Regional Sustainability ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 82-92.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2020.09.002cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2020.09.002
Wakshum Shiferawa,*( ), Sebsebe Demissewb, Tamrat Bekeleb, Ermias Aynekuluc
), Sebsebe Demissewb, Tamrat Bekeleb, Ermias Aynekuluc
Received:2020-04-21
Revised:2020-09-22
Accepted:2020-09-25
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2020-10-17
Contact:
Wakshum Shiferaw
E-mail:shiferaw.wakshum@amu.edu.et
Wakshum Shiferaw, Sebsebe Demissew, Tamrat Bekele, Ermias Aynekulu. Relationship between Prosopis juliflora invasion and livelihood diversification in the South Afar region, Northeast Ethiopia[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 82-92.
Table 1
Livestock status before and after P. juliflora invasion, according to responses of household elder key informants in the South Afar region"
| Livestock | Number before P. juliflora invasion | Number after P. juliflora invasion | Difference between before and after P. juliflora invasion | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | 362 | 158 | 204 | 56.2 |
| Sheep | 377 | 282 | 95 | 25.2 |
| Goats | 412 | 332 | 80 | 19.4 |
| Camels | 214 | 110 | 104 | 48.6 |

Fig. 2.
Household diversification activities in the South Afar region. WPPJ, wood products from P. juliflora; ChPJ, charcoal from P. juliflora; FWPJ, fuel wood from P. juliflora; ConWPJ, construction wood from P. juliflora; PoPJ, pods from P. juliflora; WPNSp, woody products from native species; CNSp, charcoal from native woody species."
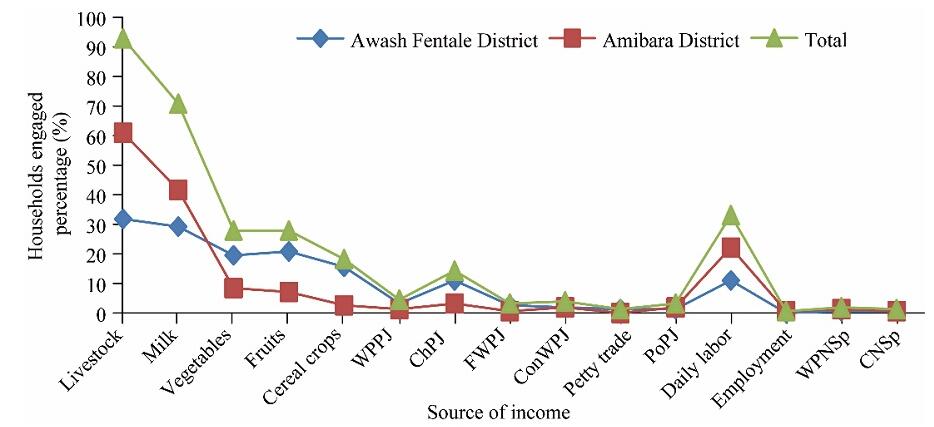
Table 4
Livelihood diversification from farm, off-farm, and non-farm activities in 2017-2018"
| Income option | Awash Fentale District | Amibara District | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE | |
| Cattle (number) | 8.88 | 1.47 | 5.11 | 0.70 |
| Sheep (number) | 11.45 | 1.21 | 11.55 | 1.33 |
| Goats (number) | 15.20 | 1.84 | 16.51 | 1.25 |
| Camels (number) | 4.98 | 1.00 | 3.16 | 0.57 |
| Donkeys (number) | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| Milk (L) | 160.60 | 1.50 | 138.80 | 0.75 |
| Cereal crops (t) | 1.25 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Vegetables (t) | 3.03 | 0.81 | 0.26 | 0.10 |
| Fruits (t) | 1.96 | 0.73 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Wood products from P. juliflora (stack) | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| Charcoal from P. juliflora (t) | 4.26 | 0.99 | 0.19 | 0.09 |
| Fuel wood from P. juliflora (stack) | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Construction wood from P. juliflora (stack) | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
| Pod from P. juiflora (t) | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.06 |
| Daily labor (d yr-1) | 4.24 | 0.95 | 5.00 | 0.68 |
| Wood products from native woody species (stack) | 4.80 | 0.05 | 5.04 | 0.04 |
| Charcoal from native woody species (t) | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.19 |
Table 5
Simpson’s diversification index (SDI) of livelihood options in the South Afar region in 2017-2018"
| Income option | Mi (USD yr-1) | Share (%) | SDI | SDI range | LoD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 218.46 | 11.10 | 0.99 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Cattle | 624.82 | 31.60 | 0.90 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Vegetables | 514.79 | 26.10 | 0.93 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Fruits | 115.51 | 5.90 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Cereal crops | 121.56 | 6.20 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Wood products from P. juliflora | 21.66 | 1.10 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Charcoal from P. juliflora | 174.29 | 8.80 | 0.99 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Fuel wood from P. juliflora | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Construction wood from P. juliflora | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Pod/seed from P. juliflora | 36.97 | 1.90 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Petty trade | 126.12 | 6.40 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Daily labor | 1.59 | 0.10 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Wood products from native species | 6.18 | 0.30 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Charcoal from native species | 8.73 | 0.40 | 1.00 | > 0.75 | Very high |
| Total | 1970.68 | 100.00 | 0.80 | > 0.75 | Very high |
Table 6
Annual household incomes from farm, off-farm, and non-farm activities in the South Afar region in 2017-2018"
| Sold item | Awash Fentale District | Amibara District | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (USD yr-1) | SE (USD yr-1) | Lower (USD yr-1) | Upper (USD yr-1) | Share (%) | Mean (USD yr-1) | SE (USD yr-1) | Lower (USD yr-1) | Upper (USD yr-1) | Share (%) | |
| Milk | 110.91 | 42.40 | 41.22 | 212.81 | 14.40 | 185.48 | 34.02 | 123.39 | 257.88 | 9.40 |
| Cattle | 154.56 | 57.25 | 58.00 | 281.62 | 20.00 | 94.47 | 13.07 | 70.93 | 121.49 | 3.60 |
| Vegetables | 235.30 | 68.36 | 123.26 | 380.16 | 30.50 | 7.30 | 2.71 | 2.72 | 13.02 | 0.70 |
| Fruits | 63.99 | 21.99 | 26.60 | 111.88 | 8.30 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 1.45 | 0.10 |
| Cereal crops | 46.02 | 31.07 | 7.86 | 116.86 | 6.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Wood products from P. juliflora | 1.11 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 3.70 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.00 | 1.44 | 0.10 |
| Charcoal from P. juliflora | 74.53 | 16.94 | 41.43 | 109.00 | 9.70 | 2.78 | 2.80 | 0.00 | 9.29 | 0.80 |
| Petty trade | 14.83 | 10.09 | 0.00 | 38.76 | 1.90 | 2.59 | 2.14 | 0.00 | 7.49 | 0.60 |
| Daily labor | 68.67 | 16.01 | 37.65 | 100.32 | 8.90 | 69.05 | 10.58 | 49.16 | 90.83 | 2.90 |
| Wood products from native species | 1.78 | 1.75 | 0.00 | 5.81 | 0.20 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 1.49 | 0.10 |
| Total | 771.71 | 363.08 | ||||||||

Fig. 3.
Male and female diversification activities in the South Afar region. WPPJ, wood products from P. juliflora; ChPJ, charcoal from P. juliflora; FWPJ, fuel wood from P. juliflora; ConWPJ, construction wood from P. juliflora; PoPJ, pods from P. juliflora; WPNSp, wood products from native species; CNSp, charcoal from native woody species."
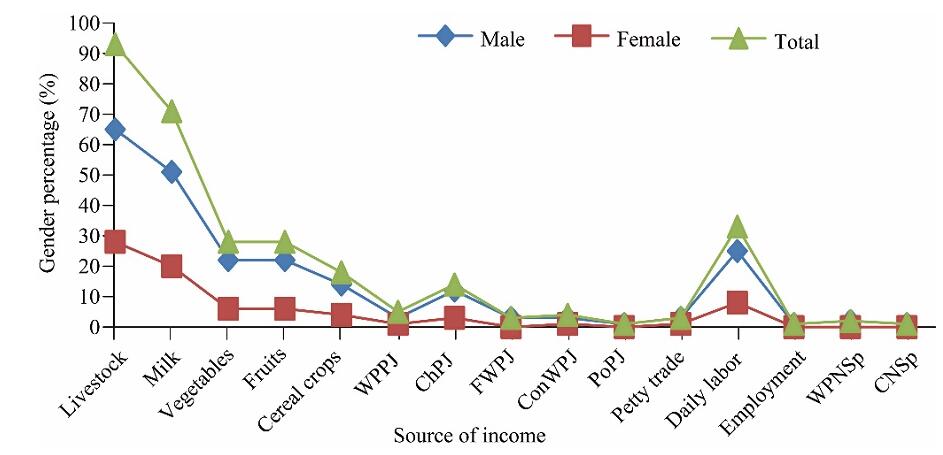
Table 7
Annual household farm, off-farm, and non-farm incomes by males and females in the South Afar region in 2017-2018"
| Sold item | Annual household income (USD yr-1) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male householders | Female householders | ||||||||||
| Mean | SE | Lower | Upper | Mean | SE | Lower | Upper | ||||
| Milk | 149.3 | 29.3 | 97.0 | 212.9 | 182.1 | 55.2 | 94.8 | 309.1 | |||
| Cattle | 129.6 | 26.9 | 81.3 | 186.9 | 79.1 | 18.8 | 45.8 | 120.2 | |||
| Vegetables | 93.8 | 33.0 | 42.2 | 164.4 | 58.7 | 29.1 | 12.5 | 124.3 | |||
| Fruits | 22.6 | 8.6 | 8.5 | 41.9 | 19.3 | 15.1 | 1.6 | 55.8 | |||
| Cereal crops | 7.1 | 3.6 | 2.2 | 15.4 | 34.6 | 33.4 | 0.0 | 113.4 | |||
| Wood products from P. juliflora | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 1.1 | |||
| Charcoal from P. juliflora | 35.5 | 8.8 | 19.1 | 53.6 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 0.0 | 19.9 | |||
| Petty trade | 3.2 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 8.2 | 15.7 | 11.0 | 0.0 | 39.8 | |||
| Daily labor | 79.4 | 11.4 | 55.4 | 101.5 | 49.5 | 13.7 | 24.7 | 78.9 | |||
| Wood products from native species | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 3.2 | |||
| Total | 522.2 | 446.6 | |||||||||
Table 8
Annual household farm, off-farm, and non-farm incomes by household educational attainment in the South Afar region in 2017-2018"
| Sold item | Annual household income (USD yr-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No formal education | Primary education | Secondary education | Post-secondary education | |||||
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | |
| Milk | 168.6 | 28.1 | 109.0 | 83.1 | 19.4 | 17.8 | 58.1 | 54.5 |
| Cattle | 116.7 | 20.9 | 36.3 | 27.7 | 18.2 | 17.5 | 121.1 | 79.7 |
| Vegetables | 82.0 | 25.6 | 36.3 | 27.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 230.1 | 109.0 |
| Fruits | 22.2 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 24.2 | 23.4 |
| Cereal crops | 15.8 | 11.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.1 | 11.7 |
| Wood products from P. juliflora | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.1 | 11.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Charcoal from P. juliflora | 26.0 | 6.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 96.9 | 93.4 |
| Petty trade | 7.3 | 4.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Daily labor | 66.1 | 8.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 160.4 | 57.6 | 205.9 | 96.5 |
| Wood products from native species | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Total | 506.1 | 181.7 | 210.1 | 748.5 | ||||
Table 9
Annual household farm, off-farm, and non-farm incomes by wealth status in the South Afar region in 2017-2018"
| Sold item | Annual household income (USD yr-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor households | Medium households | Wealthy households | ||||
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | |
| Milk | 180.3 | 39.9 | 117.7 | 25.4 | 227.7 | 202.0 |
| Cattle | 78.9 | 21.7 | 155.0 | 31.8 | 502.7 | 429.7 |
| Vegetables | 49.2 | 18.1 | 148.5 | 61.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Fruits | 12.3 | 7.9 | 37.9 | 15.7 | 24.2 | 22.5 |
| Cereal crops | 5.7 | 3.9 | 33.3 | 28.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Wood products from P. juliflora | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Charcoal from P. juliflora | 13.6 | 5.8 | 51.4 | 14.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Petty trade | 6.3 | 4.1 | 8.4 | 7.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Daily labor | 65.3 | 11.1 | 83.6 | 16.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Wood products from native species | 1.4 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Total | 413.7 | 636.9 | 754.6 | |||
Appendix A
Variables definition and measurements"
| Variable type | Item | Type and definition | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment variable | Invasion P. juliflora | Continuous, number before and after P. juliflora invasion | Number |
| Outcome variable | Income from livestock sales | Continuous, annual income from livestock sales | USD |
| Outcome variable | Income from cereal crop sales | Continuous, annual income from cereal crop sales | USD |
| Outcome variable | Income from fruit sales | Continuous, annual income from fruit sales | USD |
| Outcome variable | Income from vegetable sales | Continuous, annual income from vegetable sales | USD |
| Outcome variable | Income from petty trade | Continuous, annual income from petty trade | USD |
| Outcome variable | Income from daily labor | Continuous, annual income from daily labor | USD |
| Outcome variable | Income from charcoal and wood related sales | Continuous, annual income from charcoal and wood related sales | USD |
| Outcome variable | Income from milk sales | Continuous, annual income from milk sales | USD |
| Explanatory variable | Wealth | Ordinal, wealth class of household head | 1, poor household; 2, medium household; 3, wealthy household |
| Explanatory variable | Sex | Dummy, sex of household head | 1, male household; 2, female household |
| Explanatory variable | Educational attainment | Ordinal, educational attainment of household head | 1, no formal education; 2, primary education; 3, secondary education; 4, post-secondary education |
| Explanatory variable | Farm, off-farm, and non-farm activities | Dummy, engagement of the household head in off/off-farm/non-farm activities | 1, otherwise; 2, the household head is engaged in off/off-farm/non-farm activities |
Appendix B
Income from livelihood options in the South Afar region"
| Variable | Statistics index | Income from milk (USD yr-1) | Income from cattle (USD yr-1) | Income from daily labor (USD yr-1) | Income from vegetables (USD yr-1) | Income from fruits (USD yr-1) | Income from cereal crops (USD yr-1) | Income from WPPJ (USD yr-1) | Income from ChPJ (USD yr-1) | Income from petty trade (USD yr-1) | Income from WPNSp (USD yr-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | χ2 | 5.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 35.7 | 54.9 | 43.1 | 0.2 | 35.3 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| df | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| P value | 0.016 | 0.735 | 0.861 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.655 | <0.0001 | 0.432 | 0.950 | |
| Site | χ2 | 46.1 | 44.5 | 32.7 | 79.0 | 101.1 | 76.6 | 1.6 | 72.2 | 3.8 | 0.7 |
| df | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| P value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.662 | <0.0001 | 0.286 | 0.879 | |
| Sex | χ2 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 0.7 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 4.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| df | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| P value | 0.424 | 0.150 | 0.106 | 0.110 | 0.404 | 0.187 | 0.359 | 0.043 | 0.832 | 0.882 | |
| Educational attainment | χ2 | 7.4 | 5.3 | 7.9 | 14.5 | 14.8 | 8.6 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 6.9 | 1.2 |
| df | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| P value | 0.061 | 0.154 | 0.049 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.036 | 0.804 | 0.317 | 0.075 | 0.759 | |
| Wealth | χ2 | 1.0 | 9.0 | 2.5 | 12.6 | 5.8 | 7.7 | 0.3 | 8.4 | 0.6 | 1.9 |
| df | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| P value | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.29 | <0.0001 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 0.40 |
| [1] | Abebe, Y.T ., 2012. Ecological and economic dimensions of the paradoxical invasive species-Prosopis juliflora and policy challenges in Ethiopia. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development. 3(8), 62-70. |
| [2] | Abdulahi, M.M., Ute, J.A., Regasa, T ., 2017. Prosopis juliflora L: distribution, impacts and available control methods in Ethiopia. Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, 20, 75-89. |
| [3] | Bila, Y., Mshelia, B.S., Landi, J.H ., 2015. Off farm activities and its contribution to household income in Hawul local government area, Borno State, Nigeria. IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science. 8(10), 9-13. |
| [4] | Chiteculo, V., Lojka, B., Surovy, P ., et al., 2018. Value chain of charcoal production and implications for forest degradation: Case study of Bie Province, Angola. Environments. 5, 113. |
| [5] | CSA, 2013. Population Projection of Ethiopia for All Regions at Woreda Level from 2014-2017, Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. |
| [6] | Dubale, A. , 2008. Invasive plants and food security: the case of Prosopis juliflora in the Afar region of Ethiopia, Prepared for IUCN by FARM-Africa. http://cmsdata.iucn.org/downloads/invasive_plants_and_food_security. |
| [7] | Friis, I., Sebsebe, D., Breugel, P.V ., 2010. Atlas of potential vegetation of Ethiopia. The Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters, Biologiske Skrifter. 58, 1-315. |
| [8] | Hundessa, N., Fufa, A ., 2016. Distribution and socio-economic impacts of Prosopis juliflora in East Shewa and West Arsi Zones, Ethiopia. International Journal of African and Asian Studies. 24, 31-41. |
| [9] | IBM Corporation, 2016. IBM SPSS Statistics 24 Core System User’s Guide, USA printing. |
| [10] | Jama, B., Zeila., A ., 2005. Agroforestry in the drylands of Africa: a call to action. ICRAF Working Paper - no. 1. Nairobi: World Agroforestry Centre. |
| [11] | Kassie, G.W., Kim, S., Fellizar, Jr ., F.P., 2017. Determinant factors of livelihood diversification: Evidence from Ethiopia. Cogent Social Sciences. 3, 1369490. |
| [12] | Khatun, D., Roy, B.C ., 2012. Rural livelihood diversification in West Bengal: Determinant and constraints. Agricultural Economics Research Review. 25(1), 115-124. |
| [13] | Kotu, B.H ., 2014. Explaining the off-farm economy in rural Ethiopia. Int. Inst. Trop. Agric. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.1.2520.5364. |
| [14] | Martin, S.M., Lorenzen, K ., 2016. Livelihood diversification in rural Laos. World Dev. 83, 231-243. |
| [15] | Mat, S.H.C., Jalil, A.Z.A., Harun, M ., 2012. Does non-farm income improve the poverty and income inequality among agricultural household in rural Kedah? Procedia Economics and Finance. 1, 269-275. |
| [16] | Ojiako, I.A., Manyong, V.M., Ezedinma, C ., et al., 2009. Determinants of wealth and socioeconomic status of rural households: an application of multinomial logit model to soybean farmers in Northern Nigeria. Journal of Social Sciences. 19(1), 31-39. |
| [17] | Owitti, O.L ., 2015. Gender differences and relations in rural household livelihoods of Gog District, Anywaa Zone, Gambella Region, South-Western Ethiopia. International Journal of Gender and Women’s Studies. 3(1), 51-79. |
| [18] | Pasiecznik, N.M., Felker, P., Harris, P.J.C ., et al., 2001. The Prosopis juliflora - Prosopis pallida Complex: A Monograph, HDRA, Coventry, UK. pp. 172. |
| [19] | Pittroff, W ., 2019. Invasive alien species: the threat to sustainable livelihoods and ecosystems health. Policies and Realities-Needs for Environmental Rehabilitation in Ethiopia. 29th Annual Conference of the Biological Society of Ethiopia. May 3-4 2019,Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1-58. |
| [20] | Pujiriyani, D.W., Soetarto, E., Santosa, D.A ., et al., 2019. Rural hierarchy of prosperity: livelihood diversification and its implications on rurality. Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic Sciences. 4(88), 70-77. |
| [21] | Saha, B., Bahal, R ., 2014. Livelihood diversification pattern among the farmers of West Bengal. Economic Affairs. 59(3), 321-334. |
| [22] | Seid, M.J ., 2012. Household perception about Prosopis juliflora and its effect on pastoral livelihood diversification strategy: the case of Gewane district in Afar Regional State, Ethiopia. International Journal of Agricultural Science and Research. 2(3), 21-51. |
| [23] |
Shiferaw, H., Schaffner, U., Bewuket, W ., et al., 2019. Modeling the current fractional cover of an invasive alien plant and drivers of its invasion in dryland ecosystems. Sci Rep. 9, 1576.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36587-7 pmid: 30733452 |
| [24] | Teshome, P., Dessalegn, K., Terefe, E ., et al, 2016. Study on cattle management and marketing practices in Afar region. International Journal of Livestock Production. 7(8), 55-65. |
| [25] | Tsegaye, D., Vedeld, P., Moe, S.R ., 2013. Pastoralists and livelihoods: A case study from northern Afar, Ethiopia. J. Arid. Environ. 91, 138-146. |
| [26] | Wakie, T.T., Evangelista, P.H., Jarnevich, C.S ., et al., 2014. Mapping current and potential distribution of non-native Prosopis juliflora in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. PLoS ONE. 3, 9(11), e112854. |
| [27] | Yassin, A.Y ., 2013. Livelihood diversification in Amibara pastoral communities of Afar regional state: Determinants and challenges. MSc Thesis. Ethiopia: Addis Ababa University. |
| [1] | Saheed Olaide JIMOH, DING Wenqiang, DONG Haibin, BAI Haihua, YIN Yanting, LIU Huihui, HOU Xiangyang. Sensitivity of livelihood strategy to livestock production and marketization: An empirical analysis of grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(4): 363-374. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号