | 110.98 | -5.13 | 0.18 | |
| Max | 22.18 | 1.12 | 0.77 | 2.71 | 534.90 | 14.98 | 285.56 | 8.81 | 0.34 | 996.75 | 16.12 | 0.59 | |
| SD | 6.16 | 0.93 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 161.25 | 4.04 | 71.18 | 1.01 | 0.10 | 229.26 | 4.57 | 0.13 | |
| CV | 0.77 | 2.16 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 0.85 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 0.39 | |
| Shrubland | Mean | 6.61 | 0.38 | 0.47 | 1.88 | 175.16 | 6.83 | 162.38 | 7.05 | 0.25 | 389.41 | 6.18 | 0.45 |
| Min | 4.45 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 1.53 | 66.37 | 13.37 | 55.36 | 4.92 | 0.17 | 155.74 | -4.49 | 0.22 | |
| Max | 25.69 | 0.92 | 0.65 | 2.77 | 451.13 | 15.07 | 343.39 | 8.63 | 0.28 | 885.14 | 14.54 | 0.61 | |
| SD | 5.28 | 0.96 | 0.49 | 0.23 | 144.57 | 3.98 | 62.58 | 0.79 | 0.08 | 213..63 | 3.93 | 0.16 | |
| CV | 0.80 | 2.53 | 1.04 | 0.12 | 0.83 | 0.58 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.32 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 0.36 | |
| Desert | Mean | 2.18 | 0.13 | 0.32 | 1.84 | 25.19 | 5.11 | 144.72 | 8.13 | 0.04 | 120.15 | 3.61 | 0.13 |
| Min | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 1.68 | 10.02 | 1.35 | 42.11 | 6.99 | 0.01 | 7.87 | -11.00 | 0.01 | |
| Max | 6.93 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 2.53 | 87.55 | 7.78 | 205.95 | 9.00 | 0.08 | 212.36 | 19.93 | 0.22 | |
| SD | 2.58 | 0.58 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 58.14 | 3.93 | 59.96 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 189.16 | 6.89 | 0.09 | |
| CV | 1.18 | 4.46 | 0.69 | 0.10 | 2.31 | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.50 | 1.57 | 1.91 | 0.69 |

Fig. 2.
Soil multifunctionality (SMF) in the drylands of China under different land use and land cover (LULC) types. The dot represents the data value; the top, middle, and bottom lines of the box represent the upper quartile, median, and lower quartile, respectively; the upper whisker represents the upper quartile+1.5IQR (interquartile range); and the lower whisker represents the lower quartile-1.5IQR. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different LULC types at P<0.05 level."
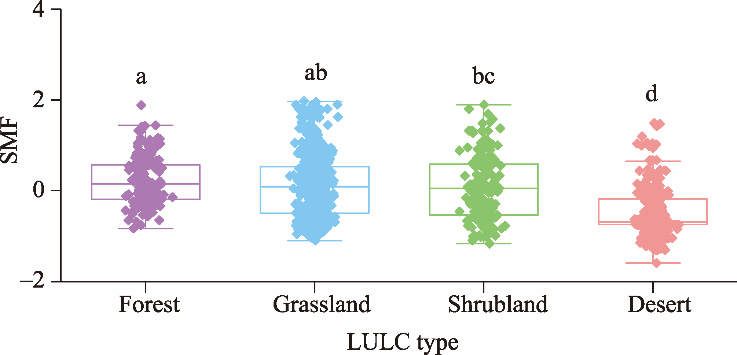
Table 3
Correlations between the SMF and environmental factors under different LULC types."
| LULC type | NDVI | pH | SM | SBI | MAT | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | 0.356*** | -0.297** | 0.145 | 0.279** | -0.682** | 0.243** |
| Grassland | 0.214** | 0.143 | 0.347** | 0.326** | -0.650*** | 0.399*** |
| Shrubland | 0.150 | -0.432*** | 0.480*** | 0.381*** | -0.428*** | 0.117 |
| Desert | 0.091 | -0.386*** | 0.231** | 0.469*** | -0.368*** | 0.586*** |
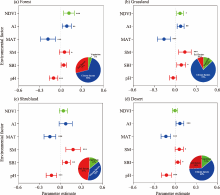
Fig. 3.
Impacts of climate factors (MAT and AI), soil factors (pH, SM, and SBI), and vegetation (NDVI) on the SMF under different LULC types. (a), forest; (b), grassland; (c), shrubland; (d), desert. The pie chart reflects the relative importance of climate factors, soil factors, and vegetation to the SMF. NDVI, normalized difference vegetation index; AI, aridity index; MAT, mean annual temperature; SM, soil moisture; SBI, soil biodiversity index; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. Error bar represents the standard deviation."
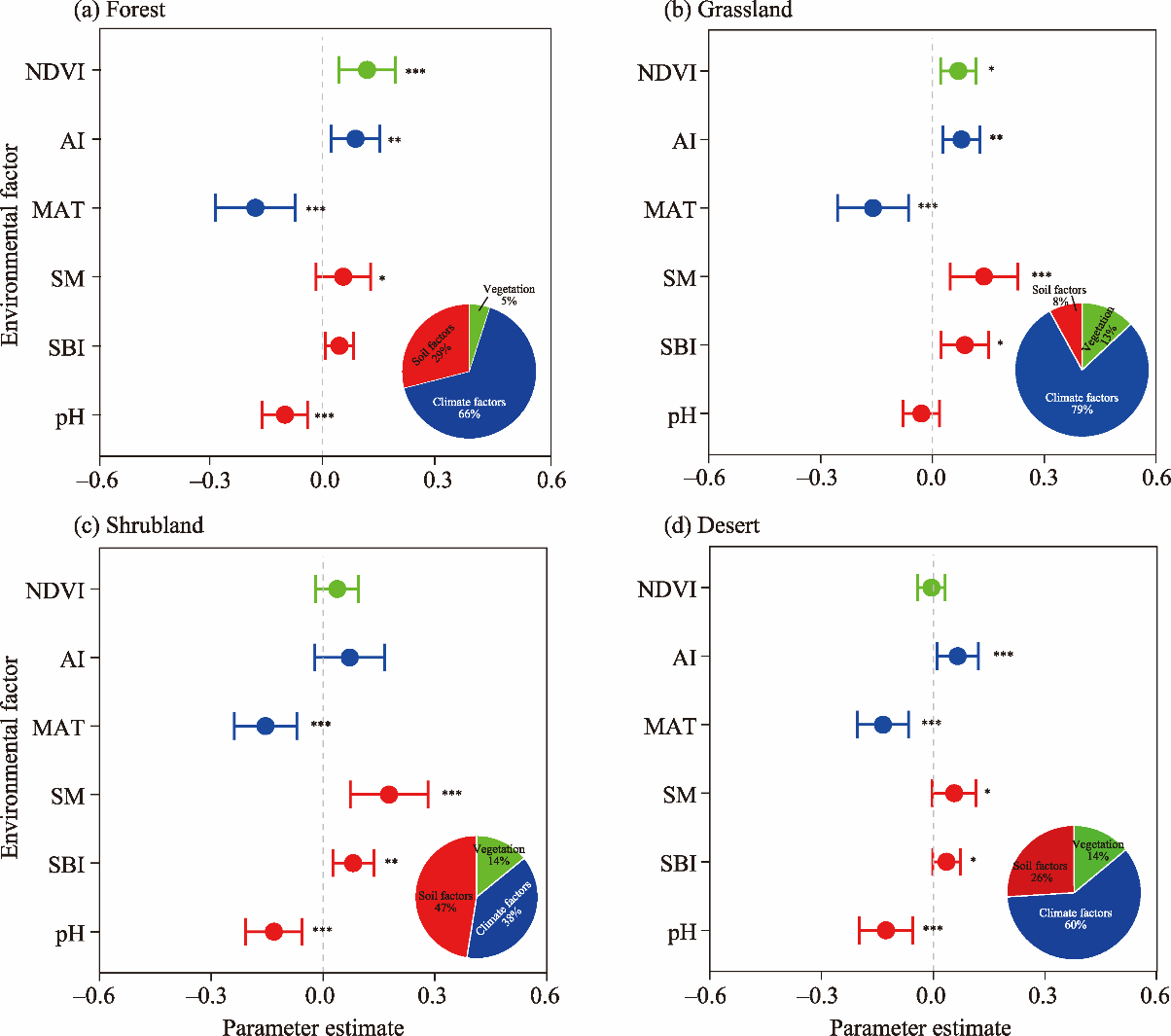
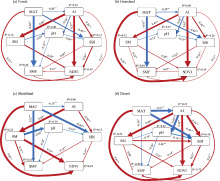
Fig. 4.
Structural equation modeling (SEM) showing the impacts of climate factors, soil factors, and vegetation on the SMF under different LULC types. (a), forest; (b), grassland; (c), shrubland; (d), desert. The red and blue lines indicate positive and negative relationships, respectively. The thickness of the line is proportional to the size of the normalized path coefficient and indicates the strength of the relationship. The arrow represents the direction of the effect. The value on the arrow indicates the effect size. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001."

| [1] | Abatzoglou J.T., Dobrowski S.Z., Parks S.A., et al., 2018. TerraClimate, a high-resolution global dataset of monthly climate and climatic water balance from 1958-2015. Sci. Data. 5, 170191, doi: 10.1038/sdata.2017.191. |
| [2] | Adelisardou F., Zhao W., Chow R., et al., 2022. Spatiotemporal change detection of carbon storage and sequestration in an arid ecosystem by integrating Google Earth Engine and InVEST (the Jiroft plain, Iran). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19(7), 5929-5944. |
| [3] |
Alkama R., Cescatti A., 2016. Biophysical climate impacts of recent changes in global forest cover. Science. 351(6273), 600-604.
doi: 10.1126/science.aac8083 pmid: 26912702 |
| [4] | Azevedo L.B., van Zelm R., Hendriks A.J., et al., 2013. Global assessment of the effects of terrestrial acidification on plant species richness. Environ. Pollut. 174, 10-15. |
| [5] |
Bastin J.F., Berrahmouni N., Grainger A., et al., 2017. The extent of forest in dryland biomes. Science. 356(6338), 635-638.
doi: 10.1126/science.aam6527 |
| [6] | Belsky A.J., Amundson R.G., Duxbury J.M., et al., 1989. The effects of trees on their physical, chemical, and biological environments in a semiarid savanna in Kenya. J. Appl. Ecol. 26(3), 1005-1024. |
| [7] |
Berdugo M., Delgado-Baquerizo M., Soliveres S., et al., 2020. Global ecosystem thresholds driven by aridity. Science. 367(6479), 787-790.
doi: 10.1126/science.aay5958 pmid: 32054762 |
| [8] | Bi X., Li B., Zhang L.X., et al., 2020. Response of grassland productivity to climate change and anthropogenic activities in arid regions of Central Asia. PeerJ. 8(6), e9797, doi: 10.7717/peerj.9797. |
| [9] | Byrnes J.E.K., Gamfeldt L., Isbell F., et al., 2014. Investigating the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: Challenges and solutions. Methods Ecol. Evol. 5(2), 111-124. |
| [10] | Cabral P., Feger C., Levrel H., et al., 2016. Assessing the impact of land-cover changes on ecosystem services: A first step toward integrative planning in Bordeaux, France. Ecosyst. Serv. 22, 318-327. |
| [11] |
Catford J.A., Dwyer J.M., Palma E., et al., 2020. Community diversity outweighs effect of warming on plant colonization. Global. Change. Biol. 26(5), 3079-3090.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.15017 pmid: 31994234 |
| [12] | Ceulemans T., Merckx R., Hens M., et al., 2013. Plant species loss from European semi-natural grasslands following nutrient enrichment-Is it nitrogen or is it phosphorus? Global. Ecol. Biogeogr. 22(1), 73-82. |
| [13] | Chen W., Li Z.W., Shen X., 2012. Influence of soil acidification on soil microorganisms in Pear Orchards. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plan. 43(13), 1833-1846. |
| [14] | Chen Y.N., Li Z., Fan Y.T., et al., 2015. Progress and prospects of climate change impacts on hydrology in the arid region of northwest China. Environ. Res. 139, 11-19. |
| [15] | Cheng X.Y., Yun Y., Wang H.M., et al., 2021. Contrasting bacterial communities and their assembly processes in karst soils under different land use. Sci. Total Environ. 751, 142263, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142263. |
| [16] | Chi W.F., Zhao Y.Y., Kuang W.H., et al., 2019. Impacts of anthropogenic land use/cover changes on soil wind erosion in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 668, 204-215. |
| [17] | Ci L., Yang X., 2010. Desertification and its Control in China. Beijing: Higher Education Press. |
| [18] |
Craven D., Eisenhauer N., Pearse W.D., et al., 2018. Multiple facets of biodiversity drive the diversity-stability relationship. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2(10), 1579-1587.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-018-0647-7 pmid: 30150740 |
| [19] | Dai Z.M., Yu M.J., Chen H.H., et al., 2020. Elevated temperature shifts soil N cycling from microbial immobilization to enhanced mineralization, nitrification and denitrification across global terrestrial ecosystems. Global Change Biol. 26(9), 5267-5276. |
| [20] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M., Eldridge D.J., Ochoa V., et al., 2017. Soil microbial communities drive the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to global change in drylands across the globe. Ecol. Lett. 20(10), 1295-1305.
doi: 10.1111/ele.12826 pmid: 28921861 |
| [21] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M., Reich P.B., Trivedi C., et al., 2020. Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 4(2), 210-220.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-019-1084-y pmid: 32015427 |
| [22] | Ding L.L., Wang P.C., 2021. Afforestation suppresses soil nitrogen availability and soil multifunctionality on a subtropical grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 761, 143663, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143663. |
| [23] |
Durán J., Delgado-Baquerizo M., Dougill A.J., et al., 2018. Temperature and aridity regulate spatial variability of soil multifunctionality in drylands across the globe. Ecology. 99(5), 1184-1193.
doi: 10.1002/ecy.2199 pmid: 29484631 |
| [24] |
Eldridge D.J., Maestre F.T., Koen T.B., et al., 2018. Australian dryland soils are acidic and nutrient-depleted, and have unique microbial communities compared with other drylands. J. Biogeogr. 45(12), 2803-2814.
doi: 10.1111/jbi.13456 pmid: 30774181 |
| [25] | Fu B.J., Zhang L.W., 2014. Land-use change and ecosystem services: Concepts, methods and progress. Progress in Geography. 33(4), 441-446 (in Chinese). |
| [26] | Gao J., Li F., Gao H., et al., 2017. The impact of land-use change on water-related ecosystem services: a study of the Guishui River Basin, Beijing, China. J. Clean Prod. 163, S148-S155. |
| [27] | Goldewijk K.K., Dekker S.C., van Zanden J.L., 2017. Per-capita estimations of long-term historical land use and the consequences for global change research. J. Land. Use. Sci. 12(5), 313-337. |
| [28] | Grace J.B., Bollen K.A., 2008. Representing general theoretical concepts in structural equation models: the role of composite variables. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 15(2), 191-213. |
| [29] | Hasan S.S., Zhen L., Miah M.G., et al., 2020. Impact of land use change on ecosystem services: A review. Environ. Dev. 34, 100527, doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2020.100527. |
| [30] |
Hodgkinson K.C., 1992. Water relations and growth of shrubs before and after fire in a semi-arid woodland. Oecologia. 90(4), 467-473.
doi: 10.1007/BF01875439 pmid: 28313565 |
| [31] | Hoover D.L., Bestelmeyer B., Grimm N.B., et al., 2020. Traversing the wasteland: A framework for assessing ecological threats to drylands. Bioscience. 70(1), 35-47. |
| [32] |
Hu W.G., Ran J.Z., Dong L.W., et al., 2021. Aridity-driven shift in biodiversity-soil multifunctionality relationships. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 5350, doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25641-0.
pmid: 34504089 |
| [33] | Hu Y.N., Peng J., Liu Y.X., et al., 2018. Integrating ecosystem services trade-offs with paddy land-to-dry land decisions: A scenario approach in Erhai Lake Basin, southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 625, 849-860. |
| [34] |
Huang J.P., Yu H.P., Guan X.D., et al., 2016. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change. 6(2), 166-171.
doi: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2837 |
| [35] | Huang J.P., Yu H.P., Dai A.G., et al., 2017. Drylands face potential threat under 2°C global warming target. Nat. Clim. Change. 7(6), 417-422. |
| [36] | Huang Y.M., Kang R.H., Ma X.X., et al., 2014. Effects of calcite and magnesite application to a declining Masson pine forest on strongly acidified soil in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 481, 469-478. |
| [37] | Jankju M., 2013. Role of nurse shrubs in restoration of an arid rangeland: Effects of microclimate on grass establishment. J. Arid. Environ. 89, 103-109. |
| [38] | Jia G.S., 2020. New understanding of land-climate interactions from IPCC special report on climate change and land. Climate Change Research. 16(1), 9-16 (in Chinese). |
| [39] | Jia J.Y., Zhang J.Z., Li Y.Z., et al., 2022. Land use intensity constrains the positive relationship between soil microbial diversity and multifunctionality. Plant Soil. doi:10.1007/s11104-022-05853-z. |
| [40] | Jiang L.L., Jiapaer G., Bao A.M., et al., 2017. Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and human activities in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 599- 600, 967-980. |
| [41] | Jiang P.H., Cheng L., Li M.C., et al., 2015. Impacts of LUCC on soil properties in the riparian zones of desert oasis with remote sensing data: A case study of the middle Heihe River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 506- 507, 259-271. |
| [42] | Jost E., Schönhart M., Skalsky R., et al., 2021. Dynamic soil functions assessment employing land use and climate scenarios at regional scale. J. Environ. Manage. 287(10), 112318, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112318. |
| [43] | Keith N., Hodapp V., Schermelleh-Engel K., et al., 2003. Cross-sectional and longitudinal confirmatory factor models for the German Test Anxiety Inventory: A construct validation. Anxiety. Stress. Copin. 16(3), 251-270. |
| [44] | Lawler J.J., Lewis D.J., Nelson E., et al., 2014. Projected land-use change impacts on ecosystem services in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(20), 7492-7497. |
| [45] | Li C.J., Fu B.J., Wang S., et al., 2021a. Drivers and impacts of changes in China’s drylands. Nat. Rev. Earth. Environ. 2(12), 858-873. |
| [46] | Li Z.L., Wang H.M., Sun Z.C., et al., 2021b. Responses of soil nitrogen to the transition from desert grassland to shrubland in eastern Ningxia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. 32(4), 1230-1240 (in Chinese). |
| [47] | Lian X., Piao S.L., Chen A.P., et al., 2021. Multifaceted characteristics of dryland aridity changes in a warming world. Nat. Rev. Earth. Environ. 2(4), 232-250. |
| [48] | Liu J., Gao G., Zhang B., 2023. Effect of shrub components on soil water and its response to precipitation at different time scales in the Loess Plateau. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health. 20(6), 4722, doi: 10.3390/ijerph20064722. |
| [49] | Liu K.H., Fang Y.T., Yu F.M., et al., 2010. Soil acidification in response to acid deposition in three subtropical forests of subtropical China. Pedosphere. 20(3), 399-408. |
| [50] | Liu Y.Q., Zhu J.L., Li E.Y., et al., 2020. Environmental regulation, green technological innovation, and eco-efficiency: The case of Yangtze river economic belt in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 155, 119993, doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2020.119993. |
| [51] | Long X.R., Lin H., An X.X., et al., 2022. Evaluation and analysis of ecosystem service value based on land use/cover change in Dongting Lake wetland. Ecol. Indic. 136, 108619, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108619. |
| [52] |
Maestre F.T., Quero J.L., Gotelli N.J., et al., 2012. Plant species richness and ecosystem multifunctionality in global drylands. Science. 335(6065), 214-218.
doi: 10.1126/science.1215442 pmid: 22246775 |
| [53] | Maimaitiaili A., Aji X., Matniyaz A., et al., 2018. Monitoring and analysing land use/cover changes in an arid region based on multi-satellite data: The Kashgar region, northwest China. Land. 7(1), 6, doi: 10.3390/land7010006. |
| [54] | McNally A., Jacob J., Arsenault K., et al., 2022. A central Asia hydrologic monitoring dataset for food and water security applications in Afghanistan. Earth. Syst. Sci. Data. 14(7), 3115-3135. |
| [55] | Meng Y.N., Li T.P., Liu H.Y., et al., 2023. Legacy effects of nitrogen deposition and increased precipitation on plant productivity in a semi-arid grassland. Plant Soil. 491(1-2), 69-84. |
| [56] |
Meyer S.T., Ptacnik R., Hillebrand H., et al., 2018. Biodiversity-multifunctionality relationships depend on identity and number of measured functions. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2(1), 44-49.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0391-4 pmid: 29180710 |
| [57] | Migliavacca M., Musavi T., Mahecha M.D., et al., 2021. The three major axes of terrestrial ecosystem function. Nature. 598(7881), 468-472. |
| [58] | Mokany K., Raison R.J., Prokushkin A.S., 2006. Critical analysis of root: shoot ratios in terrestrial biomes. Global Change Biol. 12(1), 84-96. |
| [59] | Mooney H.A., Duraiappah A., Larigauderie A., 2013. Evolution of natural and social science interactions in global change research programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(Suppl.1), 3665-3672. |
| [60] | Moyano F.E., Manzoni S., Chenu C., 2013. Responses of soil heterotrophic respiration to moisture availability: An exploration of processes and models. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 59, 72-85. |
| [61] |
Müller L.M., Bahn M., 2022. Drought legacies and ecosystem responses to subsequent drought. Global Change Biol. 28(17), 5086-5103.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.16270 pmid: 35607942 |
| [62] | Ochoa-Hueso R., Eldridge D.J., Delgado-Baquerizo M., et al., 2018. Soil fungal abundance and plant functional traits drive fertile island formation in global drylands. J. Ecol. 106(1), 242-253. |
| [63] | Peng J., Tian L., Liu Y.X., et al., 2017. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 607- 608, 706-714. |
| [64] | Peng J., Tian L., Zhang Z.M., et al., 2020. Distinguishing the impacts of land use and climate change on ecosystem services in a karst landscape in China. Ecosyst. Serv. 46, 101199, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2020.101199. |
| [65] | Pickard B.R., Van Berkel D., Petrasova A., et al., 2017. Forecasts of urbanization scenarios reveal trade-offs between landscape change and ecosystem services. Landscape. Ecol. 32(3), 617-634. |
| [66] |
Pietikäinen J., Pettersson M., Bååth E., 2005. Comparison of temperature effects on soil respiration and bacterial and fungal growth rates. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 52(1), 49-58.
pmid: 16329892 |
| [67] | Prăvălie R., 2016. Drylands extent and environmental issues. A global approach. Earth-Sci. Rev. 161, 259-278. |
| [68] | Reich P.B., Oleksyn J., 2004. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101(30), 11001-11006. |
| [69] | Rodell M., Famiglietti J.S., Chen J., et al., 2004. Basin scale estimates of evapotranspiration using GRACE and other observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31(20), L20504, doi: 10.1029/2004GL020873. |
| [70] | Roy P.S., Ramachandran R.M., Paul O., et al., 2022. Anthropogenic land use and land cover changes-A review on its environmental consequences and climate change. J. Indian. Soc. Remote. 50(8), 1615-1640. |
| [71] | Sanderson M.A., Skinner R.H., Barker D.J., et al., 2004. Plant species diversity and management of temperate forage and grazing land ecosystems. Crop Science. 44(4), 1132-1144. |
| [72] | Safriel U., Adeel Z., Niemeijer D., et al., 2005. Dryland systems. In: HassanR., ScholesR., AshN., (eds.). Ecosystems and Human Well-being:Current State and Trends. Washington: Island Press. |
| [73] |
Searle E.B., Chen H.Y.H., 2020. Complementarity effects are strengthened by competition intensity and global environmental change in the central boreal forests of Canada. Ecol. Lett. 23(1), 79-87.
doi: 10.1111/ele.13411 pmid: 31631491 |
| [74] |
Sinsabaugh R.L., Lauber C.L., Weintraub M.N., et al., 2008. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 11(11), 1252-1264.
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01245.x pmid: 18823393 |
| [75] | Smith W.K., Dannenberg M.P., Yan D., et al., 2019. Remote sensing of dryland ecosystem structure and function: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Remote. Sens. Environ. 233, 111401, doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111401. |
| [76] | Soliveres S., Maestre F.T., Eldridge D.J., et al., 2014. Plant diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality peak at intermediate levels of woody cover in global drylands. Global. Ecol. Biogeogr. 23(12), 1408-1416. |
| [77] | Soliveres S., Smit C., Maestre F.T., 2015. Moving forward on facilitation research: response to changing environments and effects on the diversity, functioning and evolution of plant communities. Biol. Rev. 90(1), 297-313. |
| [78] | Song X.P., Hansen M.C., Stehman S.V., et al., 2018. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature. 560(7720), 639-643. |
| [79] | Stavi I., Priori S., Thevs N., 2022. Editorial: Impacts of climate change and land-use on soil functions and ecosystem services in drylands. Front. Env. Sci-Switz. 10, doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.851751. |
| [80] | Stringer L.C., Mirzabaev A., Benjaminsen T.A., et al., 2021. Climate change impacts on water security in global drylands. One Earth. 4(6), 851-864. |
| [81] | Tian P., Liu S.G., Zhao X.C., et al., 2021. Past climate conditions predict the influence of nitrogen enrichment on the temperature sensitivity of soil respiration. Commun. Earth. Environ. 2(1), 251, doi: 10.1038/s43247-021-00324-2. |
| [82] |
Valencia E., Maestre F.T., Le Bagousse-Pinguet Y., et al., 2015. Functional diversity enhances the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to aridity in Mediterranean drylands. New Phytol. 206(2), 660-671.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13268 pmid: 25615801 |
| [83] | Wang C., Wang X.B., Liu D.W., et al., 2014. Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands. Nat. Commun. 5, 4799, doi: 10.1038/ncomms5799. |
| [84] | Wang Q.Z., Guan Q.Y., Lin J.K., et al., 2021. Simulating land use/land cover change in an arid region with the coupling models. Ecol. Indic. 122, 107231, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107231. |
| [85] | Wang X.M., Chen F., Hasi E., et al., 2008. Desertification in China: An assessment. Earth-Sci. Rev. 88(3-4), 188-206. |
| [86] | Wang Y.J., Qin D.H., 2017. Influence of climate change and human activity on water resources in arid region of northwest China: An overview. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 8(4), 268-278. |
| [87] |
Wu L.N., Yang S.T., Liu X.Y., et al., 2014. Response analysis of land use change to the degree of human activities in Beiluo River basin since 1976. Acta Geographica Sinica. 69(1), 54-63 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201401005 |
| [88] | Wu W., Liu H.B., 2019. Estimation of soil pH with geochemical indices in forest soils. PLoS One. 14(10), e0223764, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223764. |
| [89] | Xu H.W., Qu Q., Li G.W., et al., 2022. Impact of nitrogen addition on plant-soil-enzyme C-N-P stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 174, 108714, doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108714. |
| [90] | Xu H.W., Qu Q., Yang J.P., et al., 2024. Impact of drought on terrestrial ecosystem C-N-P stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation. Soil Tillage Res. 236, 105951, doi: 10.1016/j.still.2023.105951. |
| [91] | Yan Y.Z., Zhang Q., Buyantuev A., et al., 2020. Plant functional β diversity is an important mediator of effects of aridity on soil multifunctionality. Sci. Total Environ. 726, 138529, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138529. |
| [92] | Yang H.F., Zhong X.N., Deng S.Q., et al., 2021. Assessment of the impact of LUCC on NPP and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River basin, China. CATENA. 206, 105542, doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105542. |
| [93] | Yang Y., Chai Y.B., Xie H.J., et al., 2023. Responses of soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality to three land-use changes. Sci. Total Environ. 859, 160255, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160255. |
| [94] | Yu L., Wang H.M., Guo T.D., et al., 2021. Bistable-state of vegetation shift in the desert grassland-shrubland anthropogenic Mosaic area. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 41(24), 9773-9783 (in Chinese). |
| [95] | Zhang J.W., Wu X.F., Shi Y.J., et al., 2021a. A slight increase in soil pH benefits soil organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a semiarid grassland. Ecol. Indic. 130, 108037, doi: .1016/j.ecolind.2021.108037. |
| [96] | Zhang S.H., Chen Y.S., Guo H., et al., 2023. Changes in dryland areas and net primary productivity in China from 1980 to 2020. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 132(2), 83, doi: 10.1007/s12040-023-02100-6. |
| [97] | Zhang Z.M., Peng J., Xu Z.H., et al., 2021b. Ecosystem services supply and demand response to urbanization: A case study of the Pearl River Delta, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 49, 101274, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2021.101274. |
| [98] | Zhao Y.A., Zhao Y.F., Wang H.M., et al., 2021. Response of spatial heterogeneity and threshold value for soil water and aboveground biomass of desert grassland-shrubland anthropogenic transition in desert steppe of Ningxia, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae. 57(12), 1-12 (in Chinese). |
| [99] | Zheng Q., Hu Y.T., Zhang S.S., et al., 2019. Soil multifunctionality is affected by the soil environment and by microbial community composition and diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 136, 107521, doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107521. |
| [1] | Issa NYASHILU, Robert KIUNSI, Alphonce KYESSI. Climate change vulnerability assessment in the new urban planning process in Tanzania [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100155-. |
| [2] | Homayoon RAOUFI, Hamidreza JAFARI, Wakil Ahmad SARHADI, Esmail SALEHI. Assessing the impact of climate change on agricultural production in central Afghanistan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100156-. |
| [3] | Frank BAFFOUR-ATA, Louisa BOAKYE, Moses Tilatob GADO, Ellen BOAKYE-YIADOM, Sylvia Cecilia MENSAH, Senyo Michael KWAKU KUMFO, Kofi Prempeh OSEI OWUSU, Emmanuel CARR, Emmanuel DZIKUNU, Patrick DAVIES. Climatic and non-climatic factors driving the livelihood vulnerability of smallholder farmers in Ahafo Ano North District, Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100157-. |
| [4] | TIAN Junfeng, WANG Binyan, QIU Cheng, WANG Shijun. What are the underlying causes and dynamics of land use conflicts in metropolitan junction areas? A case study of the central Chengdu- Chongqing region in China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100161-. |
| [5] | Camillus Abawiera WONGNAA, Alex Amoah SEYRAM, Suresh BABU. A systematic review of climate change impacts, adaptation strategies, and policy development in West Africa [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100137-. |
| [6] | Suchitra PANDEY, Geetilaxmi MOHAPATRA, Rahul ARORA. Spatio-temporal variation of depth to groundwater level and its driving factors in arid and semi-arid regions of India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100143-. |
| [7] | Ramya Kundayi RAVI, Priya BABY, Nidhin ELIAS, Jisa George THOMAS, Kathyayani Bidadi VEERABHADRAIAH, Bharat PAREEK. Preparedness, knowledge, and perception of nursing students about climate change and its impact on human health in India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100116-. |
| [8] | Ashma SUBEDI, Nani RAUT, Smriti GURUNG. How Himalayan communities are changing cultivation practices in the context of climate change [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 378-389. |
| [9] | Liton Chandra VOUMIK, Md. Hasanur RAHMAN, Md. Maznur RAHMAN, Mohammad RIDWAN, Salma AKTER, Asif RAIHAN. Toward a sustainable future: Examining the interconnectedness among Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), urbanization, trade openness, economic growth, and energy usage in Australia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 405-415. |
| [10] | Rula AWAD, Hosam TITI, Aziza MOHAMED-BRAHMI, Mohamed JAOUAD, Aziza GASMI-BOUBAKER. Small ruminant value chain in Al-Ruwaished District, Jordan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 416-424. |
| [11] | WU Fan, LIANG Youjia, LIU Lijun, YIN Zhangcai, HUANG Jiejun. Identifying eco-functional zones on the Chinese Loess Plateau using ecosystem service bundles [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 425-440. |
| [12] | Enoch YELELIERE, Philip ANTWI-AGYEI, Frank BAFFOUR-ATA. Impacts of climate change on the yields of leguminous crops in the Guinea Savanna agroecological zone of Ghana [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 139-149. |
| [13] | Girma TILAHUN, Amare BANTIDER, Desalegn YAYEH. Synergies and trade-offs of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practices selected by smallholder farmers in Geshy watershed, Southwest Ethiopia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 129-138. |
| [14] | Tobias ACKERL, Lemlem Fitwi WELDEMARIAM, Mary NYASIMI, Ayansina AYANLADE. Climate change risk, resilience, and adaptation among rural farmers in East Africa: A literature review [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 185-193. |
| [15] | Arifah , Darmawan SALMAN, Amir YASSI, Eymal Bahsar DEMMALLINO. Knowledge flow analysis of knowledge co-production-based climate change adaptation for lowland rice farmers in Bulukumba Regency, Indonesia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 194-202. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号