Regional Sustainability ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (4): 373-390.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2022.11.005cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2022.11.005
• Full Length Article • Previous Articles
Sunil SAHA, Debabrata SARKAR, Prolay MONDAL*( )
)
Received:2022-08-09
Revised:2022-11-13
Accepted:2022-11-29
Published:2022-12-30
Online:2023-01-31
Contact:
Prolay MONDAL
E-mail:mon.prolay@gmail.com
Sunil SAHA, Debabrata SARKAR, Prolay MONDAL. Assessing and mapping soil erosion risk zone in Ratlam District, central India[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(4): 373-390.
Table 1
Description of data used in this study."
| Data type | Resolution | Data source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LULC | 30 m | Landsat 8 Bands ( date: 2013-03-18T15:58:14Z-2022-09-24T14:54:39; acquisition date: 15/09/2021) | |
| NDVI | 30 m | ||
| Geomorphology | Geological Survey of India ( | ||
| DEM (aspect, slope, elevation, flow accumulation, stream density, SPI, flow direction, TWI) | Resolution resample | 30 m | Alaska Data Portal ( |
| Rainfall (mm) | 30 m | Center for Hydrometeorology and Remote Sensing (CHRS) Data Portal ( | |
| Distance from river (km) | - | Google Earth pro software | |
| Sand (%) | 30 m | Soil Grid Data Portal ( | |
| Silt (%) | 30 m | ||
| Clay (%) | 30 m | ||
| SOC (%) | 30 m | ||

Fig. 2.
Flow diagram of the whole study. DEM, Digital Elevation Model; A, annual average soil erosion; R, rainfall erosivity; K, soil erodibility; LS, length of the slope and steepness; C, land cove and management; P, support practisepractice; SOC, soil organic carbon; NDVI, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index; LULC, land use and land cover; RUSLE, Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation; AHP, Analytic Hierarchy Process; TWI, Topographic Wetness Index; SPI, Stream Power Index; REP tree, Reduced Error Pruning tree."

Table 5
Area distribution of RUSLE factors (rainfall erosivity (R), soil erodibility (K), slope length steepness (LS), land cover and management (C), and support practice (P) factors) in different classes (based on natural break)."
| R factor | K factor | LS factor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class (MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a)) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Class (×10-3 kg·h·MJ/mm) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Class | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) |
| 432-500 | 442.02 | 9.09 | 0.10-0.15 | 283.88 | 5.84 | <0.52 | 3154.89 | 64.90 |
| 500-550 | 643.91 | 13.25 | 0.15-0.25 | 2733.34 | 56.23 | 0.52-2.40 | 421.48 | 8.67 |
| 550-600 | 713.84 | 14.69 | 0.25-0.30 | 292.15 | 6.01 | 2.40-6.80 | 651.48 | 13.40 |
| 600-650 | 1713.84 | 35.26 | 0.30-0.40 | 195.90 | 4.03 | 6.80-40.00 | 448.15 | 9.22 |
| 650-750 | 1347.39 | 27.72 | >0.40 | 1355.73 | 27.89 | 40.00-98.88 | 207.35 | 4.27 |
| C factor | P factor | |||||||
| Class | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Class | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | |||
| 0.02-0.04 | 212.89 | 4.38 | <0.50 | 783.59 | 16.12 | |||
| 0.04-0.050 | 731.60 | 15.05 | 0.50-0.80 | 1172.47 | 24.12 | |||
| 0.05-0.08 | 1394.03 | 28.68 | 0.80-0.90 | 390.82 | 8.04 | |||
| 0.08-0.50 | 1532.21 | 31.52 | 0.90-1.00 | 2514.11 | 51.72 | |||
| 0.50-1.00 | 990.27 | 20.37 | - | - | - | |||

Fig. 4.
Spatial distribution of the selected variables and meteorological station for the evaluation of soil erosion risk zone. (a), aspect; (b), slope; (c), elevation; (d), TWI; (e), stream density; (f), SPI; (g), NDVI; (h), distance from river; (i), rainfall; (j), flow accumulation; (k), flow direction; (l), geomorphology; (m), LULC; (n), sand; (o), silt; (p), clay; (q), SOC; (r), sample point."
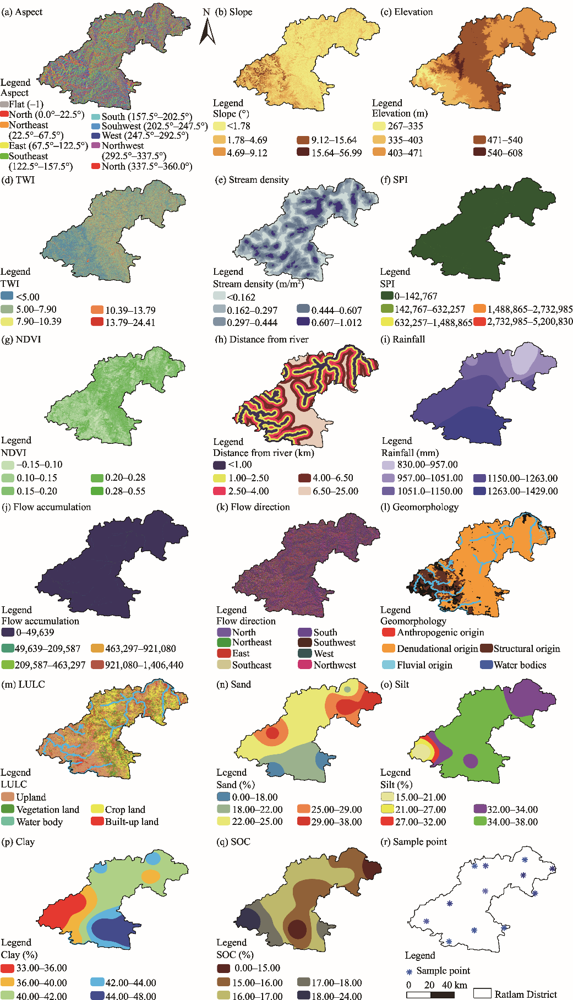
Table 7
Area distribution of different soil erosion risk zones using different techniques."
| Technique | Class of zone | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Accuracy | Kappa coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUSLE | Zone I | 1177.15 | 24.22 | 0.779 | 0.723 |
| Zone II | 959.43 | 19.74 | |||
| Zone III | 910.21 | 18.72 | |||
| Zone-IV | 1092.55 | 22.48 | |||
| Zone V | 721.66 | 14.85 | |||
| AHP | Zone I | 1381.72 | 28.42 | 0.788 | 0.736 |
| Zone II | 1139.45 | 23.44 | |||
| Zone III | 1168.47 | 24.04 | |||
| Zone IV | 636.90 | 13.10 | |||
| Zone V | 534.46 | 10.99 | |||
| Random Forest | Zone I | 50.63 | 1.04 | 0.808 | 0.760 |
| Zone II | 1686.27 | 34.69 | |||
| Zone III | 2682.64 | 55.19 | |||
| Zone IV | 410.98 | 8.45 | |||
| Zone V | 30.48 | 0.63 | |||
| REP tree | Zone I | 254.27 | 5.23 | 0.788 | 0.735 |
| Zone II | 1399.86 | 28.80 | |||
| Zone III | 2379.94 | 48.96 | |||
| Zone IV | 663.44 | 13.65 | |||
| Zone V | 163.49 | 3.36 | |||
| Average soil erosion risk zone | Zone I | 715.94 | 14.73 | 0.798 | 0.748 |
| Zone II | 1296.25 | 26.67 | |||
| Zone III | 1785.32 | 36.73 | |||
| Zone IV | 700.97 | 14.42 | |||
| Zone V | 362.52 | 7.46 |
| [1] | Ali, U., Ali, S.A., Ikbal, J., et al., 2018. Soil erosion risk and flood behaviour assessment of Sukhang Catchment, Kashmir Basin: Using GIS and remote sensing. J. Remote Sens. GIS. 7(1), 1-8. |
| [2] |
Angima, S.D., Stott, D.E., O’neill, M.K., et al., 2003. Soil erosion prediction using RUSLE for central Kenyan highland conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 97(1-3), 295-308.
doi: 10.1016/S0167-8809(03)00011-2 |
| [3] |
Arabameri, A., Chen, W., Loche, M., et al., 2020. Comparison of machine learning models for gully erosion susceptibility mapping. Geosci Front. 11(5), 1609-1620.
doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.11.009 |
| [4] | Arabameri, A., Santosh, M., Saha, S., et al., 2021. Spatial prediction of shallow landslide: application of novel rotational forest-based reduced error pruning tree. Geomatics. Nat. Haz. Risk. 12(1), 1343-1370. |
| [5] | Arnoldus, H.M.J., 1980. An Approximation of the Rainfall Factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons Ltd., 127-132. |
| [6] |
Ayalew, D.A., Deumlich, D., Šarapatka, B., et al., 2020. Quantifying the sensitivity of NDVI-based C factor estimation and potential soil erosion prediction using Space borne earth observation data. Remote Sens. 12(7), 1136, doi: 10.3390/rs12071136.
doi: 10.3390/rs12071136 |
| [7] |
Bakker, M.M., Govers, G., Ewert, F., et al., 2005. Variability in regional wheat yields as a function of climate, soil, and economic variables: assessing the risk of confounding. Agri. Ecosys. Environ. 110(3-4), 195-209.
doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2005.04.016 |
| [8] |
Bhandari, K.P., Aryal, J., Darnsawasdi, R., 2015. A geospatial approach to assessing soil erosion in a watershed by integrating socio-economic determinants and the RUSLE model. Nat. Haz. 75(1), 321-342.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1321-2 |
| [9] |
Bhattarai, R., Dutta, D., 2007. Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield using GIS at catchment scale. Water Resour. Manage. 21(10), 1635-1647.
doi: 10.1007/s11269-006-9118-z |
| [10] |
Buttafuoco, G., Conforti, M., Aucelli, P.P., et al., 2012. Assessing spatial uncertainty in mapping soil erodibility factor using geostatistical stochastic simulation. Environ. Earth. Sci. 66, 1111-1125.
doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1317-0 |
| [11] | CGWB (Central Ground Water Board), 2013. District Ground Water Information Booklet, Ratlam District, Minis. New Delhi: Ministry of Water Resources and Central Ground Water Board, 3-5. |
| [12] |
Chandio, I.A., Matori, A.N., Lawal, D.U., et al., 2011. GIS-based land suitability analysis using AHP for public parks planning in Larkana City. Mod. App. Sci. 5(4), 177, doi: 10.5539/mas.v5n4p177.
doi: 10.5539/mas.v5n4p177 |
| [13] |
Ciesiolka, C.A., Coughlan, K.J., Rose, C.W., et al., 1995. Methodology for a multi-country study of soil erosion management. Soil Technol. 8(3), 179-192.
doi: 10.1016/0933-3630(95)00018-6 |
| [14] | Colman, C.B., 2018. Impacts of climate and land use changes on soil erosion in the Upper Paraguay Basin. [2022-04-25]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328757474_IMPACTS_OF_CLIMATE_AND_LAND_USE_CHANGE_ON_SOIL_EROSION_IN_THE_UPPER_PARAGUAY_BASIN. |
| [15] | Coughlan, K.J., Rose, C.W., 1997. A New Soil Conservation Methodology and Application to Cropping Systems in Tropical Steeplands. Beltsville: Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, 144-147. |
| [16] |
Dabral, P.P., Baithuri, N., Pandey, A., 2008. Soil erosion assessment in a hilly catchment of North Eastern India using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water. Resour. Manage. 22(12), 1783-1798.
doi: 10.1007/s11269-008-9253-9 |
| [17] | Danielson, T., 2013. Utilizing a high resolution Digital Elevation Model (DEM) to Develop a Stream Power Index (SPI) for the Gilmore Creek Watershed in Winona County, Minnesota. Pap. Resour. Ana. [2022-04-25]. https://gis.smumn.edu/GradProjects/DanielsonT.pdf |
| [18] |
Das, B., Bordoloi, R., Thungon, L.T., et al., 2020. An integrated approach of GIS, RUSLE and AHP to model soil erosion in West Kameng watershed, Arunachal Pradesh. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 129(1), 1-18.
doi: 10.1007/s12040-019-1281-8 |
| [19] | de Roo, A., Jetten, V., Wesseling, C., et al., 1998. LISEM: a physically-based hydrologic and soil erosion catchment model. Mod. Soil Eros. Wat. 429-440. |
| [20] | Dissanayake, D., Morimoto, T., Ranagalage, M., 2019. Accessing the soil erosion rate based on RUSLE model for sustainable land use management: A case study of the Kotmale watershed, Sri Lanka. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ. 5(1), 291-306. |
| [21] |
Durigon, V.L., Carvalho, D.F., et al., 2014. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 35(2), 441-453.
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2013.871081 |
| [22] | Dutta, D., Das, S., Kundu, A., et al., 2015. Soil erosion risk assessment in Sanjal watershed, Jharkhand (India) using geo-informatics, RUSLE model and TRMM data. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ. 1(4), 1-9. |
| [23] | Eaton, J.W., Bateman, D., Hauberg, S., 1997. Gnu Octave. London: Network Thoery, 42. |
| [24] |
Ganasri, B.P., Ramesh, H., 2016. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS-A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 7(6), 953-961.
doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2015.10.007 |
| [25] | Gao, P., Wang, Y.M., Li, P.F., et al., 2018. Land degradation changes in the Yellow River Delta and its response to the stream flow-sediment fluxes since 1976. Land Deg. Dev. 29(9), 3212-3220. |
| [26] | Gayen, A., Saha, S., 2017. Application of weights-of-evidence (WoE) and evidential belief function (EBF) models for the delineation of soil erosion vulnerable zones: a study on Pathro river basin, Jharkhand, India. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ. 3(3), 1123-1139. |
| [27] | Gayen, A., Saha, S., Pourghasemi, H.R., 2020. Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and its validation by FR probability model. Geocar. Inter. 35(15), 1750-1768. |
| [28] | Gitas, I.Z., Douros, K., Minakou, C., et al., 2009. Multi-temporal soil erosion risk assessment in N. Chalkidiki using a modified USLE raster model. EAR. Sele. Proc. 8(1), 40-52. |
| [29] |
Guo, B., Yang, F., Fan, J.F., et al., 2022. The changes of spatiotemporal pattern of rocky desertification and its dominant driving factors in typical Karst Mountainous Areas under the background of global change. Remote Sens. 14(10), 2351, doi: 10.3390/rs14102351.
doi: 10.3390/rs14102351 |
| [30] |
Hancock, G.R., Murphy, D., Evans, K.G., 2010. Hillslope and catchment scale soil organic carbon concentration: An assessment of the role of geomorphology and soil erosion in an undisturbed environment. Geoderm. 155(1-2), 36-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.11.021 |
| [31] |
Hui, L., Chen, X.l., Lim, K.J., et al., 2010. Assessment of soil erosion and sediment yield in Liao watershed, Jiangxi Province, China, using USLE, GIS, and RS. J. Earth Sci. 21(6), 941-953.
doi: 10.1007/s12583-010-0147-4 |
| [32] |
Jain, M.K., Kothyari, U.C., 2000. Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield using GIS. Hydro. Sci. J. 45(5), 771-786.
doi: 10.1080/02626660009492376 |
| [33] |
Jain, S.K., Kumar, S., Varghese, J., 2001. Estimation of soil erosion for a Himalayan watershed using GIS technique. Water Resour. Manage. 15, 41-54.
doi: 10.1023/A:1012246029263 |
| [34] | Kachouri, S., Achour, H., Abida, H., et al., 2015. Soil erosion hazard mapping using Analytic Hierarchy Process and logistic regression: a case study of Haffouz watershed, central Tunisia. Ara. J. Geosci. 8(6), 4257-4268. |
| [35] | Kalmegh, S., 2015. Analysis of weka data mining algorithm reptree, simple cart and randomtree for classification of indian news. International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology. 2(2), 438-446. |
| [36] |
Kidane, M., Bezie, A., Kesete, N., et al., 2019. The impact of land use and land cover (LULC) dynamics on soil erosion and sediment yield in Ethiopia. Heli. 5(12), 02981, doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02981.
doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02981 |
| [37] | Kim, H.S., Julien, P.Y., 2006. Soil erosion modeling using RUSLE and GIS on the IMHA Watershed. Water Engin. Res. 7(1), 29-41. |
| [38] | Kothyari, U.C., 1996. Erosion and sediment problems in India. Proc Exeter SympEroSed Yield: Global Reg. Pers. 236, 531-540. |
| [39] | Kurande, V.H., Waagepetersen, R., Toft, E., et al., 2013. Reliability studies of diagnostic methods in Indian traditional Ayurveda medicine: an overview. J. Ayur. Integ. Med. 4(2), 67-76. |
| [40] | Laften, J.M., Lane, L.J., Foster, G.R., 1991. “WEPP: A new generation of erosion prediction technology”. J. Soil Water Conserv. 46(1), 34-38. |
| [41] | Lee, G.S., Lee, K.H., 2006. Scaling effect for estimating soil loss in the RUSLE model using remotely sensed geospatial data in Korea. J. Hyd. Earth Syst. Sci. 3, 135-157. |
| [42] |
Li, P., Mu, X., Holden, J., et al., 2017. Comparison of soil erosion models used to study the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Sci. Rev. 170, 17-30.
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.05.005 |
| [43] | Lillesand, T., Kiefer, R., 1994. Remote sensing and image interpretation. New York: John Wiley and Sons Ltd. |
| [44] | Ma, J.C., Lin, G.F., Chen, J.M., et al., 2010. An improved topographic wetness index considering topographic position. In: 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics. Beijing: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 1-4. |
| [45] |
Malczewski, J., 2000. On the use of weighted linear combination method in GIS: common and best practice approaches. Trans. GIS. 4(1), 5-22.
doi: 10.1111/1467-9671.00035 |
| [46] | Mallick, J., Talukdar, S., et al., 2021. Proposing receiver operating characteristic-based sensitivity analysis with introducing swarm optimized ensemble learning algorithms for groundwater potentiality modelling in Asir region, Saudi Arabia. Geocar. Int. 1-28. |
| [47] |
Marondedze, A.K., Schutt, B., 2020. Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model forthe Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province Zimbabwe. Sustai. 12(20), 8531, doi: 10.3390/su12208531.
doi: 10.3390/su12208531 |
| [48] | Masroor, M., Sajjad, H., Rehman, S., et al., 2022. Analysing the relationship between drought and soil erosion using vegetation health index and RUSLE models in Godavari middle sub-basin, India. Geosci. Front. 13(2), 21-33. |
| [49] |
McHugh, M.L., 2012. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochemia Medica. 22(3), 276-282.
pmid: 23092060 |
| [50] | Mohamed, W.N.H.W., Salleh, M.N.M., Omar, A.H., 2012. A comparative study of reduced error pruning method in decision tree algorithms. Int. Conf. Cont. Syst. Com. Engin. 392-397. |
| [51] |
Morgan, R.P.C., Morgan, D.D.V., Finney, H.J., 1984. A predictive model for the assessment of soil erosion risk. J. Agri. Eng. Res. 30, 245-253.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-8634(84)80025-6 |
| [52] | Morgan, R.P.C., Quinton, J.N., Rickson, R.J., 1992. EUROSEM documentation manual. Bedford: Silsoe College Cranfield University, 34. |
| [53] |
Mosavi, A., Sajedi-Hosseini, F., et al., 2020. Susceptibility mapping of soil water erosion using machine learning models. Water. 12(7), 1995, doi: 10.3390/w12071995.
doi: 10.3390/w12071995 |
| [54] | Naqvi, H.R., Mallick, J., Devi, L.M., et al., 2013. Multi-temporal annual soil loss risk mapping employing revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model in Nun Nadi Watershed, Uttrakhand (India). Ara. J. geosci. 6(10), 4045-4056. |
| [55] |
Narayan, V.V.D., Babu, R., 1983. Estimation of soil erosion in India. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 109, 419-434.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1983)109:4(419) |
| [56] | Nearing, M.A., Pruski, F.F., O’neal, M.R., 2004. Expected climate change impacts on soil erosion rates: a review. J. Soil Wat. Conserv. 59(1), 43-50. |
| [57] |
Nhu, V.H., Janizadeh, S., Avand, M., et al., 2020. Gis-based gully erosion susceptibility mapping: A comparison of computational ensemble data mining models. App. Sci. 10(6), 2039, doi: 10.3390/app10062039.
doi: 10.3390/app10062039 |
| [58] |
Onori, F., De Bonis, P., Grauso, S., 2006. Soil erosion prediction at the basin scale using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in a catchment of Sicily (southern Italy). Environ. Geo. 50(8), 1129-1140.
doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0286-1 |
| [59] | Onyando, J.O., Kisoyan, P., Chemelil, M.C., 2005. Estimation of potential soil erosion for river perkerra catchment in Kenya. Wat. Resour. Manage. 19(2), 133-143. |
| [60] | Pal, S.C., Chakrabortty, R., 2019. Modeling of water induced surface soil erosion and the potential risk zone prediction in a sub-tropical watershed of Eastern India. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ. 5(2), 369-393. |
| [61] |
Pandey, A., Mathur, A., Mishra, S.K., et al., 2009. Soil erosion modeling of a Himalayan watershed using RS and GIS. Environ. Earth Sci. 59, 399-410.
doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0038-0 |
| [62] |
Pandey, B., Reba, M., Joshi, P.K., et al., 2020. Urbanization and food consumption in India. Sci Rep. 10(1), 1-12.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56847-4 |
| [63] | Paul, S.S., Li, J., Li, Y., et al., 2021. Assessing land use-land cover change and soil erosion potential using a combined approach through remote sensing, RUSLE and random forest algorithm. Geocar. Int. 36(4), 361-375. |
| [64] | Phinzi, K., Ngetar, N.S., Ebhuoma, O., 2021. Soil erosion risk assessment in the Umzintlava catchment (T32E), Eastern Cape, South Africa, using RUSLE and random forest algorithm. S. Afr. Geog. J. 103(2), 139-162. |
| [65] | Pradeep, G.S., Krishnan, M.V., Vijith, H., 2015. Identification of critical soil erosion prone areas and annual average soil loss in an upland agricultural watershed of Western Ghats, using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and RUSLE techniques. Ara. J. Geosci. 8(6), 3697-3711. |
| [66] |
Prasannakumar, V., Shiny, R., Geetha, N., et al., 2011. Spatial prediction of soil erosion risk by remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE approach: a case study of Siruvani river watershed in Attapady valley, Kerala, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 64(4), 965-972.
doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-0913-3 |
| [67] |
Prasannakumar, V., Vijith, H., Abinod, S., et al., 2012. Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci. Front. 3(2), 209-215.
doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.11.003 |
| [68] | Renschler, C., Diekkrüger, B., Mannaerts, C., 1998. Regionalization in surface runoff and soil erosion risk evaluation. IAHS-AISH Pub. 254, 233-241. |
| [69] |
Römkens, M.J., Helming, K., Prasad, S.N., 2002. Soil erosion under different rainfall intensities, surface roughness, and soil water regimes. Catena. 46(2-3), 103-123.
doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(01)00161-8 |
| [70] |
Roslee, R., Sharir, K., 2019. Soil erosion analysis using RUSLE model at the Minitod area, Penampang, Sabah, Malaysia. J. Phys. Conf. S. 1358(1), 012066, doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1358/1/012066.
doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1358/1/012066 |
| [71] | Saaty, T., 1980. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) for Decision Making. [2022-04-25]. http://www.cashflow88.com/decisiones/saaty1.pdf |
| [72] |
Saaty, T.L., 1977. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psy. 15(3), 234-281.
doi: 10.1016/0022-2496(77)90033-5 |
| [73] | Saleh, B., Saedi, A., Al-Aqbi, A., et al., 2020. Analysis of weka data mining techniques for heart disease prediction system. Int. J. Med. Rev. 7(1), 15-24. |
| [74] |
Samaras, G., Koutitas, C.G., 2014. The impact of watershed management on coastal morphology: A case study using anintegrated approach and numerical modelling. Geomorphology. 211, 52-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.12.029 |
| [75] | Saroha, J., 2017. Soil erosion: causes, extent, and management in India. Int. J. Cre. Research Thoughts. 5(4), 1321-1330. |
| [76] |
Sharda, V.N., Mandai, D., Ojasvi, P.R., 2013. Identification of soil erosion risk areas for conservation planning in different states of India. J. Environ. Bio. 34(2), 219, doi: 10.1890/110156.
doi: 10.1890/110156 |
| [77] | Sharma, A., 2010. Integrating terrain and vegetation indices for identifying potential soil erosion risk area. Geo-Spatial Infor. Sci. 13(3), 201-209. |
| [78] | Shinde, V., Tiwari, K.N., Singh, M., 2010. Prioritization of micro watersheds on the basis of soil erosion hazard using remote sensing and geographic information system. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Engin. 5(2), 130-136. |
| [79] | Shit, P.K., Nandi, A.S., Bhunia, G.S., 2015. Soil erosion risk mapping using RUSLE model on Jhargram sub-division at West Bengal in India. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ. 1(3), 1-12. |
| [80] | Singh, G., Babu, R., Narain, P., et al., 1992. Soil erosion rates in India. J. Soil Water Conser. 47(1), 97-99. |
| [81] | Singh, G., Panda, R.K., 2017. Grid-cell based assessment of soil erosion potential for identification of critical erosion prone areas using USLE, GIS and remote sensing: A case study in the Kapgari watershed, India. Int. Soil Water Conser. Reser. 5(3), 202-211. |
| [82] | Stage, A.R., 1976. An expression for the effect of aspect, slope, and habitat type on tree growth. Forest Sci. 22(4), 457-460. |
| [83] | Tairi, A., Elmouden, A., Aboulouafa, M., 2019. Soil erosion risk mapping using the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and geographic information system in the tifnout-askaoun watershed, southern Morocco. Eur. Sci. J. 15(30), 1857-743. |
| [84] |
Tanyaş, H., Kolat, C., Süzen, M.L., 2015. A new approach to estimate cover-management factor of RUSLE and validation of RUSLE model in the watershed of Kartalkaya Dam. J. Hydro. 528, 584-598.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.06.048 |
| [85] | Teh, S.H., 2011. Soil erosion modeling using RUSLE and GIS on Cameron highlands, Malaysia for hydropower development. PhD Dissertation. Akureyri: The School for Renewable Energy Science. |
| [86] | Thapa, P., 2019. Observed and Perceived Climate Change Analysis in the Terai Region, Nepal. Dhulikhel:5th Graduate Conference on Environment and Sustainable Development, 35-43. |
| [87] |
Thapa, P., 2020. Spatial estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE modeling: a case study of Dolakha district, Nepal. Environ. Syst. Research. 9(1), 1-10.
doi: 10.1186/s40068-020-0163-z |
| [88] | Ukrainski, P., 2019. Classification accuracy assessment. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society Newsletter Confusion matrix method. |
| [89] | van der Knijff, J.M.F., Jones, R.J.A., Montanarella, L., 1999. Soil erosion risk assessment in Italy. Brussels: European Soil Bureau, European Commission. |
| [90] | Welde, K., 2016. Identification and prioritization of subwatersheds for land and water management in Tekeze dam watershed, Northern Ethiopia. Int. S. Water Conser. Research. 4(1), 30-38. |
| [91] | Williams, J.R., 1995. Chapter 25:The EPIC model. In: V.PSingh., (ed.). Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology. Highlands Ranch: Water Resources Publications, 909-1000. |
| [92] | Williams, J.R., Neitsch, S.L., Arnold, J.G., et al., 2000. Erosion Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Texas Agricultural Eksperiment Station. [2022-04-10]. https://swat.tamu.edu/media/99192/swat2009-theory.pdf |
| [93] | Wischmeier, W.H., Smith, D.D., 1965. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains: Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation. Ashington: United States Department of Agriculture. |
| [94] | Wischmeier, W.H., Smith, D.D., 1978. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: a Guide to Conservation Planning. Washington: United States Department of Agriculture. |
| [95] |
Xu, Y.Q., Shao, X.M., Peng, J., 2009. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: a case study of the Maotiao River watershed, Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Geo. 56, 1643-1652.
doi: 10.1007/s00254-008-1261-9 |
| [96] |
Zhao, G., Mu, X., Wen, Z., et al., 2013. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 24(5), 499-510.
doi: 10.1002/ldr.2246 |
| [97] |
Zhou, W., Wu, B., 2008. Assessment of soil erosion and sediment delivery ratio using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of upstream Chaobaihe River catchment, north China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 23, 167-173.
doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(08)60016-5 |
| [98] |
Zhu, M., 2015. Soil erosion assessment using USLE in the GIS environment: A case study in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 73(1), 7899-7908.
doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3947-5 |
| [1] | Soumen BISUI, Pravat Kumar SHIT. Assessing the role of forest resources in improving rural livelihoods in West Bengal of India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100141-. |
| [2] | Debanjan BASAK, Indrajit Roy CHOWDHURY. Role of self-help groups on socioeconomic development and the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) among rural women in Cooch Behar District, India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(2): 100140-. |
| [3] | Ramya Kundayi RAVI, Priya BABY, Nidhin ELIAS, Jisa George THOMAS, Kathyayani Bidadi VEERABHADRAIAH, Bharat PAREEK. Preparedness, knowledge, and perception of nursing students about climate change and its impact on human health in India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100116-. |
| [4] | Aishwarya BASU, Jyotish Prakash BASU. Impact of forest governance and enforcement on deforestation and forest degradation at the district level: A study in West Bengal State, India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 441-452. |
| [5] | Daniel ETONGO, Uvicka BRISTOL, Terence Epule EPULE, Ajith BANDARA, Sandra SINON. Expert elicitations of smallholder agroforestry practices in Seychelles: A SWOT-AHP analysis [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(3): 282-295. |
| [6] | WEI Xingtao, Oliver Valentine EBOY, CAO Guangchao, XU Lu. Spatio-temporal variation of water conservation and its impact factors on the southern slope of Qilian Mountains [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(1): 54-67. |
| [7] | Giribabu DANDABATHULA, Sudhakar Reddy CHINTALA, Sonali GHOSH, Padmapriya BALAKRISHNAN, Chandra Shekhar JHA. Exploring the nexus between Indian forestry and the Sustainable Development Goals [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(4): 308-323. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号