Regional Sustainability ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (1): 13-27.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2023.02.002cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2023.02.002
• Full Length Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-07-06
Accepted:2023-02-18
Published:2023-03-30
Online:2023-04-14
Contact:
Durdana OVAIS
E-mail:durdanaovais@bsssbhopal.edu.in
Durdana OVAIS. Students’ sustainability consciousness with the three dimensions of sustainability: Does the locus of control play a role?[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(1): 13-27.
Table 2
Factor loading and descriptive statistics of the dimensions of sustainability knowledge, attitude, behaviour, and locus of control."
| Construct | Dimension | Item code | Factor loading | Mean score | Standard deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability knowledge (SK) | Environment | SK 1 | 0.268 | 4.02 | 0.990 | -0.927 | 0.413 |
| SK 2 | 0.562 | 4.53 | 0.653 | -1.184 | 0.692 | ||
| SK 3 | 0.670 | 4.47 | 0.744 | -1.294 | 1.056 | ||
| Society | SK 4 | 0.751 | 4.39 | 0.788 | -1.299 | 1.637 | |
| SK 5 | 0.743 | 4.40 | 0.691 | -0.734 | -0.633 | ||
| SK 6 | 0.689 | 4.46 | 0.724 | -1.279 | 1.244 | ||
| Economy | SK 7 | 0.689 | 4.20 | 0.813 | -0.991 | 1.306 | |
| SK 8 | 0.741 | 4.25 | 0.829 | -0.962 | 0.610 | ||
| SK 9 | 0.712 | 4.25 | 0.853 | -1.077 | 1.075 | ||
| Sustainability attitude (SA) | Environment | SA 1 | 0.049 | 3.03 | 1.478 | -0.124 | -1.424 |
| SA 2 | 0.677 | 4.54 | 0.682 | -1.462 | 1.840 | ||
| SA 3 | 0.749 | 4.39 | 0.682 | -0.862 | 0.340 | ||
| Society | SA 4 | 0.810 | 4.40 | 0.698 | -1.184 | 2.175 | |
| SA 5 | 0.587 | 4.47 | 0.704 | -1.394 | 2.522 | ||
| SA 6 | 0.776 | 4.60 | 0.653 | -1.942 | 5.058 | ||
| Economy | SA 7 | 0.695 | 4.35 | 0.768 | -1.077 | 1.129 | |
| SA 8 | 0.735 | 4.34 | 0.707 | -1.017 | 1.695 | ||
| SA 9 | 0.608 | 4.27 | 0.774 | -0.954 | 0.991 | ||
| Sustainability behaviour (SB) | Environment | SB 1 | 0.723 | 4.21 | 0.769 | -0.715 | 0.376 |
| SB 2 | 0.749 | 4.35 | 0.710 | -1.041 | 1.702 | ||
| SB 3 | 0.725 | 4.39 | 0.696 | -0.791 | -0.224 | ||
| Society | SB 4 | 0.503 | 4.43 | 0.728 | -1.404 | 2.616 | |
| SB 5 | 0.690 | 4.03 | 0.944 | -0.835 | 0.347 | ||
| SB 6 | 0.617 | 4.59 | 0.640 | -1.645 | 2.885 | ||
| Economy | SB 7 | 0.751 | 4.24 | 0.739 | -0.487 | -0.771 | |
| SB 8 | 0.558 | 3.60 | 1.109 | -0.475 | -0.390 | ||
| SB 9 | 0.652 | 3.93 | 0.975 | -0.718 | 0.271 | ||
| Locus of control (LC) | - | LC 1 | 0.845 | 2.79 | 1.268 | -0.021 | -1.047 |
| LC 2 | 0.727 | 2.53 | 1.096 | 0.235 | -0.659 | ||
| LC 3 | 0.698 | 2.47 | 1.036 | 0.339 | -0.384 | ||
| LC 4 | 0.845 | 2.92 | 1.202 | -0.037 | -0.885 | ||
| LC 5 | 0.835 | 2.83 | 1.221 | -0.070 | -1.025 |
Table 3
Correlation analysis among the dimensions of sustainability knowledge, attitude, and behaviour."
| Construct | Dimension | Sustainability knowledge | Sustainability attitude | Sustainability behaviour | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environment | Society | Economy | Environment | Society | Economy | Environment | Society | Economy | ||
| Sustainability knowledge | Environment | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Society | 0.507** | 1.000 | . | . | . | |||||
| Economy | 0.457** | 0.701** | 1.000 | . | ||||||
| Sustainability attitude | Environment | 0.352** | 0.326** | 0.271** | 1.000 | |||||
| Society | 0.413** | 0.501** | 0.412** | 0.258** | 1.000 | |||||
| Economy | 0.332** | 0.581** | 0.553** | 0.458** | 0.620** | 1.000 | ||||
| Sustainability behaviour | Environment | 0.328** | 0.438** | 0.308** | 0.347** | 0.366** | 0.470** | 1.000 | ||
| Society | 0.373** | 0.424** | 0.411** | 0.381** | 0.527** | 0.594** | 0.582** | 1.000 | ||
| Economy | 0.348** | 0.413** | 0.340** | 0.466** | 0.274** | 0.417** | 0.592** | 0.533** | 1.000 | |
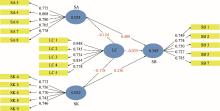
Fig. 1.
Measurement model. SA, sustainability attitude; SK, sustainability knowledge; SB, sustainability behaviour; LC, locus of control. Blue circles represents the three constructs (sustainability attitude, sustainability knowledge and sustainability behaviour) and locus of control in the study. Arrows shows the relationships between the constructs. The values in the circle represents R2. The black values on the arrow indicate the factor loading (a slight variation comes when we run the software again with deleted items which are acceptable). The red value on the arrow indicates the beta value."

Table 4
Reliability of constructs in sustainability consciousness in Smart PLS 3.0."
| Construct | Item code | Cronbach’s Alpha | rho_A | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability knowledge (SK) | SK 4 | 0.850 | 0.867 | 0.892 | 0.623 |
| SK 5 | |||||
| SK 6 | |||||
| SK 8 | |||||
| SK 9 | |||||
| Sustainability attitude (SA) | SA 3 | 0.828 | 0.834 | 0.879 | 0.593 |
| SA 4 | |||||
| SA 6 | |||||
| SA 7 | |||||
| SA 8 | |||||
| Sustainability behaviour (SB) | SB 1 | 0.815 | 0.817 | 0.871 | 0.574 |
| SB 2 | |||||
| SB 3 | |||||
| SB 5 | |||||
| SB 7 | |||||
| Locus of control (LC) | LC 1 | 0.817 | 0.831 | 0.871 | 0.574 |
| LC 2 | |||||
| LC 3 | |||||
| LC 4 | |||||
| LC 5 |
Table 5
Discriminant validity analysis through the Fornell and Larcker criterion in Smart PLS 3.0."
| Construct | Locus of control | Sustainability attitude | Sustainability behaviour | Sustainability knowledge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locus of control | 0.789 | |||
| Sustainability attitude | -0.154 | 0.770 | ||
| Sustainability behaviour | -0.139 | 0.556 | 0.758 | |
| Sustainability knowledge | -0.178 | 0.636 | 0.497 | 0.758 |
Table 7
Hypothesis testing through bootstrapping in Smart PLS 3.0."
| Hypothesis | Description | t-value | P-value | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Sustainability knowledge impacts sustainability behaviour | 3.163 | 0.002 | Accepted |
| H2 | Sustainability attitude impacts sustainability behaviour | 5.513 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| H3a | Locus of control impacts sustainability knowledge | 2.580 | 0.010 | Accepted |
| H3b | Locus of control impacts sustainability attitude | 2.022 | 0.044 | Accepted |
| H3c | Locus of control impacts sustainability behaviour | 0.434 | 0.664 | Rejected |
| H4 | Locus of control moderates the relationship between sustainability attitude and sustainability behaviour | 1.149 | 0.251 | Rejected |
| H5 | Locus of control moderates the relationship between sustainability knowledge and behaviour | 1.112 | 0.267 | Rejected |
Table 8
Multi-group analysis to study the variance of two groups (the internal and external locus of control) in Smart PLS 3.0."
| Hypothesis | Path coefficients (group with the internal locus of control to group with the external locus of control) | t-value | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group with the internal locus of control | Group with the external locus of control | Group with the internal locus of control | Group with the external locus of control | ||
| H1 | -0.281 | 0.296 | 3.247 | 0.767 | 0.001 |
| H2 | 0.124 | 2.825 | 2.344 | 0.005 | 0.019 |
| H3a | -0.627 | 5.153 | 1.545 | 0.000 | 0.123 |
| H3b | -0.831 | 7.371 | 1.749 | 0.000 | 0.081 |
| H3c | -0.402 | 2.985 | 0.417 | 0.003 | 0.677 |
| H4 | 0.081 | 0.725 | 0.128 | 0.469 | 0.898 |
| H5 | -0.090 | 0.412 | 0.368 | 0.680 | 0.713 |
Table S1
Descriptions of the questions selected in this study."
| Construct | Dimension | Item code | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability knowledge (SK) | Environment | SK 1 | Reducing water consumption is necessary for sustainable development. |
| SK 2 | Preserving the variety of living creatures is necessary for sustainable development (preserving biological diversity). | ||
| SK 3 | For sustainable development, people need to be educated in how to protect themselves against natural disasters. | ||
| Society | SK 4 | A culture where conflicts are resolved peacefully through discussion is necessary for sustainable development. | |
| SK 5 | Respecting human rights is necessary for sustainable development. | ||
| SK 6 | To achieve sustainable development, all the people in the world must have access to good education. | ||
| Economy | SK 7 | Sustainable development requires that companies act responsibly towards their employees, customers and suppliers. | |
| SK 8 | Sustainable development requires a fair distribution of goods and services among people in the world. | ||
| SK 9 | Wiping out poverty in the world is necessary for sustainable development. | ||
| Sustainability attitude (SA) | Environment | SA 1 | I think that using more natural resources than we need does not threaten the health and well-being of people in the future. |
| SA 2 | I think that we need stricter laws and regulations to protect the environment. | ||
| SA 3 | I think that it is important to take measures against problems which have to do with climate change. | ||
| Society | SA 4 | I think that everyone ought to be given the opportunity to acquire the knowledge, values and skills that are necessary to live sustainably. | |
| SA 5 | I think that we who are living now should make sure that people in the future enjoy the same quality of life as we do today. | ||
| SA 6 | I think that women and men throughout the world must be given the same opportunities for education and employment. | ||
| Economy | SA 7 | I think that companies have a responsibility to reduce the use of packaging and disposable articles. | |
| SA 8 | I think it is important to reduce poverty. | ||
| SA 9 | I think that companies in rich countries should give employees in poor nations the same conditions as in rich countries. | ||
| Sustainability behaviour (SB) | Environment | SB 1 | I recycle as much as I can. |
| SB 2 | I always separate food waste before putting out the rubbish when I have the chance. | ||
| SB 3 | I have changed my personal lifestyle to reduce waste (e.g., throwing away less food or not wasting materials). | ||
| Society | SB 4 | When I use a computer or mobile to chat, text, play games and so on, I always treat others as respectfully as I would in real life. | |
| SB 5 | I support an aid organization or environmental group. | ||
| SB 6 | I show the same respect to men and women, boys and girls. | ||
| Economy | SB 7 | I do things which help poor people. | |
| SB 8 | I often purchase second-hand goods over the internet or in a shop. | ||
| SB 9 | I avoid buying goods from companies with a bad reputation for looking after their employees and the environment. | ||
| Locus of control (LC) | - | LC 1 | I have often found that what is going to happen will happen. |
| LC 2 | Many times, we might just as well decide what to do by flipping a coin. | ||
| LC 3 | Who gets to be the boss often depends on who was lucky enough to be in the right place first. | ||
| LC 4 | Most people do not realize the extent to which their lives are controlled by accidental happenings. | ||
| LC 5 | Many times, I feel that I have little influence over the things that happen to me. |
| [1] |
Agbedahin A.V., 2019. Sustainable development, education for sustainable development, and the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development: emergence, efficacy, eminence, and future. Sustain. Dev. 27(4), 669-680.
doi: 10.1002/sd.1931 |
| [2] | Ajzen I., Fishbein M., 1980. Understanding Attitudes and Predicting Social Behavior. New Jersey: Prentiss-Hall. |
| [3] |
Ajzen I., 1991. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Dec. 50, 179-211.
doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T |
| [4] |
Aleixo A.M., Azeiteiro U., Leal S., 2018. The implementation of sustainability practices in Portuguese higher education institutions. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 19(1), 146-178.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-02-2017-0016 |
| [5] |
Allcott H., Mullainathan S., 2010. Behavior and energy policy. Science. 327(5970), 1204-1205.
doi: 10.1126/science.1180775 pmid: 20203035 |
| [6] |
Al-Naqbi A.K., Alshannag Q., 2018. The status of education for sustainable development and sustainability knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors of UAE University students. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 19(3), 566-588.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-06-2017-0091 |
| [7] |
Ambusaidi A., Al Washahi M., 2016. Prospective teachers’ perceptions about the concept of sustainable development and related issues in Oman. J. Educ. Sustain. Dev. 10(1), 3-19.
doi: 10.1177/0973408215625528 |
| [8] |
Archer R.P., 1979. Relationships between locus of control, trait anxiety, and state anxiety: An interactionist perspective. J. Pers. 47(2), 305-316.
pmid: 469699 |
| [9] |
Arushanyan Y., Ekener E., Moberg Å., 2017. Sustainability assessment framework for scenarios-SAFS. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 63, 23-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2016.11.001 |
| [10] |
Azeiteiro U.M., Bacelar-Nicolau P., Caetano F.J.P., et al., 2015. Education for sustainable development through e-learning in higher education: Experiences form Portugal. J. Clean. Prod. 106, 308-319.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.11.056 |
| [11] |
Ballantyne R., Packer J., 2005. Promoting environmentally sustainable attitudes and behaviour through free-choice learning experiences: what is the state of the game?Environ. Educ. Res. 11(3), 281-295.
doi: 10.1080/13504620500081145 |
| [12] |
Balundė A., Perlaviciute G., Steg L., 2019. The relationship between people’s environmental considerations and pro-environmental behavior in Lithuania. Front. Psychol. 2319, doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02319.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02319 |
| [13] |
Barth M., Rieckmann M., 2012. Academic staff development as a catalyst for curriculum change towards education for sustainable development: an output perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 26, 28-36.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.12.011 |
| [14] | Barth M., 2014. Implementing Sustainability in Higher Education: Learning in an Age of Transformation. London: Routledge. |
| [15] | Batth K.K., 2020. Sustainability awareness in India. In: Issa T., Issa T., Issa T.B., (eds.). Sustainability Awareness and Green Information Technologies. Berlin: Springer, 71-99. |
| [16] |
Baumgartner R.J., Rauter R., 2017. Strategic perspectives of corporate Sustainability management to develop a sustainable organization. J. Clean. Prod. 140, 81-92.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.146 |
| [17] |
Biasutti M., Frate S., 2017. A validity and reliability study of the attitudes toward sustainable development scale. Environ. Educ. Res. 23(2), 214-230.
doi: 10.1080/13504622.2016.1146660 |
| [18] | Borges F., 2019. Knowledge, attitudes and behaviours concerning sustainable development: a study among prospective elementary teachers. High. Educ. Stud. 9(2), 22-32. |
| [19] |
Brody S.D., Ryu H.C., 2006. Measuring the educational impacts of a course on sustainable development. Environ. Educ. Res. 12(2), 179-199.
doi: 10.1080/13504620600688955 |
| [20] | Buckler C., Creech H., 2014. Shaping the Future We Want: UN Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005-2014). Paris: United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. |
| [21] | Burmeister M., Eilks I., 2013. An understanding of sustainability and education for sustainable development among German student teachers and trainee teachers of chemistry. Sci. Educ. Int. 24(2), 167-194. |
| [22] |
Cheung M.F., To W.M., 2019. An extended model of value-attitude-behavior to explain Chinese consumers’ green purchase behavior. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 50, 145-153.
doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2019.04.006 |
| [23] |
Chiang Y.T., Fang W.T., Kaplan U., et al., 2019. Locus of control: The mediation effect between emotional stability and pro-environmental behavior. Sustainability. 11(3), 820, doi: 10.3390/su11030820.
doi: 10.3390/su11030820 |
| [24] | Chin W.W., 1998. Commentary: Issues and opinion on structural equation modeling. MIS Quarterly. 22, 7-16. |
| [25] | Chin W.W., 2010. How to write up and report PLS analyses. In: Vinzi V.E., Chin W.W., Henseler J., (eds.). Handbook of Partial Least Squares. Berlin: Springer, 655-690. |
| [26] | Chouinard Y., Ellison J., Ridgeway R., 2011. The sustainable economy. Harv. Bus. Rev. 89(10), 52-62. |
| [27] |
Čiarnienė R., Vienažindienė M., Adamonienė R., 2020. Sustainable behaviour: evidence from Lithuania. Engineering Management in Production and Services. 12(1), 80-92.
doi: 10.2478/emj-2020-0007 |
| [28] | Clugston R., Caldar W., 1999. Critical dimensions of sustainability in higher education. Sustainability and University Life. 5(1), 31-46. |
| [29] |
Cooper D.R., Gutowski T.G., 2017. The environmental impacts of reuse: a review. J. Ind. Ecol. 21(1), 38-56.
doi: 10.1111/jiec.2017.21.issue-1 |
| [30] |
Cotton D.R., Warren M.F., Maiboroda O., et al., 2007. Sustainable development, higher education and pedagogy: A study of lecturers’ beliefs and attitudes. Environ. Educ. Res. 13(5), 579-597.
doi: 10.1080/13504620701659061 |
| [31] | Dahl L.A., 2001. Values as the foundation for sustainable behaviour. In:5thAnnual Conference of the International Environment Forum (ACIEF). ACIEF. Hluboka nad Vltavou, Czech Republic. |
| [32] |
Davis S.A., Edmister J.H., Sullivan K., et al., 2003. Educating sustainable societies for the twenty-first century. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 4(2), 169-179.
doi: 10.1108/14676370310467177 |
| [33] |
Derdowski L.A., Grahn Å.H., Hansen H., et al., 2020. The new ecological paradigm, pro-environmental behaviour, and the moderating effects of locus of control and self-construal. Sustainability. 12(18), 7728, doi: 10.3390/su12187728.
doi: 10.3390/su12187728 |
| [34] |
Di Fabio A., Saklofske D.H., 2019. Positive relational management for sustainable development: beyond personality traits—The contribution of emotional intelligence. Sustainability. 11(2), 330, doi: 10.3390/su11020330.
doi: 10.3390/su11020330 |
| [35] |
Djordjevic A., Cotton D.R.E., 2011. Communicating the sustainability message in higher education institutions. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 12(4), 381-394.
doi: 10.1108/14676371111168296 |
| [36] | Dunlap R.E., Jones R.E., 2002. Environmental concern:Conceptual and measurement issues. Handbook of Environmental Sociology. 3(6), 482-524. |
| [37] |
Emanuel R., Adams J.N., 2011. College students’ perceptions of campus sustainability. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 12(1), 79-92.
doi: 10.1108/14676371111098320 |
| [38] |
Ewert A., Baker D., 2001. Standing for where you sit: An exploratory analysis of the relationship between academic major and environment beliefs. Environ. Behav. 33(5), 687-707.
doi: 10.1177/00139160121973197 |
| [39] |
Fielding K.S., Head B.W., 2012. Determinants of young Australians’ environmental actions: The role of responsibility attributions, locus of control, knowledge and attitudes. Environ. Educ. Res. 18(2), 171-186.
doi: 10.1080/13504622.2011.592936 |
| [40] | Fishbein M., Ajzen I., 1977. Belief, Attitude, Intention, and Behavior:An Introduction to Theory and Research. Boston:Addison-Wesley, 177-188. |
| [41] |
Fornell C., Larcker D.F., 1981. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 18(1), 39-50.
doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104 |
| [42] |
Francis A., Sarangi G.K., 2022. Sustainable consumer behaviour of Indian millennials: Some evidence. Current Research in Environmental Sustainability. 4, 100109, doi: 10.1016/j.crsust.2021.100109.
doi: 10.1016/j.crsust.2021.100109 |
| [43] | Gagne R., Briggs L., Wager W., 1992. Principles of Instructional Design Belmont CA:Wadsworth. New York:Thomson Learning. |
| [44] | Galang A.P., 2010. Environmental education for sustainability in higher education institutions in the Philippines. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 5(2), 173-183. |
| [45] |
Gatersleben B., Steg L., Vlek C., 2002. Measurement and determinants of environmentally significant consumer behavior. Environ. Behav. 34(3), 335-362.
doi: 10.1177/0013916502034003004 |
| [46] |
Gefen D., Straub D., Boudreau M.C., 2000. Structural equation modeling and regression: Guidelines for research practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 4(1), 7, doi: 10.17705/1CAIS.00407.
doi: 10.17705/1CAIS.00407. |
| [47] | Geiger S.M., Dombois C., Funke J., 2018. The role of environmental knowledge and attitude: Predictors for ecological behavior across cultures. An analysis of Argentinean and German Students. Umweltpsychologie. 22, 69-87. |
| [48] |
Gericke N., Boeve-de Pauw J., Berglund T., et al., 2019. The sustainability consciousness questionnaire: the theoretical development and empirical validation of an evaluation instrument for stakeholders working with sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 27(1), 35-49.
doi: 10.1002/sd.1859 |
| [49] |
Gibbons L.V., Cloutier S.A., Coseo P.J., et al., 2018. Regenerative development as an integrative paradigm and methodology for landscape Sustainability. Sustainability. 10(6), 1910, doi: 10.3390/su10061910.
doi: 10.3390/su10061910 |
| [50] | Giddings B., Hopwood B., O’brien G., 2002. Environment, economy and society: Fitting them together into sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 10(4), 187-196. |
| [51] | Glasser H., Calder W., Fadeeva Z., 2005. Definition: Research in Higher Education for Sustainability. Halifax: Nova Scotia. |
| [52] |
Gough S., 2002. Increasing the value of the environment: A ‘real options’ metaphor for learning. Environ. Educ. Res. 8(1), 61-72.
doi: 10.1080/13504620120109664 |
| [53] | Gough S., Scott W., 2008. Higher Education and Sustainable Development: Paradox and Possibility. London: Routledge. |
| [54] |
Grant L.K., 2010. Sustainability: From excess to aesthetics. Behav. Soc. Iss. 19(1), 7-47.
doi: 10.5210/bsi.v19i0.2789 |
| [55] |
Grubor A., Milovanov O., 2017. Brand strategies in the era of sustainability. Interdiscip. Descr. Complex Syst. 15(1), 78-88.
doi: 10.7906/indecs.15.1.6 |
| [56] | Gündüz Ş., 2017. A research about attitudes and behaviors of university students with having different cultures towards the environment through sustainable development. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. 13(6), 1881-1892. |
| [57] | Haenlein M., Kaplan A.M., 2004. A beginner’s guide to partial least squares analysis. Understanding Statistics. 3(4), 283-297. |
| [58] | Hair Jr J.F., Sarstedt M., Ringle C.M., et al., 2017. Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. London: Sage publications. |
| [59] | Hair J.F., Risher J.J., Sarstedt M., et al., 2019. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 31(1), 2-24. |
| [60] |
Han H., Hwang J., Lee M.J., et al., 2019. Word-of-mouth, buying, and sacrifice intentions for eco-cruises: Exploring the function of norm activation and value-attitude-behavior. Tour. Manag. 70, 430-443.
doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2018.09.006 |
| [61] |
Hansmann R., Mieg H.A., Frischknecht P., 2012. Principal sustainability components: empirical analysis of synergies between the three pillars of sustainability. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 19(5), 451-459.
doi: 10.1080/13504509.2012.696220 |
| [62] |
Haron S.A., Paim L., Yahaya N., 2005. Towards sustainable consumption: an examination of environmental knowledge among Malaysians. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 29(5), 426-436.
doi: 10.1111/ijc.2005.29.issue-5 |
| [63] |
Hartmann C., Lazzarini G., Funk A., et al., 2021. Measuring consumers’ knowledge of the environmental impact of foods. Appetite. 167, 105622, doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2021.105622.
doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2021.105622 |
| [64] |
Heeren A.J., Singh A.S., Zwickle A., et al., 2016. Is sustainability knowledge half the battle? An examination of Sustainability knowledge, attitudes, norms, and efficacy to understand sustainable behaviours. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 17(5), 613-632.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-02-2015-0014 |
| [65] | Heimlich J.E., Mony P., Yocco V., 2013. Belief to behavior:a vital link. In: Stevenson R.B., Brody M., Dillon J., (eds.). International Handbook of Research on Environmental Education (1stedition). London:Routledge, 262-274.. |
| [66] | Henseler J., Ringle C.M., Sarstedt M., 2015. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. 43(1), 115-135. |
| [67] |
Homer P.M., Kahle L.R., 1988. A structural equation test of the value-attitude-behavior hierarchy. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 54(4), 638, doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.54.4.638.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.54.4.638 |
| [68] |
Hulland J., 1999. Use of partial least squares PLS in strategic management research: A review of four recent studies. Strateg. Manag. J. 20(2), 195-204.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0266 |
| [69] |
Hungerford H.R.,Volk T.L., 1990. Changing learner behavior through environmental education. J. Environ. Educ. 21(3), 8-21.
doi: 10.1080/00958964.1990.10753743 |
| [70] |
Hwang Y.H., Kim S.I., Jeng J.M., 2000. Examining the causal relationships among selected antecedents of responsible environmental behavior. J. Environ. Educ. 31(4), 19-25.
doi: 10.1080/00958960009598647 |
| [71] |
Jackson C., 1993. Doing what comes naturally? Women and environment in development. World Dev. 21(12), 1947-1963.
doi: 10.1016/0305-750X(93)90068-K |
| [72] |
Kalsoom Q., Khanam A., Quraishi U., 2017. Sustainability consciousness of pre-service teachers in Pakistan. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 18(7), 1090-1107.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-11-2016-0218 |
| [73] | Karavasilis G., Nerantzaki D.M., Pantelidis P., et al., 2015. What generation y in Greece thinks about green hotels. World J. Entrep. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 11(4), 268-280. |
| [74] |
Karpudewan M., 2019. The relationships between values, belief, personal norms, and climate conserving behaviors of Malaysian primary school students. J. Clean. Prod. 237, 117748, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117748.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117748 |
| [75] |
Keles Ö., 2017. Investigation of pre-service science teachers’ attitudes towards sustainable environmental education. High. Educ. Stud. 3(7), 171-180.
doi: 10.1080/03075077812331376229 |
| [76] |
Kim M.J., Hall C.M., Kim D.K., 2020. Predicting environmentally friendly eating out behavior by value-attitude-behavior theory: does being vegetarian reduce food waste?J. Sustain. Tour. 28(6), 797-815.
doi: 10.1080/09669582.2019.1705461 |
| [77] |
Kollmuss A., Agyeman J., 2002. Mind the gap: why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior?Environ. Educ. Res. 8(3), 239-260.
doi: 10.1080/13504620220145401 |
| [78] | Kroshus E., Sherman R.T., Thompson R.A., et al., 2014. Gender differences in high school coaches’ knowledge, attitudes, and communication about the female athlete triad. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 22(3), 193-208. |
| [79] |
Lacy P., Arnott J., Lowitt E., 2009. The challenge of integrating Sustainability into talent and organization strategies: investing in the knowledge, skills and attitudes to achieve high performance. Corporate Governance: The international journal of business in society. 9(4), 484-494.
doi: 10.1108/14720700910985025 |
| [80] | Lee L.K., 1996. Sustainability and land-use dynamics. J. Soil Water Conserv. 51(4), 295. https://www.jswconline.org/content/51/4/295.short. |
| [81] | Lefcourt H.M., 1991. Locus of control. In: Robinson J.P., Shaver P.R., Wrightsman L.S., (eds.).Measures of Personality and Social Psychological Attitudes. Pittsburgh:Academic Press, 413-499. |
| [82] |
Legault L., Pelletier L.G., 2000. Impact of an environmental education program on students’ and parents’ attitudes, motivation, and behaviours. Can. J. Behav. Sci. 32(4), 243-250.
doi: 10.1037/h0087121 |
| [83] | Leiserowitz A.A., Kates R.W., Parris T.M., 2005. Do global attitudes and behaviors support sustainable development?Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development. 47(9), 22-38. |
| [84] | Levenson H., 1981. Differentiating between internality, powerful others, and chance. In: Lefcourt H.M., (ed.). Research with the Locus of Control Construct:Assessment methods. New York:Academic Press, 15-63. |
| [85] | Levi L., Rothstein B., 2018. Universities Must Lead on Sustainable Development Goals. [2022-12-11].https://www.universityworldnews.com/post.php?story=20181106131352348. |
| [86] |
Littledyke M., Manolas E., Littledyke R.A., 2013. A systems approach to education for sustainability in higher education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 14(4), 367-383.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-01-2012-0011 |
| [87] |
Lozano R., 2008. Envisioning sustainability three-dimensionally. J. Clean. Prod. 16(17), 1838-1846.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.02.008 |
| [88] | MacCormack C.P., 1980. Nature, Culture and Gender:A Critique. New York:Cambridge University Press, 1-24. |
| [89] |
Macnaghten P., Jacobs M., 1997. Public identification with sustainable development: investigating cultural barriers to participation. Global Environmental Change. 7(1), 5-24.
doi: 10.1016/S0959-3780(96)00023-4 |
| [90] |
Mahat H., Hashim M., Saleh Y., et al., 2019. Environmental sustainability knowledge, attitude and practices among pre-school students. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 286(1), 012003, doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/286/1/012003.
doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/286/1/012003 |
| [91] | Maidou A., Plakitsi K., Polatoglou H., 2019. Knowledge, perceptions and attitudes on education for sustainable development of pre-service early childhood teachers in Greece. World J. Educ. 9(5), 1-15. |
| [92] |
McCarty J.A., Shrum L.J., 1994. The recycling of solid wastes: Personal values, value orientations, and attitudes about recycling as antecedents of recycling behavior. J. Bus. Res. 30(1), 53-62.
doi: 10.1016/0148-2963(94)90068-X |
| [93] |
McCarty J.A., Shrum L.J., 2001. The influence of individualism, collectivism, and locus of control on environmental beliefs and behavior. J. Public Policy Mark. 20(1), 93-104.
doi: 10.1509/jppm.20.1.93.17291 |
| [94] | McKeown R., Hopkins C., 2005. Guidelines and Recommendations for Reorienting Teacher Education to Address Sustainability. Paris: United Nations Decade of Education for Sustainable Development, 1-71. |
| [95] |
Meinzen-Dick R., Kovarik C., Quisumbing A.R., 2014. Gender and sustainability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 39, 29-55.
doi: 10.1146/energy.2014.39.issue-1 |
| [96] |
Michalos A.C., Creech H., Swayze N., et al., 2012. Measuring knowledge, attitudes and behaviours concerning sustainable development among tenth grade students in Manitoba. Soc. Indic. Res. 106 (2), 213-238.
doi: 10.1007/s11205-011-9809-6 |
| [97] |
Mihelcic J.R., Crittenden J.C., Small M.J., et al., 2003. Sustainability science and engineering: the emergence of a new metadiscipline. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37(23), 5314-5324.
pmid: 14700315 |
| [98] | Miller S., 2001. Social action:A Teleological Account. New York:Cambridge University Press. |
| [99] | Moir S., Carter K., 2012. Diagrammatic representations of Sustainability-a review and synthesis. In: Smith S.D., (ed.). Procs 28th Annual ARCOM Conference.Edinburgh:Association of Researchers in Construction Management, 1479-1489. |
| [100] | Montano D.E., Kasprzyk D., 2015. Theory of reasoned action, theory of planned behavior, and the integrated behavioral model. In: Glanz K., Rimer B.K., Viswanath K., (eds.). Health Behavior:Theory, Research and Practice. Hoboken:John Wiley and Sons, 231. |
| [101] | Mori K., Christodoulou A., 2012. Review of sustainability indices and indicators: Towards a new city sustainability index (CSI). Environ.. Impact Assess Rev. 32(1), 94-106. |
| [102] |
Msengi I., Doe R., Wilson T., et al., 2019. Assessment of knowledge and awareness of “Sustainability” initiatives among college students. Renewable Energy and Environmental Sustainability. 4(6), doi: 10.1051/rees/2019003.
doi: 10.1051/rees/2019003 |
| [103] |
Murray J., 2018. Student-led action for sustainability in higher education: A literature review. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 19(6), 1095-1110.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-09-2017-0164 |
| [104] | National Research Council, 1999. Improving student learning:A strategic plan for education research and its utilization. Pittsburgh:National Academies Press. |
| [105] | Nickerson R.S., 2002. Psychology and Environmental Change. New York:Psychology Press. |
| [106] | Nunnally J.C., 1978. An overview of psychological measurement. Clinical Diagnosis of Mental Disorders. 97-146. |
| [107] |
Olsson D., Gericke N., Chang Rundgren S.N., 2016. The effect of implementation of education for sustainable development in Swedish compulsory schools-assessing pupils’ sustainability consciousness. Environ. Educ. Res. 22(2), 176-202.
doi: 10.1080/13504622.2015.1005057 |
| [108] |
Olsson D., Gericke N., Boeve-de Pauw J., et al., 2019. Green schools in Taiwan-Effects on student sustainability consciousness. Glob. Environ. Change. 54, 184-194.
doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2018.11.011 |
| [109] | Perloff R., 2016. Playing the hand that’s dealt you:My life and times so far as a psychologist. In: Keller P.A., (ed.). Academic Paths (1st edition). New York:Psychology Press, 121-134. |
| [110] |
Peyton R.B., Miller B.A., 1980. Developing an internal locus of control as a prerequisite to environmental action taking. Curr. 4, 173-192.
doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(94)00042-4 |
| [111] | Prabawani B., Hanika I.M., Pradhanawati A., et al., 2017. Primary schools eco-friendly education in the frame of education for sustainable development. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 12(4), 607-616. |
| [112] |
Purvis B., Mao Y., Robinson D., 2019. Three pillars of sustainability: in search of conceptual origins. Sustain. Sci. 14(3), 681-695.
doi: 10.1007/s11625-018-0627-5 |
| [113] |
Ranjbari M., Esfandabadi Z.S., Zanetti M.C., et al., 2021. Three pillars of sustainability in the wake of COVID-19: A systematic review and future research agenda for sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 297, 126660, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126660.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126660 |
| [114] |
Ray I., 2007. Women, water, and development. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 32, 421-449.
doi: 10.1146/energy.2007.32.issue-1 |
| [115] | Redman E., 2013. Advancing educational pedagogy for sustainability: Developing and implementing programs to transform behaviors. International Journal of Environmental & Science Education. 8(1), 1-34. |
| [116] | Ringle C.M., Sinkovics R.R., 2009. The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. Adv. Int. Mark. 20, 277-319. |
| [117] | Robertson M., 2014. Sustainability Principles and Practice. London: Routledge. |
| [118] | Rotter J.B., 1954. Social Learning and Clinical Psychology. London: Prentice-Hall. |
| [119] | Rotter J.B., 1966. Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied. 80(1), 1-28. |
| [120] | Sachs J., Kroll C., Lafortune G., et al., 2021. Sustainable Development Report 2021. New York:Cambridge University Press. |
| [121] | Sachs J., Kroll C., Lafortune G., et al., 2022. Sustainable Development Report 2022. New York:Cambridge University Press. |
| [122] |
Sayed A., Asmuss M., 2013. Benchmarking tools for assessing and tracking sustainability in higher educational institutions: Identifying an effective tool for the University of Saskatchewan. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 14(4), 449-463.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-08-2011-0052 |
| [123] | Schultz P., 2002. Inclusion with nature:The psychology of human-nature relations. In: Psychology of Sustainable Development. Boston:Springer, 61-78. |
| [124] |
Schwepker Jr C.H., Cornwell T.B., 1991. An examination of ecologically concerned consumers and their intention to purchase ecologically packaged products. J. Public Policy Mark. 10(2), 77-101.
doi: 10.1177/074391569101000205 |
| [125] |
Sedgwick P., 2012. Pearson’s correlation coefficient. British Medical Journal. 345(7864), doi: 10.1136/bmj.e4483.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.e4483 |
| [126] | Sharma B., Steward B., Ong S.K., et al., 2014. Understanding engineering students’ perceptions and knowledge about sustainable development and sustainability. In: 2014 American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE) North Midwest Section Conference. Iowa City:University of Iowa. |
| [127] |
Sherren K., 2006. Core issues: Reflections on sustainability in Australian university coursework programs. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 7(4), 400-413.
doi: 10.1108/14676370610702208 |
| [128] |
Shrum L.J., Lowrey T.M., McCarty J.A., 1994. Recycling as a marketing problem: A framework for strategy development. Psychol. Mark. 11(4), 393-416.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1520-6793 |
| [129] |
Sibbel A., 2009. Pathways towards Sustainability through higher education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 10(1), 68-82.
doi: 10.1108/14676370910925262 |
| [130] |
Singer-Brodowski M., 2017. Pedagogical content knowledge of sustainability-A missing piece in the puzzle of professional development of educators in higher education for sustainable development. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 18(6), 841-856.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-02-2016-0035 |
| [131] |
Spector P.E., 1982. Behavior in organizations as a function of employee’s locus of control. Psychol. Bull. 91(3), 482-497.
doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.91.3.482 |
| [132] |
Steg L., Vlek C., 2009. Encouraging pro-environmental behaviour: An integrative review and research agenda. J. Environ. Psychol. 29(3), 309-317.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp.2008.10.004 |
| [133] |
Torres R., Vieira R.M., Rodrigues A.V., et al., 2017. Education for sustainable development: an exploratory study in a Portuguese University. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 18(6), 956-970.
doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-05-2016-0082 |
| [134] | UNESCO(United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization), 2016. Global Education Monitoring Report:Inclusive and Sustainable Cities. Paris:UNESCO. |
| [135] | Urbach N., Ahlemann F., 2010. Structural equation modeling in information systems research using partial least squares. Journal of Information Technology Theory and Application. 11(2), 5-39. |
| [136] | Vandana S., María M., 1993. Ecofeminism. Philadelphia:Temple University Press. |
| [137] |
Velazquez L., Munguia N., Sanchez M., 2005. Deterring Sustainability in higher education institutions: An appraisal of the factors which influence Sustainability in higher education institutions. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 6(4), 383-391.
doi: 10.1108/14676370510623865 |
| [138] |
Vicente-Molina M.A., Fernández-Sáinz A., Izagirre-Olaizola J., 2013. Environmental knowledge and other variables affecting pro-environmental behaviour: comparison of university students from emerging and advanced countries. J. Clean. Prod. 61, 130-138.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.05.015 |
| [139] | Vos R.O., 2007. Defining sustainability: a conceptual orientation. Journal of Chemical Technology Biotechnology: International Research in Process, Environmental Clean Technology. 82 (4), 334-339. |
| [140] |
Waas T., Hugé J., Verbruggen A., et al., 2011. Sustainable development: A bird’s eye view. Sustainability. 3(10), 1637-1661.
doi: 10.3390/su3101637 |
| [141] |
Wals A.E., Jickling B., 2002. “Sustainability” in higher education: From doublethink and newspeak to critical thinking and meaningful learning. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 3(3), 221-232.
doi: 10.1108/14676370210434688 |
| [142] |
Wals A.E., Benavot A., 2017. Can we meet the Sustainability challenges? The role of education and lifelong learning. Eur. J. Educ. 52(4), 404-413.
doi: 10.1111/ejed.2017.52.issue-4 |
| [143] |
Walshe N., 2008. Understanding students’ conceptions of sustainability. Environ. Educ. Res. 14(5), 537-558.
doi: 10.1080/13504620802345958 |
| [144] | Watling A., Zhou E., 2011. Attitudes towards sustainability: a quantitative study of sustainable Ålidhem. Bachelor Thesis. Umeå: Umeå E5; School of Business. |
| [145] |
Watson D., Clark L.A., 1984. Negative affectivity: the disposition to experience aversive emotional states. Psychol. Bull. 96(3), 465-490.
pmid: 6393179 |
| [146] | WCED World Commission on Environment and Development, 1987. World commission on environment and development.Our Common Future. 17(1), 1-91. |
| [147] |
Wright T.S., 2007. Developing research priorities with a cohort of higher education for Sustainability experts. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 8(1), 34-43.
doi: 10.1108/14676370710717571 |
| [148] | Wright T., Horst N., 2013. Exploring the ambiguity: what faculty leaders really think of Sustainability in higher education.Int. J Sustain. High. Educ. 14(2), 209-227. |
| [149] | Wyer Jr R.S., Albarracín D., 2005. Belief formation, organization, and change:Cognitive and motivational influences. In: Albarracín D.B., JohnsonT., Zanna M.P., (eds.). The Handbook of Attitudes. Lawrence:Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers, 273-322. |
| [150] |
Yarime M., Trencher G., Mino T., et al., 2012. Establishing sustainability science in higher education institutions: towards an integration of academic development, institutionalization, and stakeholder collaborations. Sustain. Sci. 7(1), 101-113.
doi: 10.1007/s11625-012-0157-5 |
| [151] |
Zhao Q.D., Liu X.W., Ma Y.H., et al., 2020. Application of the modified college impact model to understand Chinese engineering undergraduates’ Sustainability consciousness. Sustainability. 12(7), 2614, doi: 10.3390/su12072614.
doi: 10.3390/su12072614 |
| [152] |
Zijp M.C., Heijungs R., Van der Voet E., et al., 2015. An identification key for selecting methods for sustainability assessments. Sustainability. 7(3), 2490-2512.
doi: 10.3390/su7032490 |
| [153] |
Zilahy G., Huisingh D., 2009. The roles of academia in regional sustainability initiatives. J. Clean. Prod. 17(12), 1057-1066.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.03.018 |
| [1] | Setyardi Pratika MULYA, Delik HUDALAH. Agricultural intensity for sustainable regional development: A case study in peri-urban areas of Karawang Regency, Indonesia [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100117-. |
| [2] | LIU Binsheng, ZHANG Xiaohui, TIAN Junfeng, CAO Ruimin, SUN Xinzhang, XUE Bin. Rural sustainable development: A case study of the Zaozhuang Innovation Demonstration Zone in China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 390-404. |
| [3] | Surendra Singh JATAV, Kalu NAIK. Measuring the agricultural sustainability of India: An application of Pressure-State-Response (PSR) model [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(3): 218-234. |
| [4] | Kwaku ADDAI, Berna SERENER, Dervis KIRIKKALELI. Can environmental sustainability be decoupled from economic growth? Empirical evidence from Eastern Europe using the common correlated effect mean group test [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(1): 68-80. |
| [5] | Taiwo Oladapo BABALOLA. Land tenure security, place satisfaction and loyalty in the peri-urban area of Ibadan City, Nigeria [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(4): 346-355. |
| [6] | Sabir HUSSAIN, Sheenu SHARMA, Anand Narain SINGH. Evaluation of ecosystem supply services and calculation of economic value in Kargil District [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(2): 157-169. |
| [7] | Scott Daniel HARDY. Transaction costs for collaboration in the watershed management of the Cuyahoga River Area of Concern [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(2): 146-156. |
| [8] | ZHOU Lian, HUANG Xueyuan, ZHAO Chunmei, PU Tiancun, ZHANG Lei. Regional landscape transformation and sustainability of the rural homegarden agroforestry system in the Chengdu Plain, China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(1): 68-81. |
| [9] | Ahmed Mohammed Sayed MOHAMMED, Tetsuya UKAI, Michael HALL. Towards a sustainable campus-city relationship: A systematic review of the literature [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(1): 53-67. |
| [10] | Giribabu DANDABATHULA, Sudhakar Reddy CHINTALA, Sonali GHOSH, Padmapriya BALAKRISHNAN, Chandra Shekhar JHA. Exploring the nexus between Indian forestry and the Sustainable Development Goals [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(4): 308-323. |
| [11] | Md. Habibur RAHMAN, Bishwajit ROY, Md. Shahidul ISLAM. Contribution of non-timber forest products to the livelihoods of the forest-dependent communities around the Khadimnagar National Park in northeastern Bangladesh [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(3): 280-295. |
| [12] | Honghu MENG, Xiaoyang GAO, Yigang SAONG, Guanlong CAO, Jie LI. Biodiversity arks in the Anthropocene [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(2): 109-115. |
| [13] | Peter Uchenna Okoye, Chukwuemeka Ngwu. Assessing the adequacy and sustainability performance of multi-family residential buildings in Anambra State, Nigeria [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(1): 23-35. |
| [14] | Mobeen Akhtar, Yuanyuan Zhao, Guanglei Gao, Qudsia Gulzar, Azfar Hussain, Abdus Samie. Assessment of ecosystem services value in response to prevailing and future land use/cover changes in Lahore, Pakistan [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 37-47. |
| [15] | Yupeng Liu, Jiajia Li, Linlin Duan, Min Dai, Wei-qiang Chen. Material dependence of cities and implications for regional sustainability [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 31-36. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号
