Regional Sustainability ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (4): 324-336.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2022.01.001cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2022.01.001
• Review Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Muhammad Ali Khan BURKIa, Umar BURKIb,c,*( ), Usama NAJAMd
), Usama NAJAMd
Received:2021-08-06
Revised:2021-11-06
Accepted:2022-01-15
Published:2021-10-30
Online:2022-03-18
Contact:
Umar BURKI
E-mail:Umar.Burki@usn.no
Muhammad Ali Khan BURKI, Umar BURKI, Usama NAJAM. Environmental degradation and poverty: A bibliometric review[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(4): 324-336.
Table 1
Top 12 journals with the most articles in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field."
| Journal | Number of articles | Total citations | Average citations | Average normalized citations | TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World Development | 6 | 134 | 22.33 | 0.95 | 80 |
| Forests | 4 | 74 | 18.50 | 0.61 | 41 |
| International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology | 4 | 31 | 7.75 | 0.79 | 5 |
| Geographical Journal | 3 | 160 | 53.33 | 1.46 | 45 |
| Land Use Policy | 3 | 127 | 42.33 | 1.52 | 20 |
| Land Degradation & Development | 3 | 69 | 23.00 | 1.18 | 8 |
| Environmental Science & Policy | 3 | 45 | 15.00 | 1.72 | 6 |
| Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 3 | 6 | 2.00 | 0.19 | 27 |
| International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health | 2 | 308 | 154.00 | 2.76 | 3 |
| Energy Policy | 2 | 159 | 79.50 | 2.41 | 3 |
| Journal of Environmental Management | 2 | 135 | 67.50 | 1.30 | 10 |
| Environment and Development Economics | 2 | 107 | 53.50 | 0.72 | 42 |

Fig. 2.
Co-citation network of 105 journals in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field. Nodes show the relative number of co-citations for specific journal. Different colors classify the nodes of the co-citation network. The arrangement of journals into different nodes indicates a series of similarities. The closer the journals are to the co-citation network map, the stronger the relatedness between them. Popul. Dev. Rev., Population and Development Review; Ny Times, New York Times; Q. J. Econ., Quarterly Journal of Economics; Rev. Econ. Stud., Review of Economic Studies; Rev. Econ. Stat., Review of Economics and Statistics; J. Econom., Journal of Econometrics; Nat. Resour. Froum, Natural Resources Forum; Resour. Policy, Resources Policy; Renew. Energy, Renewable Energy; J. Clean. Prod., Journal of Cleaner Production; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., Environmental Science and Pollution Research; Agric. Econ., Agricultural Economics; Land Econ., Land Economics; J. Dev. Econ., Journal of Development Economics; Environ. Dev. Econ., Environment and Development Economics; Econ. J., Economic Journal; World Dev., World Development; J. Environ. Econ. Manage., Journal of Environmental Economics and Management; Dev. Change, Development and Change; Soc. Sci. Med., Social Science & Medicine; J. Soil Water Conserv., Journal of Soil and Water Conservation; Am. J. Agr. Econ., American Journal of Agricultural Economics; J. Arid. Environ., Journal of Arid Environments; Agric. Syst., Agricultural Systems; Hum. Ecol., Human Ecology; Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr., Annals of the Association of American Geographers; Nat. Geosci., Nature Geoscience; Land Use Pol., Land Use Policy; Ecol. Econ., Ecological Economics; Environ. Conserv., Environmental Conservation; Conserv. Biol., Conservation Biology; Sustain. Sci., Sustainability Science; Sci. Total Environ., Science of the Total Environment; Ecol. Indic., Ecological Indicators; Ecol. Soc., Ecology and Society; Forest Policy Econ., Forest Policy and Economics; Int. For. Rev., International Forestry Review; Environ. Urban., Environment and Urbanization; Habitat Int., Habitat International; Waste Manage., Waste Management; Land Degrad. Dev., Land Degradation & Development; Agrofor. Syst., Agroforestry Systems; Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci., Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences; For. Ecol. Manage., Forest Ecology and Management; J. Environ. Manage., Journal of Environmental Management; Crop Sci., Crop Science; Soil Tillage Res., Soil & Tillage Research; Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment; Clim. Change, Climatic Change; Agric. Water Manage., Agricultural Water Management; Front. Ecol. Environ., Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment; Ecol. Appl., Ecological Applications; Environ. Manage., Environmental Management; Ocean Coastal Manage., Ocean & Coastal Management; Ices J. Mar. Sci., Ices Journal of Marine Science. The order of the full name is from left to right and top to bottom in the map."

Table 2
Top 16 contributing institutions in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field."
| Institution | Number of articles | Total citations | Average citations | Average normalized citations | TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charles Sturt University | 2 | 192 | 96.00 | 2.17 | 3 |
| Santa Clara University | 2 | 134 | 67.00 | 1.97 | 39 |
| International Livestock Research Institute | 3 | 89 | 29.67 | 1.46 | 39 |
| University of Gothenburg | 2 | 76 | 38.00 | 1.72 | 38 |
| London School of Economics and Political Science, University of London | 2 | 74 | 37.00 | 1.92 | 25 |
| University of North Carolina | 2 | 70 | 35.00 | 1.27 | 26 |
| Colorado State University | 4 | 60 | 15.00 | 1.69 | 63 |
| World Agroforestry Centre | 2 | 60 | 30.00 | 1.11 | 56 |
| Boston University | 2 | 56 | 28.00 | 0.50 | 268 |
| University of Namur | 2 | 56 | 28.00 | 0.50 | 268 |
| Wageningen University & Research | 2 | 54 | 27.00 | 2.55 | 156 |
| National Institute of Agricultural Research | 2 | 45 | 22.50 | 1.89 | 186 |
| Center for International Forestry Research | 2 | 32 | 16.00 | 1.67 | 142 |
| United Nations Development Programme | 2 | 31 | 15.50 | 1.63 | 140 |
| Auburn University | 2 | 27 | 13.50 | 0.30 | 136 |
| Fujian Normal University | 2 | 27 | 13.50 | 0.30 | 136 |
Table 3
Top 18 countries in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field."
| Country | Number of articles | Total citations | Average normalized citations | TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 47 | 2077 | 1.17 | 2232 |
| India | 16 | 158 | 0.43 | 775 |
| China | 14 | 370 | 1.05 | 1679 |
| Australia | 11 | 358 | 0.97 | 618 |
| England | 11 | 130 | 0.72 | 835 |
| Germany | 9 | 89 | 0.96 | 1306 |
| Kenya | 8 | 329 | 1.66 | 818 |
| South Africa | 8 | 52 | 0.46 | 241 |
| France | 6 | 130 | 0.94 | 504 |
| Netherlands | 6 | 140 | 1.65 | 828 |
| Brazil | 5 | 164 | 1.23 | 639 |
| Belgium | 4 | 407 | 2.23 | 869 |
| Canada | 4 | 55 | 1.38 | 158 |
| Ethiopia | 4 | 404 | 2.20 | 402 |
| Mexico | 4 | 61 | 1.00 | 160 |
| Saudi Arabia | 4 | 11 | 1.11 | 84 |
| South Korea | 4 | 23 | 0.35 | 412 |
| Turkey | 4 | 52 | 1.99 | 44 |
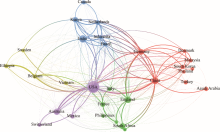
Fig. 3.
Network visualization of the dominant countries in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field. Nodes show the relative number of co-citations for a specific country. Different colors classify the nodes of the co-citation network. The arrangement of countries into different nodes indicates a series of similarities. The closer the items are to the co-citation network map, the stronger the relatedness between them."


Fig. 5.
Co-authorship networks analysis. Nodes show the relative amount of co-authorship of various countries. Different colors classify the nodes of the co-citation network. The arrangement of items in different nodes indicates a series of similarities. The closer the countries are in the co-authorship network map, the stronger the relatedness between them. The larger the circle size, the higher the number of authors representing a country."
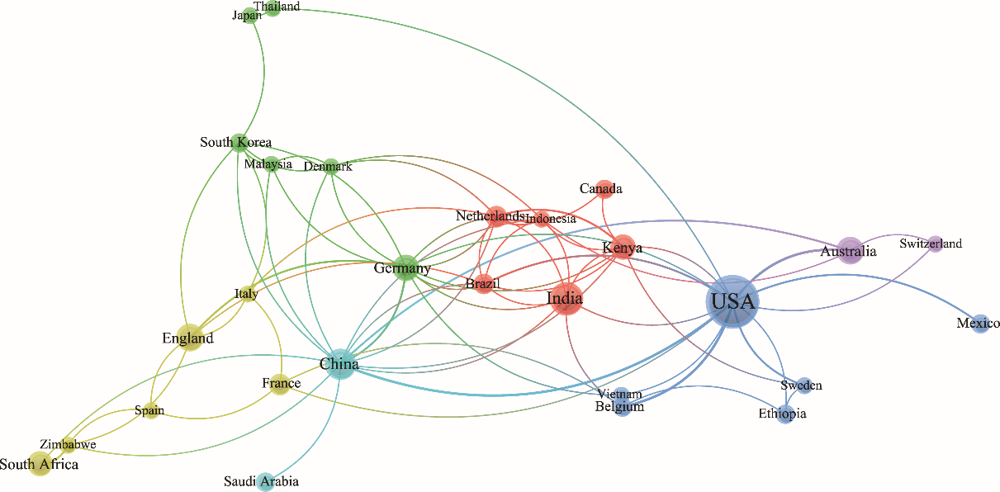
Table 4
Top 24 highly cited articles in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field."
| Title | Author(s) | Total citations | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Show me the money: Do payments supply environmental services in developing countries? | 341 | 1 | |
| Human impact on the environment in the Ethiopian and Eritrean highlands—a state of the art | 315 | 2 | |
| Global urbanization and impact on health | 196 | 3 | |
| The political economy of energy poverty: A review of key challenges | 172 | 4 | |
| A downward spiral? Research evidence on the relationship between poverty and natural resource degradation | 164 | 5 | |
| Cautionary Tales: Adaptation and the global poor | 147 | 6 | |
| Determinants of household energy consumption in India | 125 | 7 | |
| Payments for environmental services as neoliberal market-based forest conservation in Vietnam: Panacea or problem? | 119 | 8 | |
| Soil erosion in developing countries: a socio-economic appraisal | 115 | 9 | |
| Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: Implications for water governance and public policy | 112 | 10 | |
| Poverty, development, and environment | 102 | 11 | |
| Agriculture in Brazil: impacts, costs, and opportunities for a sustainable future | 96 | 12 | |
| A geographical perspective on poverty-environment interactions | 92 | 13 | |
| Linking climate change research with food security and poverty reduction in the tropics | 91 | 14 | |
| Innovative grassland management systems for environmental and livelihood benefits | 80 | 15 | |
| Harnessing innovation for change: Sustainability and poverty in developing countries | 74 | 16 | |
| The economic determinants of land degradation in developing countries | 72 | 17 | |
| Estimating returns to soil conservation adoption in the northern Ethiopian highlands | 64 | 18 | |
| The trends, promises and challenges of urbanization in the world | 63 | 19 | |
| Community participation and benefits in REDD+: A review of initial outcomes and lessons | 60 | 20 | |
| Design challenges for achieving reduced emissions from deforestation and forest degradation through conservation: Leveraging multiple paradigms at the tropical forest margins | 57 | 21 | |
| The nature, causes and consequences of desertification in the drylands of Africa | 55 | 22 | |
| The environmental impact of poverty: Evidence from firewood collection in rural Nepal | 53 | 23 | |
| Poverty, urbanization, and environmental degradation: Urban streams in the developing world | 50 | 24 |

Fig. 6.
Keyword co-occurrence network visualization. Nodes show the relative number of co-occurrences for a specific keyword. Different colors classify the nodes of the co-occurrence network. The arrangement of keywords in different nodes indicates a series of similarities. The closer the keywords are to the co-occurrence network map, the stronger the relatedness between them. EKC, environmental Kuznets curve."

Table 5
Thematic clusters of various keywords in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field."
| Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | Cluster 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Africa (8) Agriculture (10) Climate change (12) Environment (11) Food security (7) Health (5) Impact (10) Land (5) Policy (12) Sustainability (14) | Deforestation (14) Degradation (10) Developing country (28) Economic growth (10) EKC (6) Growth (7) Management (14) Population (7) Soil conservation (5) | Biodiversity (5) Conservation (17) Development (6) Ecosystem services (10) Forests (5) Land-use (8) Payments (7) Poverty alleviation (9) | Consumption (9) Desertification (5) Environmental degradation (10) Impact (6) Land degradation (11) Livelihoods (9) Poverty (41) Sustainable development (22) |
Table 6
Occurrence and relevance score of top 23 terms in the environmental degradation-poverty nexus research field."
| Term | Occurrence | Relevance score |
|---|---|---|
| Forest degradation | 15 | 6.6741 |
| Deforestation | 28 | 3.2978 |
| Emission | 25 | 2.9394 |
| Forest | 24 | 2.5119 |
| Land degradation | 15 | 1.2734 |
| Household | 22 | 1.2035 |
| Sustainable development | 21 | 1.1491 |
| Water | 20 | 1.0811 |
| Economic growth | 18 | 0.9478 |
| Nature | 17 | 0.9304 |
| Environmental degradation | 88 | 0.9199 |
| Poverty alleviation | 17 | 0.9119 |
| Food security | 20 | 0.7493 |
| Country | 151 | 0.7379 |
| Agriculture | 31 | 0.7305 |
| Climate change | 30 | 0.6644 |
| Technology | 29 | 0.5978 |
| Economic development | 16 | 0.5833 |
| Income | 32 | 0.5512 |
| Opportunity | 28 | 0.3557 |
| Community | 40 | 0.3391 |
| Population | 32 | 0.3323 |
| Strategy | 47 | 0.2925 |
| [1] | Agten, S., 2021. “Made in China” No longer means cheap. In: Adventures in the Chinese Economy: 16 Years from the Inside. Singapore: Palgrave Macmillan, 1-18. |
| [2] | Ahluwalia, M.S., Carter, N.G., Chenery, H.B., 1979. Growth and poverty in developing countries. J.Dev. Econ. 6(3), 299-341. |
| [3] |
Akinlo, T., Dada, J.T., 2021. The moderating effect of foreign direct investment on environmental degradation-poverty reduction nexus: evidence from sub-Saharan African countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23, 15764-15784.
doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01315-1 |
| [4] |
Al-Mulali, U., Binti Che Sab, C.N., 2012. The impact of energy consumption and CO2 emission on the economic growth and financial development in the Sub Saharan African countries. Energy. 39(1), 180-186.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2012.01.032 |
| [5] | Ananda, J., Herath, G., 2003. Soil erosion in developing countries: a socio-economic appraisal. J.Environ. Manage. 68, 343-353. |
| [6] |
Asongu, S.A., Roux, L.S., Biekpe, N., 2017. Environmental degradation, ICT and inclusive development in Sub-Saharan Africa. Energy Policy. 111, 353-361.
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2017.09.049 |
| [7] | Baland, J.M., Bardhan, P., Das, S., et al., 2010. The environmental impact of poverty: Evidence from firewood collection in rural Nepal. Econ. Dev. Cult. Change. 1, 23-61. |
| [8] | Barbier, E.B., 1997. The economic determinants of land degradation in developing countries. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 352(1356), 891-899. |
| [9] |
Barbier, E.B., 2010. Poverty, development, and environment. Environ. Dev. Econ. 15(6), 635-660.
doi: 10.1017/S1355770X1000032X |
| [10] |
Bhattacharya, S., Basu, P.K., 1998. Mapping a research area at the micro level using co-word analysis. Scientometrics. 43(3), 359-372.
doi: 10.1007/BF02457404 |
| [11] |
Capps, K.A., Bentsen, C.N., Ramirez, A., 2016. Poverty, urbanization, and environmental degradation: Urban streams in the developing world. Freshw. Sci. 35(1), doi: 10.1086/684945.
doi: 10.1086/684945 |
| [12] |
Chakravarty, D., Mandal, S.K., 2020. Is economic growth a cause or cure for environmental degradation? Empirical evidences from selected developing economies. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators. 7, 100045, doi: 10.1016/j.indic.2020.100045.
doi: 10.1016/j.indic.2020.100045 |
| [13] | Clayton, E., 1983. Agriculture, Poverty and Freedom in Developing Countries. London: Palgrave. |
| [14] |
Darkoh, M.B.K., 1998. The nature, causes and consequences of desertification in the drylands of Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 9, 1-20.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-145X |
| [15] |
Dorin, M., Maier, A., Aschilean, I., et al., 2020. The relationship between innovation and sustainability: A bibliometric review of the literature. Sustainability. 12(10), 4083, doi: 10.3390/su12104083.
doi: 10.3390/su12104083 |
| [16] |
Duraiappah, A.K., 1998. Poverty and environmental degradation: A review and analysis of the nexus. World Dev. 26(12), 2169-2179.
doi: 10.1016/S0305-750X(98)00100-4 |
| [17] |
Ekholm, T., Kery, V., Pachauri, S., et al., 2010. Determinants of household energy consumption in India. Energy Policy. 38(10), 5696-5707.
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2010.05.017 |
| [18] |
Gray, L.C., Moseley, W.G., 2005. A geographical perspective on poverty-environment interactions. Geogr. J. 171(1), 9-23.
doi: 10.1111/geoj.2005.171.issue-1 |
| [19] | Hanjra, M.A., Blackwell, J., Carr, G., et al., 2012. Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: Implications for water governance and public policy . Int. J.Hyg. Environ. Health. 215(3), 255-269. |
| [20] | IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), 2018. Global Warming of 1. 5°C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5°C above Pre-industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty. [2021-02-10]. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/2/2019/06/SR15_Full_Report_High_Res.pdf. |
| [21] | Jain, L.C., 1988. Poverty, environment, development: A view from Gandhi’s window. Econ. Polit. Week. 23(7), 311-320. |
| [22] |
Jian, J.H., Fan, X.J., He, P.L., et al., 2019. The effects of energy consumption, economic growth and financial development on CO2 emissions in China: A VECM Approach. Sustainability. 11(18), 4850, doi: 10.3390/su11184850.
doi: 10.3390/su11184850 |
| [23] | Johnson, D.L., Ambrose, S.H., Bassett, T.J., et al., 1997. Meanings of environmental terms. J.Environ. Qual. 26(3), 581-589. |
| [24] | Kassie, M., Pender, J., Yesuf, M., et al., 2008. Estimating returns to soil conservation adoption in the northern Ethiopian highlands. Agricultural Economists. 38(2), 213-232. |
| [25] | Kates, R.W., 2000. Cautionary tales: Adaptation and the global poor. In: Kane, S.M., Yohe, G.W., (eds.). Societal Adaptation to Climate Variability and Change. Dordrecht:Springer, 5-17. |
| [26] |
Kemp, D.R., Han, G.D., Hou, X.Y., et al., 2013. Innovative grassland management systems for environmental and livelihood benefits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(21), 8369-8374.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208063110 |
| [27] | Khavul, S., Bruton, G.D., 2013. Harnessing innovation for change: Sustainability and poverty in developing countries. J.Manage. Stud. 50(2), 285-306. |
| [28] |
Kousar, S., Shabbir, A., 2021. Analysis of environmental degradation mechanism in the nexus among energy consumption and poverty in Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 27528-27541.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-12140-w |
| [29] | Kumar, S.K., Hotchkiss, D., 1988. Consequences of deforestation for women’s time allocation, agricultural production and nutrition in hill areas of Nepal. In: Research Report. International Food Policy Research Institute. Washington, D.C.,USA, 69-72. |
| [30] |
Lawlor, K., Madeira, E.M., Blockhus, J., et al., 2013. Community participation and benefits in REDD+: A review of initial outcomes and lessons. Forests. 4, 296-318.
doi: 10.3390/f4020296 |
| [31] |
Malerba, D., 2020. Poverty alleviation and local environmental degradation: An empirical analysis in Colombia. World Dev. 127, 104776, doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104776.
doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104776 |
| [32] | Martinelli, L.A., Naylor, R., Vitousek, P.M., et al., 2010. Agriculture in Brazil: impacts, costs, and opportunities for a sustainable future. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2(5-6), 431-438. |
| [33] | Masron, T.A., Subramaniam, Y., 2019. Does poverty cause environmental degradation? Evidence from developing countries. J.Poverty. 23(1), 44-64. |
| [34] |
McElwee, P.D., 2012. Payments for environmental services as neoliberal market-based forest conservation in Vietnam: Panacea or problem? Geoforum. 43(3), 412-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.geoforum.2011.04.010 |
| [35] |
Minang, P.A., van Noordwijk, M., 2013. Design challenges for achieving reduced emissions from deforestation and forest degradation through conservation: Leveraging multiple paradigms at the tropical forest margins. Land Use Pol. 31, 61-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.04.025 |
| [36] | Moore, M., Gould, P., Keary, B.S., 2003. Global urbanization and impact on health. Int. J.Hyg. Environ. Health. 206(4-5), 269-278. |
| [37] |
Moral-Muñoz, J.A., Herrera-Viedma, E., Santisteban-Espejo, A., et al., 2020. Software tools for conducting bibliometric analysis in science: An up-to-date review. El profesional de la informaci ón. 29(1), e290103, doi: 10.3145/epi.2020.ene.03.
doi: 10.3145/epi.2020.ene.03 |
| [38] |
Nyssen, J., Poesen, J., Moeyersons, J., et al., 2004. Human impact on the environment in the Ethiopian and Eritrean highlands—a state of the art. Earth-Sci. Rev. 64(3-4), 273-320.
doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(03)00078-3 |
| [39] | Pandey, S., Dogan, E., Taskin, D., 2020. Production-based and consumption-based approaches for the energy-growth-environment nexus: Evidence from Asian countries. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 23, 274-281. |
| [40] | Pattanayak, S.K., Wunder, S., Ferraro, P.J., 2010. Show me the money: Do payments supply environmental services in developing countries? Rev. Env. Econ. Policy. 4(2), 254-274. |
| [41] | Perianes-Rodriguez, A., Waltman, L., van Eck, N.J., 2016. Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting. J.Informetr. 10(4), 1178-1195. |
| [42] |
Ravnborg, H.M., 2003. Poverty and environmental degradation in the Nicaraguan hillsides. World Dev. 31(11), 1933-1946.
doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2003.06.005 |
| [43] |
Reardon, T., Vosti, S.A., 1995. Links between rural poverty and the environment in developing countries: Asset categories and investment poverty. World Dev. 23(9), 1495-1506.
doi: 10.1016/0305-750X(95)00061-G |
| [44] |
Sanchez, P.A., 2000. Linking climate change research with food security and poverty reduction in the tropics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 82(1-3), 371-383.
doi: 10.1016/S0167-8809(00)00238-3 |
| [45] |
Sarkodie, S.A., Strezov, V., 2019. A review on Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis using bibliometric and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 649, 128-145.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.276 |
| [46] |
Scherr, S.J., 2000. A downward spiral? Research evidence on the relationship between poverty and natural resource degradation . Food Policy. 25(4), 479-498.
doi: 10.1016/S0306-9192(00)00022-1 |
| [47] | Shaista, A., 2010. Globalization, poverty and environmental degradation: Sustainable development in Pakistan. Journal of Sustainable Development. 3(3), 103-114. |
| [48] |
Sovacool, B.K., 2012. The political economy of energy poverty: A review of key challenges. Energy Sustain Dev. 16(3), 272-282.
doi: 10.1016/j.esd.2012.05.006 |
| [49] | United, Nations., 2021. The 17 Sustainable Development Goals. [2021-02-10]. https://sdgs.un.org/goals. |
| [50] |
van Eck, N.J., Waltman, L., 2010. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 84(2), 523-538.
doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 |
| [51] | van Eck, N.J., Waltman, L., Dekker, R., et al., 2010. A comparison of two techniques for bibliometric mapping: Multidimensional scaling and VOS. J.Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 61(12), 2405-2416. |
| [52] | van Eck, N.J., Waltman, L., 2020. VOSviewer Manual. [2021-02-20]. https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.16.pdf. |
| [53] | World, Bank, 1992. World Development Report 1992: Development and the Environment. New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [54] |
Zhang, X.Q., 2016. The trends, promises and challenges of urbanization in the world. Habitat Int. 54(3), 241-252.
doi: 10.1016/j.habitatint.2015.11.018 |
| [55] |
Zhong, S.Z., Geng, Y., Liu, W.J., et al., 2016. A bibliometric review on natural resource accounting during 1995-2014. J.Clean. Prod. 139, 122-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.039 |
| [56] |
Zupic, I., Čater, T., 2015. Bibliometric Methods in Management and Organization. Organ. Res. Methods. 18(3), 429-472.
doi: 10.1177/1094428114562629 |
| [1] | WANG Tao, ZHOU Daojing, FAN Jie. Spatial differences of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) among counties (cities) on the northern slope of the Kunlun Mountains [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(1): 100108-. |
| [2] | Dervis KIRIKKALELI, Emrah SOFUOĞLU, Kashif Raza ABBASI, Kwaku ADDAI. Economic complexity and environmental sustainability in eastern European economies: Evidence from novel Fourier approach [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(4): 349-358. |
| [3] | Sadat Daaki SSEKIBAALA, Twaha Ahmed KASULE. Examination of the poverty-environmental degradation nexus in Sub-Saharan Africa [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(3): 296-308. |
| [4] | Firoz AHMAD, Nazimur Rahman TALUKDAR, Laxmi GOPARAJU, Chandrashekhar BIRADAR, Shiv Kumar DHYANI, Javed RIZVI. GIS-based assessment of land-agroforestry potentiality of Jharkhand State, India [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(3): 254-268. |
| [5] | Jianjun Ding, Zhang Wang, Yanhong Liu, Fangwei Yu. Rural households’ livelihood responses to industry-based poverty alleviation as a sustainable route out of poverty [J]. Regional Sustainability, 2020, 1(1): 68-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号