Regional Sustainability ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (3): 309-321.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2023.08.008
• Review Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qamer RIDWANa, Zishan Ahmad WANIb, Nahila ANJUMa, Jahangeer Ahmad BHATc, Mohd HANIEFa,*( ), Shreekar PANTd,*(
), Shreekar PANTd,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-21
Revised:2023-07-05
Accepted:2023-08-30
Online:2023-09-30
Published:2023-10-20
Contact:
*E-mail address: Qamer RIDWAN, Zishan Ahmad WANI, Nahila ANJUM, Jahangeer Ahmad BHAT, Mohd HANIEF, Shreekar PANT. Human-wildlife conflict: A bibliometric analysis during 1991-2023[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2023, 4(3): 309-321.
Table 1
Top 20 productive and cited authors related to human-wildlife conflict (HWC) research topic during January 1991-February 2023."
| Author | Number of publications | Total citations |
|---|---|---|
| David Macdonald | 29 | 834 |
| Andrew Loveridge | 15 | 449 |
| Catherine Hill | 14 | 731 |
| Stewart Breck | 11 | 247 |
| Justin O’Riain | 11 | 228 |
| Ruth Kansky | 10 | 383 |
| Charudutt Mishra | 10 | 632 |
| Colleen Cassady Clair | 10 | 256 |
| Young Julie | 10 | 69 |
| Nils Bunnefeld | 9 | 231 |
| Meredith Gore | 9 | 280 |
| Krithi Karanth | 9 | 177 |
| Igor Khorozyan | 9 | 55 |
| Silvio Marchini | 9 | 242 |
| Sindhu Radhakrishna | 9 | 88 |
| Steve Redpath | 9 | 404 |
| Rosie Woodroffe | 9 | 491 |
| Daniel Blumstein | 8 | 293 |
| Colleen Downs | 8 | 81 |
| Russell Hill | 8 | 81 |
Table 2
Number of articles by the authors related to HWC research topic during January 1991-February 2023."
| Number of publications | Number of authors | Proportion of authors (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4108 | 82.24 |
| 2 | 555 | 11.10 |
| 3 | 176 | 3.52 |
| 4 | 76 | 1.52 |
| 5 | 29 | 0.58 |
| 6 | 17 | 0.34 |
| 7 | 10 | 0.20 |
| 8 | 7 | 0.14 |
| 9 | 8 | 0.16 |
| 10 | 4 | 0.08 |
| 11 | 2 | 0.04 |
| 14 | 1 | 0.02 |
| 15 | 1 | 0.02 |
| 29 | 1 | 0.02 |
Table 3
Top 20 productive and cited scientific journal sources related to HWC research topic during January 1991-February 2023."
| Source | Number of publications | Total citations |
|---|---|---|
| Biological Conservation | 104 | 3769 |
| Oryx | 88 | 2795 |
| Human Dimensions of Wildlife | 60 | 555 |
| PLoS ONE | 42 | 1067 |
| Global Ecology and Conservation | 38 | 250 |
| European Journal of Wildlife Research | 38 | 445 |
| Conservation Biology | 37 | 1716 |
| Wildlife Research | 32 | 652 |
| Animal Conservation | 30 | 1396 |
| Journal of Wildlife Management | 29 | 449 |
| Journal of Applied Ecology | 29 | 920 |
| Biodiversity and Conservation | 22 | 550 |
| Conservation and Society | 21 | 278 |
| Wildlife Society Bulletin | 20 | 316 |
| Journal for Nature Conservation | 20 | 238 |
| Ambio | 18 | 384 |
| Human Ecology | 16 | 328 |
| International Journal of Primatology | 15 | 553 |
| Environmental Management | 14 | 357 |
| Journal of Mammalogy | 10 | 268 |
Table 4
Top 20 global cited articles on the HWC research topic during January 1991-February 2023."
| Title | Author(s) | Journal | Publication year | Total citations | Total citations per year | Normalized total citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complexities of conflict: the importance of considering social factors for effectively resolving human-wildlife conflict | Amy Dickman | Animal Conservation | 717 | 51 | 11.10 | |
| Human-felid conflict: a review of patterns and priorities worldwide | Chole Inskip and Alexandra Zimmermann | Oryx | 452 | 30 | 5.00 | |
| Diet of wild boar Sus scrofa in Western Europe, with particular reference to consumption of agricultural crops | Laurant Schley and Timothy Roper | Mammal Review | 335 | 16 | 2.42 | |
| Human-wildlife conflict and coexistence | Philip Nyhus | Annual Review of Environment and Resources | 272 | 34 | 10.23 | |
| The hidden dimensions of human-wildlife conflict: Health impacts, opportunity and transaction costs. | Maan Barua, Shonil Bhagwat, and Sushrut Jadhav | Biological Conservation | 271 | 25 | 9.22 | |
| Fencing for conservation: restriction of evolutionary potential or a riposte to threatening processes? | Matt Hayward and Graham Kerley | Biological Conservation | 247 | 16 | 2.73 | |
| Suitability of amphibians and reptiles for translocation | Jennifer Germano and Phillip Bishop | Conservation Biology | 246 | 16 | 2.72 | |
| Conservation's blind spot: The case for conflict transformation in wildlife conservation | Francine Madden and Brian McQuinn | Biological Conservation | 244 | 24 | 8.25 | |
| Livestock depredation by large carnivores in the Indian trans-Himalaya: conflict perceptions and conservation prospects | Charudutt Mishra | Environmental Conservation | 219 | 8 | 1.00 | |
| Livestock predation by lions, leopards, spotted hyenas, and their vulnerability to retaliatory killing in the Maasai steppe, Tanzania | Bernard Kissui | Animal Conservation | 217 | 14 | 3.95 | |
| Rearticulating the myth of human-wildlife conflict | Markus Nils Peterson, Jessie Birckhead, Kirsten Leong, et al. | Conservation Letters | 212 | 15 | 3.28 | |
| Human-wildlife interactions in urban areas: a review of conflicts, benefits and opportunities | Carl Soulsbury and Piran White | Wildlife Research | 210 | 23 | 7.88 | |
| Food cleaning in gorillas: Social learning is a possibility but not a necessity | Damien Neadle, Matthias Allritz, and Claudio Tennie | PLoS ONE | 203 | 23 | 7.62 | |
| Conflict of interest between people and baboons: crop raiding in Uganda | Catherine Hill | International Journal of Primatology | 202 | 8 | 1.43 | |
| Living with large carnivores: predation on livestock by the snow leopard (Uncia uncia) | Sumanta Bagchi and Charudutt Mishra | Journal of Zoology | 188 | 10 | 3.26 | |
| Tilting at wildlife: reconsidering human-wildlife conflict | Stephen Mark Redpath, Saloni Bhatia, and Juliette Young | Oryx | 186 | 21 | 6.98 | |
| Leopard (Panthera pardus) status, distribution, and the research efforts across its range | Andrew Jacobson, Peter Gerngross, Rebecca Schoonover, et al. | PeerJ | 169 | 21 | 6.36 | |
| Effects of trophy hunting on lion and leopard populations in Tanzania | Craig Packer, Henry Brink, Bernard Kissui, et al. | Conservation Biology | 158 | 12 | 4.42 | |
| A review of flight-initiation distances and their application to managing disturbance to Australian birds | Mike Weston, Emily Mcleod, Daniel Blumstein, et al. | Emu-Austral Ornithology | 155 | 13 | 3.84 | |
| Urban mammals: what does the future hold? An analysis of the factors affecting patterns of use of residential gardens in Great Britain | Philip Baker and Stephen Harris | Mammal Review | 154 | 9 | 2.48 |
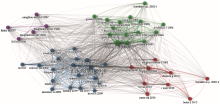
Fig. 5.
Co-citation network of the studies on the HWC research topic with article as the unit of analysis. The width of the connective line between two nodes shows the degree of co-citation, and the size of the node indicates how many citations the article has received. Red nodes represent articles focusing on human-carnivore conflicts, blue nodes represent articles focusing on the complexity of HWCs and multiple factors in conflict resolution, green nodes represent articles focusing on the issue of livestock predation by carnivores and its impact on human livelihoods, and violet nodes represent articles focusing on crop raiding by wildlife."


Fig. 8.
Co-occurrence network of keywords on the HWC research topic during January 1991-February 2023. Keywords are represented by points, and the proximity of points indicates the frequency of their co-occurrence in the articles, i.e., points that are closer together signify a higher likelihood of being mentioned together in the articles, while points that are farther apart indicate a lower likelihood of co-occurrence. The width of the connective line between two points shows the degree of correlation. Red points represent keywords related to the interaction between carnivore and human and livestock; blue points represent keywords related to the management of HWCs, conservation, and local perception; green points represent keywords related to HWC with respect to elephant; violet points represent keywords related to the interaction between carnivore and livestock; yellow points represent keywords of conflict; brown points represent keywords of human-wildlife."

| [1] | Ahmi A., Saidin S.Z., Mohd Nasir M.H., et al., 2020. Applicability of Lotka's Law in eXtensible business reporting language (XBRL) studies. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology. 29(6), 282-289. |
| [2] | Allen L., Jones C., Dolby K., et al., 2009. Looking for landmarks: the role of expert review and bibliometric analysis in evaluating scientific publication outputs. PLoS ONE. 4(6), e5910, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005910. |
| [3] |
Aria M., Cuccurullo C., 2017. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 11(4), 959-975.
doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007 |
| [4] |
Bagchi S., Mishra C., 2006. Living with large carnivores: predation on livestock by the snow leopard (Uncia uncia). J. Zool. 268(3), 217-224.
doi: 10.1111/jzo.2006.268.issue-3 |
| [5] |
Baker H.K., Kumar S., Pattnaik D., 2021. Research constituents, intellectual structure, and collaboration pattern in the Journal of Forecasting: A bibliometric analysis. J. Forecast. 40(4), 577-602.
doi: 10.1002/for.v40.4 |
| [6] |
Baker P.J., Harris S., 2007. Urban mammals: what does the future hold? An analysis of the factors affecting patterns of use of residential gardens in Great Britain. Mammal Rev. 37(4), 297-315.
doi: 10.1111/mam.2007.37.issue-4 |
| [7] | Barua M., Bhagwat S.A., Jadhav S., 2013. The hidden dimensions of human-wildlife conflict: Health impacts, opportunity and transaction costs. Biol. Conserv. 157, 309-316. |
| [8] | Brika S.K.M., Algamdi A., Chergui K., et al., 2021. Quality of higher education: A bibliometric review study. Front. Educ. 6, 666087, doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.666087. |
| [9] | Carter N.H., Riley S.J., Shortridge A., et al., 2014. Spatial assessment of attitudes toward tigers in Nepal. Ambio. 43, 125-137. |
| [10] | Carter N.H., Linnell J.D.C., 2016. Co-adaptation is key to coexisting with large carnivores. Trends Ecol. Evol. 31(8), 575-578. |
| [11] |
Chapron G., López-Bao J.V., 2014. Conserving carnivores: politics in play. Science. 343(6176), 1199-1200.
doi: 10.1126/science.343.6176.1199-b pmid: 24626913 |
| [12] |
Chapron G., López-Bao J.V., 2020. The place of nature in conservation conflicts. Conserv. Biol. 34(4), 795-802.
doi: 10.1111/cobi.13485 pmid: 32406544 |
| [13] |
Choudhri A.F., Siddiqui A., Khan N.R., et al., 2015. Understanding bibliometric parameters and analysis. Radiographics. 35(3), 736-746.
doi: 10.1148/rg.2015140036 pmid: 25969932 |
| [14] |
Dickman A.J., 2010. Complexities of conflict: the importance of considering social factors for effectively resolving human-wildlife conflict. Anim. Conserv. 13(5), 458-466.
doi: 10.1111/acv.2010.13.issue-5 |
| [15] | Dickman A.J., Macdonald E.A., Macdonald D.W., 2011. A review of financial instruments to pay for predator conservation and encourage human-carnivore coexistence. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 108(34), 13937-13944. |
| [16] | Donthu N., Kumar S., Mukherjee D., et al., 2021a. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 133, 285-296. |
| [17] |
Donthu N., Kumar S., Pandey N., 2021b. A retrospective evaluation of marketing intelligence and planning: 1983-2019. Mark. Intell. Plan. 39(1), 48-73.
doi: 10.1108/MIP-02-2020-0066 |
| [18] | Frank B., Glikman J.A., 2019. Human-wildlife conflicts and the need to include coexistence. In: Frank, B., Glikman, J.A., Marchini, S., (eds.). Human-Wildlife Interactions: Turning Conflict into Coexistence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1-19. |
| [19] |
Freire R.R., Veríssimo J.M.C., 2021. Mapping co-creation and co-destruction in tourism: A bibliographic coupling analysis. Anatolia. 32(2), 207-217.
doi: 10.1080/13032917.2020.1855594 |
| [20] | Gargallo E., 2021. Human-wildlife conflict in a ‘successful’ community conservation programme: economic and territorial impacts on Namibia's conservancies. J. Arid Environ. 193, 104591, doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2021.104591. |
| [21] |
Germano J.M., Bishop P.J., 2009. Suitability of amphibians and reptiles for translocation. Conserv. Biol. 23(1), 7-15.
doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2008.01123.x pmid: 19143783 |
| [22] |
Gmür M., 2003. Co-citation analysis and the search for invisible colleges: a methodological evaluation. Scientometrics. 57(1), 27-57.
doi: 10.1023/A:1023619503005 |
| [23] | Gourikeremath G., Hiremath R., Hadagali G., 2021. Application of Bradford's Law to the scientific literature of two UPE (University with Potential for Excellence) status universities of India: A study based on the Web of Science database. J. Advan. Lib. Inform. Sci. 10(3), 160-165. |
| [24] |
Goyal K., Kumar S., 2021. Financial literacy: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 45(1), 80-105.
doi: 10.1111/ijcs.v45.1 |
| [25] | Gross E., Jayasinghe N., Brooks A., et al., 2021. A Future for All: The Need for Human-Wildlife Coexistence. [2023-01-05]. https://files.worldwildlife.org/wwfcmsprod/files/Publication/file/8zhcghahmt_A_future_for_all_the_need_for_human_willdife_coexistence.pdf. |
| [26] | Hasana U., Swain S.K., George B., 2022. A bibliometric analysis of ecotourism: A safeguard strategy in protected areas. Reg. Sustain. 3(1), 27-40. |
| [27] |
Hayward M.W., Kerley G.I.H., 2009. Fencing for conservation: restriction of evolutionary potential or a riposte to threatening processes? Biol. Conserv. 142(1), 1-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2008.09.022 |
| [28] | Hill C.M., 2000. Conflict of interest between people and baboons: crop raiding in Uganda. Int. J. Primatol. 21, 299-315. |
| [29] |
Inskip C., Zimmermann A., 2009. Human-felid conflict: a review of patterns and priorities worldwide. Oryx. 43(1), 18-34.
doi: 10.1017/S003060530899030X |
| [30] | IUCN-SSC (International Union of Conservation of Nature-Species Survival Commission), 2020. What Is Human-Wildlife Conflict? Briefing Paper by the IUCN SSC Human-Wildlife Conflict Task Force. [2023-01-18]. .https://www.hwctf.org/_files/ugd/7acc16_c026ab9ffce44ea7900580771cba1cb4.pdf |
| [31] | IUCN-SSC, 2022. Perspectives on Human-Wildlife Coexistence. Briefing Paper by the IUCN SSC Human-Wildlife Conflict Task Force. [2023-01-12]. https://www.hwctf.org/post/new-publication-perspectives-on-human-wildlife-coexistence-briefing-paper. |
| [32] | Jacobson A.P., Gerngross P., Lemeris Jr J.R., et al., 2016. Leopard (Panthera pardus) status, distribution, and the research efforts across its range. PeerJ. 4, e1974, doi: 10.7717/peerj.1974. |
| [33] | Kesch M.K., Bauer D.T., Loveridge A.J., 2015. Break on through to the other side: the effectiveness of game fencing to mitigate human-wildlife conflict. Afr. J. Wildl. Res. 45(1), 76-87. |
| [34] |
Kissui B.M., 2008. Livestock predation by lions, leopards, spotted hyenas, and their vulnerability to retaliatory killing in the Maasai steppe, Tanzania. Anim. Conserv. 11(5), 422-432.
doi: 10.1111/acv.2008.11.issue-5 |
| [35] |
Kolowski J.M., Holekamp K.E., 2006. Spatial, temporal, and physical characteristics of livestock depredations by large carnivores along a Kenyan reserve border. Biol. Conserv. 128(4), 529-541.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2005.10.021 |
| [36] |
König H.J., Kiffner C., Kramer-Schadt S., et al., 2020. Human-wildlife coexistence in a changing world. Conserv. Biol. 34(4), 786-794.
doi: 10.1111/cobi.13513 pmid: 32406977 |
| [37] |
Linkie M., Dinata Y., Nofrianto A., et al., 2007. Patterns and perceptions of wildlife crop raiding in and around Kerinci Seblat National Park, Sumatra. Anim. Conserv. 10(1), 127-135.
doi: 10.1111/acv.2007.10.issue-1 |
| [38] | Lotka A.J., 1926. The frequency distribution of scientific productivity. J. Washington Acad. Sci. 16, 317-323. |
| [39] | Madden F., McQuinn B., 2014. Conservation's blind spot: The case for conflict transformation in wildlife conservation. Biol. Conserv. 178, 97-106. |
| [40] | Majiwala H., Kant R., 2023. A bibliometric review of a decade’ research on industry 4.0 & supply chain management. Materials Today: Proceedings. 72(3), 824-833. |
| [41] |
Mishra C., 1997. Livestock depredation by large carnivores in the Indian trans-Himalaya: conflict perceptions and conservation prospects. Environ. Conserv. 24(4), 338-343.
doi: 10.1017/S0376892997000441 |
| [42] | Mukherjee D., Lim W.M., Kumar S., et al., 2022. Guidelines for advancing theory and practice through bibliometric research. J. Bus. Res. 148, 101-115. |
| [43] | Naughton-Treves L., 1997. Farming the forest edge: vulnerable places and people around Kibale National Park, Uganda. Geogr. Rev. 87(1), 27-46. |
| [44] |
Naughton-Treves L., Treves A., Chapman C., et al., 1998. Temporal patterns of crop-raiding by primates: linking food availability in croplands and adjacent forest. J. Appl. Ecol. 35(4), 596-606.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2664.1998.3540596.x |
| [45] |
Naughton-Treves L., Grossberg R., Treves A., 2003. Paying for tolerance: rural citizens’ attitudes toward wolf depredation and compensation. Conserv. Biol. 17(6), 1500-1511.
doi: 10.1111/cbi.2003.17.issue-6 |
| [46] | Naughton-Treves L., Treves A., 2005. Socio-ecological factors shaping local support for wildlife:crop-raiding by elephants and other wildlife in Africa. In: Woodroffe, R., Thirgood, S., Rabinowitz, A., (eds.). People and Wildlife:Conflict or Coexistence? Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 252-277. |
| [47] | Neadle D., Allritz M., Tennie C., 2017. Food cleaning in gorillas: social learning is a possibility but not a necessity. PLoS ONE. 12(12), e0188866, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188866. |
| [48] | Nyhus P.J., 2016. Human-wildlife conflict and coexistence. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 41, 143-171. |
| [49] |
Packer C., Brink H., Kissui B.M., et al., 2011. Effects of trophy hunting on lion and leopard populations in Tanzania. Conserv. Biol. 25(1), 142-153.
doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2010.01576.x pmid: 20825444 |
| [50] |
Patterson B.D., Kasiki S.M., Selempo E., et al., 2004. Livestock predation by lions (Panthera leo) and other carnivores on ranches neighboring Tsavo National Parks, Kenya. Biol. Conserv. 119(4), 507-516.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2004.01.013 |
| [51] |
Peterson M.N., Birckhead J.L., Leong K., et al., 2010. Rearticulating the myth of human-wildlife conflict. Conserv. Lett. 3(2), 74-82.
doi: 10.1111/conl.2010.3.issue-2 |
| [52] | Redpath S.M., Young J., Evely A., et al., 2013. Understanding and managing conservation conflicts. Trends Ecol. Evol. 28(2), 100-109. |
| [53] |
Redpath S.M., Bhatia S., Young J., 2015. Tilting at wildlife: reconsidering human-wildlife conflict. Oryx. 49(2), 222-225.
doi: 10.1017/S0030605314000799 |
| [54] | Rejeb A., Abdollahi A., Rejeb K., et al., 2022. Drones in agriculture: A review and bibliometric analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 198, 107017, doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2022.107017. |
| [55] | Ripple W.J., Estes J.A., Beschta R.L., et al., 2014. Status and ecological effects of the world's largest carnivores. Science. 343(6167), 1241484, doi: 10.1126/science.1241484. |
| [56] |
Schley L., Roper T.J., 2003. Diet of wild boar Sus scrofa in Western Europe, with particular reference to consumption of agricultural crops. Mammal Rev. 33(1), 43-56.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2907.2003.00010.x |
| [57] | Seoraj-Pillai N., Pillay N., 2017. A meta-analysis of human-wildlife conflict: South African and global perspectives. Sustainability. 9(1), 34, doi: 10.3390/su9010034. |
| [58] |
Sharma R., Shishodia A., Gunasekaran A., et al., 2022. The role of artificial intelligence in supply chain management: mapping the territory. Int. J. Prod. Res. 60(24), 7527-7550.
doi: 10.1080/00207543.2022.2029611 |
| [59] |
Singh R., Sibi P.S., Sharma P., 2022. Journal of ecotourism: a bibliometric analysis. J. Ecotourism. 21(1), 37-53.
doi: 10.1080/14724049.2021.1916509 |
| [60] |
Small H., 1973. Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 24(4), 265-269.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4571 |
| [61] |
Soulsbury C.D., White P.C.L., 2015. Human-wildlife interactions in urban areas: a review of conflicts, benefits and opportunities. Wildl. Res. 42(7), 541-553.
doi: 10.1071/WR14229 |
| [62] | Treves A., Karanth K.U., 2003. Human-carnivore conflict and perspectives on carnivore management worldwide. Conserv. Boil. 17(6), 1491-1499. |
| [63] |
Treves A., Wallace R.B., Naughton-Treves L., et al., 2006. Co-managing human-wildlife conflicts: A review. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 11(6), 383-396.
doi: 10.1080/10871200600984265 |
| [64] | Treves A., 2009. The human dimensions of conflicts with wildlife around protected areas. In: Manfredo, M.J., Vaske, J.J., Brown, P.J., et al., (eds.). Wildlife and Society: The Science of Human Dimensions. Washington D.C.: Island Press, 214-228. |
| [65] | Wallin J.A., 2005. Bibliometric methods: pitfalls and possibilities. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 97(5), 261-275. |
| [66] |
Wang S.W., Macdonald D.W., 2006. Livestock predation by carnivores in Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park, Bhutan. Biol. Conserv. 129(4), 558-565.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2005.11.024 |
| [67] |
Weston M.A., McLeod E.M., Blumstein D.T., et al., 2012. A review of flight-initiation distances and their application to managing disturbance to Australian birds. Emu. 112(4), 269-286.
doi: 10.1071/MU12026 |
| [68] | Woodroffe R., Thirgood S., Rabinowitz A., 2005. The impact of human-wildlife conflict on natural systems. In: Woodroffe, R., Thirgood, S., Rabinowitz, A., (eds.). People and Wildlife, Conflict or Co-existence? Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 9. |
| [69] |
Wuchty S., Jones B.F., Uzzi B., 2007. The increasing dominance of teams in production of knowledge. Science. 316(5827), 1036-1039.
doi: 10.1126/science.1136099 pmid: 17431139 |
| [70] | Zimmermann A., McQuinn B., Macdonald D.W., 2020. Levels of conflict over wildlife: Understanding and addressing the right problem. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2(10), e259, doi: 10.1111/csp2.259. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号