Regional Sustainability ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 100112.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2024.03.006cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2024.03.006
• Full Length Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ratan PAL*( ), Buddhadev HEMBRAM, Narayan Chandra JANA
), Buddhadev HEMBRAM, Narayan Chandra JANA
Received:2022-10-11
Accepted:2024-02-29
Published:2024-03-30
Online:2024-04-30
Contact:
E-mail address: Ratan PAL, Buddhadev HEMBRAM, Narayan Chandra JANA. Assessment of soil erosion in the Irga watershed on the eastern edge of the Chota Nagpur Plateau, India[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100112.

Fig. 2.
Methodological flow chart of this study. DEM, digital elevation model; NDVI, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index; LULC, land use and land cover; RUSLE, Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation; A, average annual rate of soil erosion; R, rainfall-runoff erosivity; LS, slope length and steepness; C, cover-management; P, support practice; K, soil erodibility."
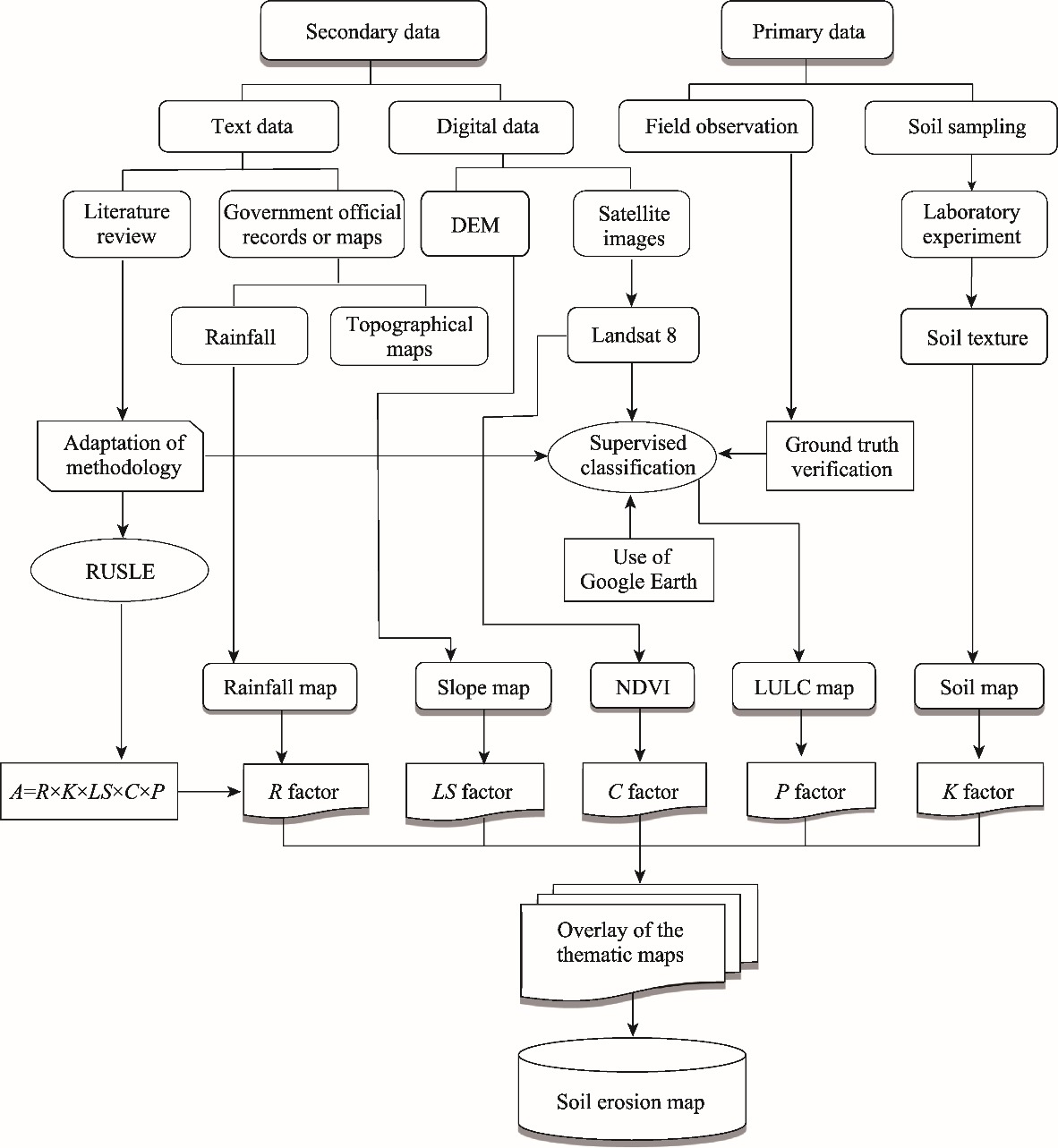
Table 2
Description of the collected 19 soil samples."
| Soil sample | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Weight of sand (g) | Weight of silt (g) | Weight of clay (g) | Percentage of sand (%) | Percentage of silt (%) | Percentage of clay (%) | Soil texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1 | 24°25′57′′ | 85°54′48′′ | 139.72 | 44.17 | 66.11 | 55.89 | 17.67 | 26.44 | Sandy clay loam |
| b2 | 24°25′57′′ | 85°57′23′′ | 124.11 | 50.73 | 75.16 | 49.64 | 20.29 | 30.06 | Sandy clay loam |
| b3 | 24°25′58′′ | 86°00′49′′ | 133.01 | 51.02 | 65.97 | 53.20 | 20.41 | 26.39 | Sandy clay loam |
| b4 | 24°25′59′′ | 86°03′17′′ | 103.68 | 45.15 | 101.17 | 41.47 | 18.06 | 40.47 | Clay |
| c2 | 24°23′38′′ | 85°57′24′′ | 118.59 | 47.87 | 83.54 | 47.44 | 19.15 | 33.42 | Sandy clay loam |
| c3 | 24°23′37′′ | 86°00′39′′ | 89.10 | 55.86 | 105.04 | 35.64 | 22.34 | 42.02 | Clay |
| c4 | 24°23′57′′ | 86°03′46′′ | 145.18 | 61.09 | 43.73 | 58.07 | 24.44 | 17.49 | Sandy loam |
| c5 | 24°23′55′′ | 86°06′22′′ | 112.55 | 75.87 | 61.58 | 45.02 | 30.35 | 24.63 | Loam |
| d2 | 24°20′43′′ | 85°57′56′′ | 163.65 | 43.55 | 42.8 | 65.46 | 17.42 | 17.12 | Sandy loam |
| d3 | 24°20′45′′ | 86°00′11′′ | 104.74 | 57.01 | 88.25 | 41.90 | 22.80 | 35.30 | Clay loam |
| d4 | 24°20′56′′ | 86°03′57′′ | 136.96 | 50.79 | 62.25 | 54.78 | 20.32 | 24.90 | Sandy clay loam |
| d5 | 24°20′25′′ | 86°06′35′′ | 131.61 | 63.92 | 54.47 | 52.64 | 25.57 | 21.79 | Sandy clay loam |
| e3 | 24°17′21′′ | 86°00′20′′ | 101.42 | 73.46 | 75.12 | 40.57 | 29.38 | 30.05 | Clay loam |
| e4 | 24°17′49′′ | 86°03′10′′ | 106.38 | 65.76 | 77.86 | 42.55 | 26.30 | 31.14 | Clay loam |
| e5 | 24°17′ 46′′ | 86°07′10′′ | 116.59 | 73.24 | 60.17 | 46.64 | 29.30 | 24.07 | Loam |
| f3 | 24°14′27′′ | 86°00′54′′ | 126.30 | 86.53 | 37.17 | 50.52 | 34.61 | 14.87 | Loam |
| f4 | 24°14′42′′ | 86°03′33′′ | 179.27 | 38.76 | 31.97 | 71.71 | 15.50 | 12.79 | Sandy loam |
| f5 | 24°14′22′′ | 86°05′48′′ | 134.86 | 66.97 | 48.17 | 53.94 | 26.79 | 19.27 | Sandy loam |
| g4 | 24°12′22′′ | 86°03′30′′ | 114.75 | 65.67 | 69.58 | 45.90 | 26.27 | 27.83 | Sandy clay loam |
Table 3
Soil erodibility (K) factor and soil organic carbon (SOC) of the collected 19 soil samples."
| Soil sample | fcsand | fcl−si | forgc | fhisand | K factor (t/(hm2•h•MJ•mm)) | SOC content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1 | 0.200002 | 0.759957 | 0.978409 | 0.996884 | 0.148248 | 1.66 |
| b2 | 0.200012 | 0.761346 | 0.975602 | 0.999146 | 0.148436 | 2.04 |
| b3 | 0.200006 | 0.77961 | 0.974846 | 0.998209 | 0.151732 | 2.34 |
| b4 | 0.200050 | 0.702759 | 0.976176 | 0.999847 | 0.137217 | 1.92 |
| c2 | 0.200016 | 0.738636 | 0.978914 | 0.999462 | 0.144546 | 1.62 |
| c3 | 0.200251 | 0.728054 | 0.983048 | 0.999956 | 0.143316 | 1.38 |
| c4 | 0.200004 | 0.850468 | 0.985746 | 0.995129 | 0.166856 | 1.26 |
| c5 | 0.200098 | 0.836715 | 0.982229 | 0.999676 | 0.164396 | 1.42 |
| d2 | 0.200000 | 0.814362 | 0.985746 | 0.978726 | 0.157136 | 1.26 |
| d3 | 0.200076 | 0.755338 | 0.991004 | 0.999833 | 0.149740 | 1.04 |
| d4 | 0.200004 | 0.786618 | 0.985276 | 0.997517 | 0.154626 | 1.28 |
| d5 | 0.200013 | 0.831183 | 0.988640 | 0.998405 | 0.164097 | 1.14 |
| e3 | 0.200196 | 0.809519 | 0.987670 | 0.999873 | 0.160044 | 1.18 |
| e4 | 0.200098 | 0.791087 | 0.986702 | 0.999808 | 0.156160 | 1.22 |
| e5 | 0.200065 | 0.835349 | 0.990543 | 0.999545 | 0.165468 | 1.06 |
| f3 | 0.200064 | 0.898337 | 0.988640 | 0.998975 | 0.177501 | 1.14 |
| f4 | 0.200000 | 0.834899 | 0.981460 | 0.932127 | 0.152761 | 1.46 |
| f5 | 0.200012 | 0.849956 | 0.985276 | 0.997913 | 0.167149 | 1.28 |
| g4 | 0.200052 | 0.805135 | 0.978914 | 0.999610 | 0.157611 | 1.62 |
| [1] | Achibeta, M., Balevb, S., Dutotb, A., et al., 2014. A model of road network and buildings extension co-evolution agent-based modeling and simulation of cities. Procedia Computer Science. 32, 828-833. |
| [2] | Almagro, A., Thome, T.C., Colman, C.B., et al., 2019. Improving cover and management factor (C-factor) estimation using remote sensing approaches for tropical regions. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 7(4), 325-334. |
| [3] | Ayoub, A.T., Olderman, L.R., Hakkeling, R.T.A., et al., 1991. World Map of the Status of Human-Induced Soil Degradation. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), International Soil Reference and Information Centre (ISRIC), 1-27. |
| [4] | Babu, R., Tejwani, K.G., Agarwal, M.P., et al., 1978. Distribution of erosion index and iso-erosion map of India. Indian Journal of Soil Conservation. 6(1), 1-12. |
| [5] |
Bhandari, A.K., Kumar, A., Singh, G.K., 2012. Feature extraction using Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI): A case study of Jabalpur City. Procedia Technology. 6(9), 612-621.
doi: 10.1016/j.protcy.2012.10.074 |
| [6] |
Bhattacharyya, T., Chandran, P., Ray, S.K., et al., 2015. Walkley-Black recovery factor to reassess soil organic matter: Indo-Gangetic Plains and black soil region of India case studies. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 46(20), 2628-2648.
doi: 10.1080/00103624.2015.1089265 |
| [7] | Biggelaar, C., Lal, R., Wiebe, K., et al., 2003. The global impact of soil erosion on productivity. Adv. Agron. 81, 49-95. |
| [8] | Brown, L.R., Wolf, E., 1984. Soil Erosion: Quiet Crisis in the World Economy. Washington: World Watch Institute, 1-44. |
| [9] | Colman, C.B., Oliveira, P.T.S., Almagro, A., et al., 2018. Impacts of climate and land use changes on soil erosion in the Upper Paraguay Basin. Campo Grande: Federal University of Mato Grosso do Sul, 66-78. |
| [10] |
Deep, S., Saklani, A., 2014. Urban Sprawl modelling using cellular automata. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences. 17(2), 179-187.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrs.2014.07.001 |
| [11] | Ding, L., Chen, K.L., Cheng, S.G., et al., 2015. Water ecological carrying capacity of urban lakes in the context of rapid urbanization: A case study of East Lake in Wuhan. Phys. Chem. Earth. 89- 90, 104-113. |
| [12] | Don, L., Leet, S.J., 1965. Physical Geology. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 143-144. |
| [13] |
Durigon, V.L., Carvalho, D.F., Antunes, M.A.H., et al., 2014. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 35(2), 441-453.
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2013.871081 |
| [14] | Eaton, D., 1996. The Economics of Soil Erosion: A Model of Farm Decision-Making. Environmental Economics Programme. London: International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), 1-52. |
| [15] |
El-Swaify, S.A., 1997. Factors affecting soil erosion hazards and conservation needs for tropical steep lands. Soil Technol. 11(1), 3-16.
doi: 10.1016/S0933-3630(96)00111-0 |
| [16] | FAO Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2019. Soil Erosion: The Greatest Challenge to Sustainable Soil Management. [2022-12-25]. https://www.rural21.com/english/news/detail/article/soil-erosion-the-greatest-challenge-for-sustainable-soil-management.html. |
| [17] | Gandhi, G.M., Parthiban, S., Thummalu, N., et al., 2015. NDVI: Vegetation change detection using remote sensing and GIS-A case study of Vellore District. Procedia Computer Science. 57, 1199-1210. |
| [18] | Hu, Y.F., Ban, Y.F., Zhang, Q., et al., 2008. Spatial-temporal pattern of GIMMS NDVI and its dynamics in Mongolian Plateau. In: 2008 International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE). Beijing, China. |
| [19] |
Issaka, S., Ashraf, M.A., 2017. Impact of soil erosion and degradation on water quality: A review. Geology, Ecology, and Landscapes. 1(1), 1-11.
doi: 10.1080/24749508.2017.1301053 |
| [20] | Kumar, M., Denis, D.M., Suryavanshi, S., 2016. Long-term climatic trend analysis of Giridih district, Jharkhand (India) using statistical approach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2, doi: 10.1007/s40808-016-0162-2. |
| [21] | Lal, R., 1994. Soil erosion by wind and water:Problems and prospects. In: Lal, R., (ed.). Soil Erosion Research Methods. London: Routledge, 1-9. |
| [22] | Leh, M., Bajwa, S., Chaubey, I., 2011. Impact of land use change on erosion risk: An integrated remote sensing, geographic information system, and modelling methodology. Land Degrad. Develop. 24(5), 409-421. |
| [23] | Liu, Y., 2016. Landscape connectivity in Soil Erosion Research: concepts, implication, quantification. Geogr. Res. 35(1), 195-202. |
| [24] | Mhaske, S.N., Pathak, K., Dash, S.S., et al., 2021. Assessment and management of soil erosion in the hilltop mining dominated catchment using GIS integrated RUSLE model. J. Environ. Manage. 294(11), doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112987. |
| [25] |
Moncef, B., Leidig, M., Gloaguen, R., 2011. Optimal parameter selection for qualitative regional erosion risk monitoring: A remote sensing study of SE Ethiopia. Geosci Front. 2(2), 237-245.
doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.03.004 |
| [26] |
Montgomery, D.R., Huang, M.Y.F., Huang, A.Y.L., 2014. Regional soil erosion in response to land use and increased typhoon frequency and intensity, Taiwan. Quat. Res. 81(1), 15-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2013.10.005 |
| [27] |
Moore, L.D., Burch, G.J., 1985. Physical basis of the length-slope factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50(5), 1294-1298.
doi: 10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000050042x |
| [28] |
Nadeu, E., Berhe, A.A., de Vente, J., et al., 2012. Erosion, deposition, and replacement of soil organic carbon in Mediterranean catchments: A geomorphological, isotopic and land use change approach. Biogeosciences. 9(3), 1099-1111.
doi: 10.5194/bg-9-1099-2012 |
| [29] |
Nageswara, P.P.R., Shobha, S.V., Ramesh, K.S., et al., 2005. Satellite-based assessment of agricultural drought in Karnataka State. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 33(3), 429-434.
doi: 10.1007/BF02990014 |
| [30] |
Narayan, V.V.D., Babu, R., 1983. Estimation of soil erosion in India. J. Irrig. Drainage Eng-ASCE. 109(4), 419-434.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1983)109:4(419) |
| [31] | NBSS & LUP National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning, 2014. Soil erosion in Jharkhand. Nagpur: NBSS & LUP Publication, 159. |
| [32] |
Niu, X.Y., Wang, Y.H., Hao, Y., et al., 2015. Effect of land use on soil erosion and nutrients in Dianchi Lake Watershed, China. Pedosphere. 25(1), 103-111.
doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(14)60080-1 |
| [33] | Oldeman, L.R., 1992. The global extent of soil degradation. In: Greenland, D.J., Szabolcs, T., (eds.). Soil Resilience and Sustainable Land Use. Wallingford: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau International, 99-118. |
| [34] | Oliveira, A.H., da Silva, M.A., Silva, M.L.N., et al., 2013. Development of topographic factor modeling for application in soil erosion models. In: Soriano, H.M.C., (ed.). Soil Processes and Current Trends in Quality Assessment. Shanghai: InTech Open Access Publisher, 111-138. |
| [35] | Pandey, A., Chowdary, V.M., Mal, B.C., 2007. Identification of critical erosion prone areas in the small agricultural watershed using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 21, 729-746. |
| [36] | Pimentel, D., 2006. Soil erosion: A food and environmental threat. Environment, Development and Sustainability. 8, 119-137. |
| [37] | Rahaman, S.A., Aruchamy, S., Jegankumar, R., et al., 2015. Estimation of annual average soil loss, based on RUSLE Model in Kallar Watershed, Bhavani Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. In: ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences. Joint International Geoinformation Conference 2015. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. |
| [38] | Rebecca, B., 2009. Soil Survey Field and Laboratory Methods Manual. Nebraska: U.S.Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, 38-42. |
| [39] | Renard, K.G., Foster, G.R., Weesies, G.A., et al., 1997. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Washington: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, 1-366. |
| [40] |
Roy, P., 2019. Application of USLE in a GIS environment to estimate soil erosion in the Irga watershed, Jharkhand, India. Phys. Geogr. 40(4), 361-383.
doi: 10.1080/02723646.2018.1550301 |
| [41] | Shit, P.K., Nandi, A.K., Bhunia, G.S., 2015. Soil erosion risk mapping using RUSLE model on Jhargram sub-division at West Bengal in India, Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 1(28), 1-12. |
| [42] | Singh, G., Babu, R., Narain, P., et al., 1992. Soil erosion rates in India. J. Soil Water Conserv. 47(1), 97-99. |
| [43] | Smoot, J.L., Smith, R.D., 1999. Soil Erosion Prevention and Sediment Control. Knoxville: The University of Tennessee, 7-8. |
| [44] | UNEP United Nations Environment Programme, 2001. India: State of the Environment 2001. [2022-11-17]. http://envfor.nic.in/soer/ 2001/ind_toc.pdf. |
| [45] | USDA-NRCS United States Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2000. Soil Texture Calculator. [2022-12-25]. . |
| [46] | USDA-SCS United States Department of Agriculture-Soil Conservation Service, 1972. National Engineering Handbook. Washington: USDA-SCS, 1-12. |
| [47] | van der Knijff, J., Jones, R., Montanarella, L., 2000. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Europe. Ispra: European Soil Bureau, 1-38. |
| [48] | Velayutham, M., Mandal, D.K., Mandal, C., et al., 1999. Agro-Ecological Subregions of India for Planning and Development. Nagpur: National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning, 28-32. |
| [49] |
Walkley, A., Black, I.A., 1934. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 37(1), 29-38.
doi: 10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003 |
| [50] | Williams, J.R., 1995. The EPIC Model. In: Singh, V.P., (ed.). Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology. Colorado: Water Resources Publications, 909-1000. |
| [51] | Wischmeier, W.H., Smith, D.D., 1965. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains. Washington: U.S Department of Agriculture, 47. |
| [52] | Wu, J., Xie, H., 2011. Research on characteristics of changes of lakes in Wuhan’s main urban area. Procedia Engineering. 21, 395-404. |
| [53] | Xie, Y.W., Zhao, X.J., Li, L.L., et al., 2010. Calculating NDVI for landsat 7-ETM data after atmospheric Correction using 6s model: A case study in Zhangye City, China. In: 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics. IEEE. Beijing, China, 1-4. |
| [54] | Zuazo, V.H.D., Pleguezuelo, C.R.R., 2009. Soil erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers:A review. In: Lichtfouse, E., Navarrete, M., Debaeke, P., et al., (eds.). Sustainable Agriculture. Dordrecht: Springer, 785-811. |
| [1] | Sunil SAHA, Debabrata SARKAR, Prolay MONDAL. Assessing and mapping soil erosion risk zone in Ratlam District, central India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(4): 373-390. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号