Regional Sustainability ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 1-10.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2020.08.001cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2020.08.001
Yuanming Zhang*( ), Daoyuan Zhang, Wenjun Li, Yaoming Li, Chi Zhang, Kaiyun Guan, Borong Pan
), Daoyuan Zhang, Wenjun Li, Yaoming Li, Chi Zhang, Kaiyun Guan, Borong Pan
Received:2020-06-15
Revised:2020-07-30
Accepted:2020-08-04
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2020-10-14
Contact:
Yuanming Zhang
E-mail:zhangym@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Yuanming Zhang, Daoyuan Zhang, Wenjun Li, Yaoming Li, Chi Zhang, Kaiyun Guan, Borong Pan. Characteristics and utilization of plant diversity and resources in Central Asia[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 1-10.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
URL: http://regsus.xjegi.com/EN/10.1016/j.regsus.2020.08.001
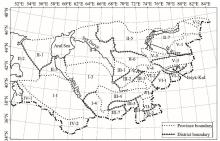
Fig. 3.
Plant geographical divisions of Central Asia. I. Turan Province: 1, Karakum District; 2, Messerian District; 3, South Kyzylkum District; and 4, Bukhara District. II. Central Kazakhstan Province: 1, Ustyurt District; 2, Mangyshlak District; 3, Amu Darya River District; 4, North Kyzylkum District; 5, Betpakdala District; 6, Muyunkum District; and 7, South Balkhash District. III. South Turkestan mountains Province: 1, Karatau District; 2, West Tianshan District; 3, Ferghan District; 4, Kuhistan District; 5, Gissar-Darvaz District; 6, Badakhshan District; and 7, South Tajikistan District. IV. Turkmenistan-Iran Province: 1, Kopet Dag District; and 2, Bathyz District. V. Junggar-Tianshan Province: 1, Junggar forest meadow District; 2, Tarbagatai District; 3, Yili mountain District; 4, Kyrgyzstan District; 5, Chu-Ili District; and 6, Talas District. VI. Central Tianshan Province: 1, Southwestern steppe District; 2, Northwestern meadow District; 3, Eastern mountain District; 4, Alai steppe District; and 5, Issyk-Kul meadow-steppe District. VII. Eastern Pamir Province: 1, Northeastern District; and 2, Southeastern District."
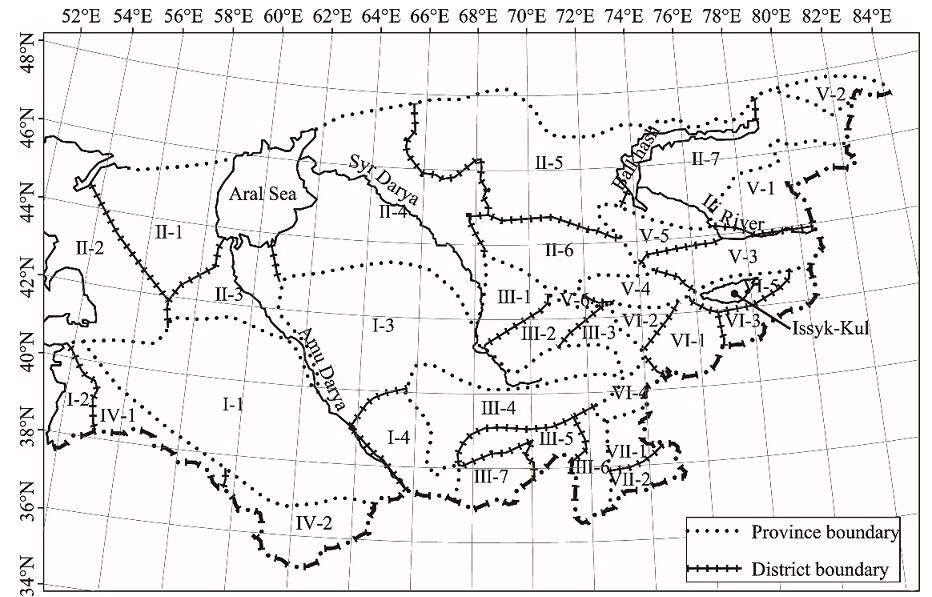
Table 1
Floristic data of Central Asia"
| Country/region | Flora, checklist and Red Data Book | Species count | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Asia | Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae, 1-11 | 9341 | |
| Plant Resources and Utilization in Central Asia | 9346 | ||
| Checklist of Vascular Plants of Central Asia | 9520 | Li et al. (unpublished) | |
| Kazakhstan | Flora Kazakhstana, 1-9 | 5631 | |
| Checklist of Vascular Plants of Kazakhstan | 5658 | ||
| Red Data Book of Kazakhstan, Volume 2: Plant | 387 | ||
| Kyrgyzstan | Flora Kirgizskoj SSR, 1-11; Supplementary 1-2 | 3576 | |
| Checklist of Vascular Plants of Kyrgyzstan | 3927 | ||
| The Red Data Book of the Kyrgyz Republic | 87 | ||
| Tajikistan | Flora Tadzikskoj SSR, 1-10 | 4445 | |
| The Red Data Book of the Republic of Tajikistan Volume 1 | 267 | ||
| Turkmenistan | Flora Turkmenii, 1-7 | 2607 | |
| Manual of Vascular Plants of Turkmenistan | 2800 | ||
| Red Data Book of Turkmenistan Volume 1: Plants and Fungi (3rd ed.) | 115 | ||
| Uzbekistan | Flora Uzbekistanica, 1-6 | 4148 | |
| Flora of Uzbekistan, 1-3 | 375 | ||
| Red Data Book of Uzbekistan 1: Plants | 324 | ||
| Xinjiang of China | Flora Xinjiangensis, 1-6 | 3875 |
Table 2
Classification system of plant resources in Central Asia (according to the system by Wu et al. (1983))"
| Category | Subcategory | Representative species |
|---|---|---|
| Edible plant resources | Starch plants | Ulmus pumila, Agriophyllum squarrosum, Oryza sativa, Triticum petropavlovskyi, and Eremurus inderiensis |
| Protein plants | Medicago sativa, Glycyrrhiza inflata, and Sophora alopecuroides | |
| Edible oils and fats | Juglans regia, Capparis spinosa, Carthamus tinctorius, Eruca sativa, and Brassica napas | |
| Vitamin plants | Nitraria tangutorum, Elaeagnus angustifolia, Hippophae rhamnoides, Rosa beggeriana, and Rubus idaeus | |
| Beverage plants | Crataegus songorica, Morus alba, Vitis vinifera, Punica granatum, and Cerasus fruticosa | |
| Food pigment plants | Daucus carota, Lycopersicon esculentum, Capsicum annuum, Urtica dioica, and Sambucas sibirica | |
| Spice plants | Cumimum cyminum, Mentha haplocalyx, Artemisia dracunculus, Origanam vulgare, and Carum carvi | |
| Plant sweeteners | Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Crataegus sanguinea, Vaccinium sp., Beta vulgaris, and Acer plantanoides | |
| Forage plants | Alhagi sparsifolia, Aristida pennata, Kochia prostrata, Sorghum sudanense, and Carex praecox | |
| Honey plants | Cirsium setosum, Ziziphora bungeana, Elsholtzia densa, Elaeagnus angustifolia, and Arctium lappa | |
| Medicinal plant resources | Chinese herbal medicine | Astragalus membranaceus, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Cistanche deserticola, Ephedra intermedia, Saussurea involucrata, Fritillaria walujewii, Ferula sinkiangensis, and Adonis amurensis |
| Plant pesticides | Anabasis aphylla, Portulaca oleracea, Artemisia annua, Solanum nigrum, and Stellera chamaejasme | |
| Toxic plants | Astragalus variabilis, Oxytropis glabra, Ceratocephalus testiculatus, telleropsis tianschanica, and Aconitum spp. | |
| Plant resources for industry use | Timber plants | Picea schrenkiana, Pinus sibirica, Populus tomentosa, Abies sibirica, and Populus tremula |
| Fibrous plants | Achnatherum splendens, Poacynum hendersonii, Phragmites australis, and Typha ssp. | |
| Tanning plant | Polygonum bistorta, Epilobium angustifolium, and Limonium gmelinii | |
| Aromatic plants | Elaeagnus angustifolia, Calligonum mongolicum, Rosa rugosa, Lavandula angustifolia, and Syringa persica | |
| Industrial oils and fats | Sphaerophysa salsula, Cannabis sativa, Thalictrum simplex, Asparagus offieinalis, and Ricinus communis | |
| Gum plants | Sesnania cannabina, Astragalus membranaceus, Elaeagnus angustifolia, Amygdalus davidiana, and Armeniaca vulgaris | |
| Plant dyes for industrial use | Isatis indigotica, Arnebia euchroma, Carthamus tinctorius, Lycium ruthenicum, and Anthemis tinctoria | |
| Energy plants | Typha latifolia, Haloxylon ammodendron, Tamarix chinensis, Calligonum mongolicum, and Reaumuria soongoarica | |
| Host plants of economic insects | Fraxinus sodgiana and Brachythe reflexum | |
| Other resources plants | Betula pendula, Orostachys sp., and Suaeda glauca | |
| Protection/ landscaping plant resources | Windbreak and sand-fixing plants | Calligonum mongolicum, Haloxylon ammodendron, Tamarix chinensis, Inula salsoloides, Kalidium foliatum, Halimodendron halodendron, Nitraria sibirica, and Seriphidium santolinum |
| Plants for soil and water conservation | Caragana leucophloea, Tamarix chinensis, and Ammodendron bifolium | |
| Green manure plants | Sophora alopecuroides, Medicago falcate, Melilotus albus, and Sphaerophysa salsula | |
| Flower plants | Limonium sinense, Acanthophyllum pungens, Aquilegia viridiflora, Anemone cathayensis, Clematis florida, Iris tectorum, Tulipa gesneriana, and Androsace umbellata | |
| Indicator plants | Moss and Salsola nitaria | |
| Anti-polluting plants | Tamarix Chinensis, Juniperus sabina, Hibiscus syriacus, and Punica granatum | |
| Plant germplasm resources | Endemic plants | Salix burqinensis, Betula Halopyila, Atraphaxis jrtyschensis, Polygonum tianxchanicum, Pyrola xinjiangensis, Seseli grubovii, Stenocoelium popovii, Oxytropis przewalskii, Oxytropis bogdoxchanica, Calophaca chinensis, Stellaria divnogorskjae, Calligonum roborovskii, and Zygophyllum kaschgarica |
| Germplasm resources of crop variety | Aegilops tauschi, Leymus racemosum, Eremopyrum sp., Learsia oryzoides, Aegopodium podagraria, Lactuca sativa, Lactuca altaica, Lactuca auriculata, Lactuca undulata, Lactuca serriola, Malus sieversii, Juglans regia, Arabidopsis tuemurica, and Arabidopsis qaranica |
| [1] | Abdulina, S.A ., 1999. Checklist of vascular plants of Kazakhstan. Academy of Sciences of Kazakhstan, Alma-Ata, 1-87. |
| [2] | Adylov, T.A ., 1983. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 7. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [3] | Adylov, T.A ., 1987. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 9. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [4] | Adylov, T.A., Zuckerwanik, T.I ., 1993. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 10. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [5] | Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG), 2016. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot.[J]. Linnean Soc. 181(1), 1-20. |
| [6] | Annabayramov, B ., 2011. The Red Data Book of Turkmenistan. Volume 1: Plants and Fungi (3 rd ed.), Revised and updated . Ashgabat: Ylym, 288. |
| [7] | Baitulin, I.O ., 2014. Red Data Book of Kazakhstan. Volume 2: Plant. Astana: LTD "AprPrintXXI". |
| [8] |
Bellard, C., Leclerc, C., Leroy, B ., et al., 2014. Vulnerability of biodiversity hotspots to global change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 23(12), 1376-1386
doi: 10.1111/geb.2014.23.issue-12 |
| [9] | Bondarenko, O.N., Nabiev, M.M ., 1972. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 3. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [10] | Chen, L ., 2012. Study on present situation of invasive alien species in Xinjiang. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang. 34(1), 21-27. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | Commissione Redactorum Florae Xinjiangensis, 1993-2011. Flora Xinjiangensis. Xinjiang Science and Technology Publishing House. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Convention on Biological Diversity Report of Turkmenistan, 2014. Fifth National Report on Implementation of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity at National Level. Ashgabat, Turkmenistan. |
| [13] | Christenhusz, M.J.M., Reveal, J.L., Farjon, A ., et al., 2011. A new classification and linear sequence of extant gymnosperms. Phytotaxa. 19, 55-70. |
| [14] | Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund (CEPF), 2017. Ecosystem Profile. Mountains of Central Asia Biodiversity Hotspot. Draft for Submission to the CEPF Donor Council. |
| [15] | Fedtschenko, B.A., Popov, M.G., Shishkin, B.K ., 1932. Flora Turkmenii, 1. Leningrad: An SSSR. |
| [16] | Fedtscihenko, B.A., Popov, M.G., Shishkin, B.K ., 1937. Flora Turkmenii, 2. Askhabad: Gosizdat. |
| [17] | Fedtscihenko, B.A., Popov, M.G., Shishkin, B.K ., 1948-1960. Flora Turkmenii, 3-7. Turkmensk: An SSSR. |
| [18] | Fritsch, R.M. , 2016. A Preliminary Review of Allium subg. Melanocrommyum in Central Asia. Gatersleben (Germany). http://www.ipk-gatersleben.de/. |
| [19] | Frodin, D. , 2001. Guide to Standard Floras of the World (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [20] | Hodgson, J.A., Thomas, C.D., Wintle, B.A ., et al., 2009. Climate change, connectivity and conservation decision making: back to basics. J. Appl. Ecol. 46(5), 964-969. |
| [21] | Kamelin, R.V., Kovalevskaya, S.S., Nabiev, M.M ., 1981. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 6. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [22] | Kamelin, R.V ., 1998. Materials on the history of Asian flora (Altai Mountain Country). Barnaul: Altai State University. |
| [23] | Khan, F., Sohail, Z., Khan, T. , et al., 2018. Deforestation: A continuous battle-A case study from Central Asia and other countries. In: Egamberdieva, D., Öztürk, M. (eds.). Vegetation of Central Asia and Environs. Switzerland: Springer, Cham.. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99728-5_4. |
| [24] | Khassanov, F.O., Pratov, U.P. , 2009. Red Data Book of Uzbekistan 1. Plants. Tashkent: Chinor ENK Press. |
| [25] | Khassanov, F.O ., 2015. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 11. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [26] | Khassanov, F.O., Rakhimova, N.K ., 2016. Typification in Iris L. s.l.(Iridaceae) from Middle Asia. Stapfia. 105, 51-58. |
| [27] | Korovin, E.P ., 1961-1962. The Vegetation of Central Asia and Southern Kazakhstan 1-2. Tashkent: Academy of Sciences of the Uzbek SSR. |
| [28] | Kovalevskaya, S.S ., 1968-1971. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 1-2. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [29] | Lazkov, G.A., Sultanova, B.A ., 2014. Checklist of Vascular Plants of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek: United Nations Development Programme. |
| [30] | Malcolm, J.R., Markham, A ., 2000. Global Warming and Terrestrial Biodiversity Decline. Washington, DC: WWF. |
| [31] | Ministry of Environment and Water Resources of the Republic of Kazakhstan, 2014. The Fifth National Report on Progress in Implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity. Astana, Kazakhstan. |
| [32] | Mittermeier, R.A., Gil, P.R., Hoffman, N ., et al., 2006. Hotspots revisited: Earth’s biologically richest and most threatened terrestrial ecoregions. UNESCO-UNF Conservation International, 343. |
| [33] | Nabiev, M.M ., 1986. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 8. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [34] | Nafisi, H., Kazempour-Osaloo, S., Mozaffarian, V ., et al., 2019. Molecular phylogeny and divergence times of the genus Hedysarum (Fabaceae) with special reference to section Multicaulia in Southwest Asia. Plant Syst. Evol. 305(10), 1001-1017. |
| [35] | Nikitin, V.G., Geldykhanov, A.M ., 1988. Manual of Vascular Plants of Turkmenistan. Leningrad: Science Publishers. |
| [36] | Ovchinnikov, P.N ., 1957-1991. Flora of the Tajik SSR 1-10. Moscow & Leningrad: Academy of Sciences of the USSR. |
| [37] | Pakhomova, M.G ., 1974-1976. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 4-5. Tashkent: Science Publishers. |
| [38] | Pavlov, N.V. , 1956-1966. Flora Kazakhstana 1-9. Alma-Ata: A Kazakhsk SSR Press. |
| [39] | Peterson, A., Harpke, D., Levichev, I.G ., et al., 2016. Morphological and molecular investigations of Gagea (Liliaceae) in southeastern Kazakhstan with special reference to putative altitudinal hybrid zones. Plant Syst. Evol. 302, 985-1007. |
| [40] | PPG (Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group) I, 2016. A community-derived classification for extant lycophytes and ferns. J. Syst. Evol. 54(6), 563-603. |
| [41] | Rahimi, F., Ibodzoda, K., Abdusalyamov, I ., et al., 2017. The Red Data Book of the Republic of Tajikistan, Volume 1, Flora. Dushanbe, Tajikistan. |
| [42] | Safarov, N., Novikova, T., Shermatov, K ., et al., 2014. Fifth National Report on Preservation of Biodiversity of the Republic of Tajikistan. Dushanbe, Tajikistan. |
| [43] | Schreder, R.R., Vvedenskyi, A.I. , 1941-1962. Flora Uzbekistanica 1-6. Tashkent: Fan Press. |
| [44] | Sennikov, A ., 2016. Flora of Uzbekistan 1. Tashkent: Navruz. |
| [45] | Sennikov, A ., 2017. Flora of Uzbekistan 2. Tashkent: Navruz. |
| [46] | Sennikov, A. , 2019. Flora of Uzbekistan 3. Tashkent: Manaviyat Press. |
| [47] | Sennikov, A.N., Tojibaev, K.S., Khassanov, F.O ., et al., 2016. The flora of Uzbekistan project. Phytotaxa. 282(2), 107-118. |
| [48] | Shen, G.M. , 2010. The Economic Plants and Utilization in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese) |
| [49] | Shishkin, B.K., Vvedensky, A.Z ., 1950-1962. Flora Kirgizskoj SSR 1-11. Bishkek: A Kirgizskoj SSSR. |
| [50] | Shukurov, E.D ., 2006. The Red Book of the Kyrgyz Republic. Bishkek. |
| [51] |
Simberloff, D., Martin, J.L., Genovesi, P ., et al., 2013. Impacts of biological invasions: what’s what and the way forward. Trends Ecol. Evol. 28(1), 58-66.
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2012.07.013 pmid: 22889499 |
| [52] | Takhtajan, A.L. , 1978. Floristic Region of Earth. Leningrad. Leningrad: Science Press. |
| [53] |
Tojibaev, K., Beshko, N ., 2015. Reassessment of diversity and analysis of distribution in Tulipa (Liliaceae) in Uzbekistan. Nord. J. Bot. 33(3), 324-334.
doi: 10.1111/njb.00616 |
| [54] | UNEP, Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development of Central Asia. 2009. The Regional Sustainable Development Strategy of Central Asia. http://www.mkurca.org/documenty/ssur/. |
| [55] | Vvedenskyi, A.I., Kamelin, R.V. , 1963-1993. Conspectus Florae Asiae Mediae 10. Tashkent: Fan Press. |
| [56] | Vykhodsev, Y.V ., 1967. Flora Kirgizskoj SSR, supplement 1. Bishkek: A Kirgizskoj SSSR. |
| [57] | Vykhodsev, Y.V ., 1970. Flora Kirgizskoj SSR, supplement 2. Bishkek: A Kirgizskoj SSSR. |
| [58] | Wu, Z.Y., Zhou, J., Pei, S.J ., 1983. Reasonable utilization and protection of plant resources. Reports and Abstracts Presented at a Meeting Commemorating the 50 th Anniversary of the Botanical Society of China . Beijing: Botanical Society of China. (in Chinese) |
| [59] | Yu, Y., Pi, Y.Y., Yu, X ., et al., 2019. Climate change, water resources and sustainable development in the arid and semi-arid lands of Central Asia in the past 30 years. J. Arid Land. 11(1), 1-14. |
| [60] | Zhang, P., Cui, Z.J., Xu, H ., et al., 2020. Thirst or malnutrition: The impacts of invasive insect Agrilus mali on the physiological status of wild apple trees. Forests. 11(4), 440, https://doi.org/10.3390/f11040440. |
| [61] | Zhang, Y.M., Li, Y.M., Shen, G.M. , et al., 2013. Plant Resources and Utilization in Central Asia. Beijing: China Meteorological Press. (in Chinese) |
| [62] | Zhao, W.Y., Li, J.L., Qi, J.G ., et al., 2005. Analysis on the problems and actuality of the steppe ecological security in Xinjiang and the solving measures. Arid Zone Research, 22(1), 45-50. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | HAO Yun, WU Miao, ZHANG Xiaoyun, WANG Lixian, HE Jingjing. Research on the implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity among the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation countries [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(3): 322-331. |
| [2] | Angelo Rellama AGDUMA, Francisco Gil GARCIA, Ma. Teodora CABASAN, Jonald PIMENTEL, Renee Jane ELE, Meriam RUBIO, Sedra MURRAY, Bona Abigail HILARIO-HUSAIN, Kier Celestial Dela CRUZ, Sumaira ABDULLAH, Shiela Mae BALASE, Krizler Cejuela TANALGO. Overview of priorities, threats, and challenges to biodiversity conservation in the southern Philippines [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(2): 203-213. |
| [3] | Mrinmay MANDAL, Nilanjana Das CHATTERJEE. Forest landscape and its ecological quality: a stepwise spatiotemporal evaluation through patch-matrix model in Jhargram District, West Bengal State, India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(2): 164-176. |
| [4] | Honghu MENG, Xiaoyang GAO, Yigang SAONG, Guanlong CAO, Jie LI. Biodiversity arks in the Anthropocene [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(2): 109-115. |
| [5] | Wakshum Shiferaw, Sebsebe Demissew, Tamrat Bekele, Ermias Aynekulu. Relationship between Prosopis juliflora invasion and livelihood diversification in the South Afar region, Northeast Ethiopia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 82-92. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号