Regional Sustainability ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (1): 36-46.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2021.01.002cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2021.01.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Peng He, Lishuai Xu*( ), Zhengchun Liu, Yaodong Jing, Wenbo Zhu
), Zhengchun Liu, Yaodong Jing, Wenbo Zhu
Received:2020-09-02
Revised:2020-12-31
Accepted:2021-01-15
Published:2021-01-20
Online:2021-03-11
Contact:
Lishuai Xu
E-mail:sdytxu@126.com
Peng He, Lishuai Xu, Zhengchun Liu, Yaodong Jing, Wenbo Zhu. Dynamics of NDVI and its influencing factors in the Chinese Loess Plateau during 2002-2018[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2021, 2(1): 36-46.

Fig. 4.
Mann-Kendall mutation test of NDVI in the CLP (a), as well as in different vegetation cover types (crops (b), steppes (c), scrub (d), broadleaved forests (e), desert (f), meadows (g), grasses (h), and coniferous forests (i)) from 2002 to 2018. The black dotted line represents the critical value at the 5% significance level (±1.96). UFk and UBk represent forward sample sequence statistics and reverse sample sequence statistics, respectively."
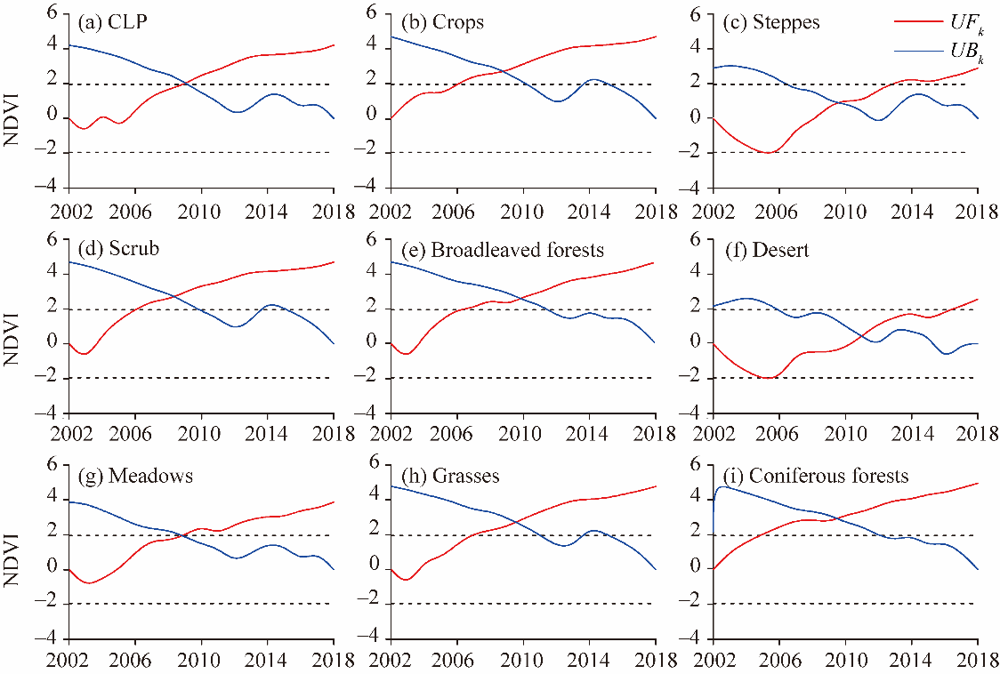
Table 1
Linear regression between NDVI and time series for different vegetation cover types."
| Vegetation cover type | Area percentage (%) | Regression equation | R2 | P | Increasing contribution rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crops | 44.99 | y=0.006x-12.193 | 0.814 | 0.01 | 50.97 |
| Steppes | 24.40 | y=0.005x-9.965 | 0.502 | 0.01 | 23.04 |
| Scrub | 7.61 | y=0.005x-8.879 | 0.870 | 0.01 | 7.18 |
| Broadleaved forests | 5.69 | y=0.004x-6.641 | 0.860 | 0.01 | 4.30 |
| Deserts | 5.16 | y=0.004x-8.517 | 0.342 | 0.01 | 3.90 |
| Meadows | 4.35 | y=0.003x-6.005 | 0.701 | 0.01 | 2.46 |
| Grasses | 4.15 | y=0.007x-13.488 | 0.887 | 0.01 | 5.49 |
| Coniferous forests | 3.15 | y=0.004x-8.159 | 0.924 | 0.01 | 2.38 |
| Others | 0.50 | y=0.003x-5.531 | 0.653 | 0.01 | 0.28 |
| [1] | Al-husban, Y., 2019. Urban expansion and shrinkage of vegetation cover in Al-Balqa Governorate, the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. Environ. Earth Sci. 78(21), 620. |
| [2] | Cao, L.J., Dong, W.J., Xu, Y.L., et al., 2007. Validating the runoff from the PRECIS model using a large-scale routing model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 24(5), 855-862. |
| [3] | Chakraborty, T., Hsu, A., Manya, D., et al., 2020. A spatially explicit surface urban heat island database for the United States: Characterization, uncertainties, and possible applications. ISPRS- J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 168, 74-88. |
| [4] | Cui, L.L., Shi, J., Yang, Y.M., et al., 2009. Ten-day response of vegetation NDVI to the variations of temperature and precipitation in Eastern China. Acta Geographica Sinica. 64(7), 850-860 (in Chinese). |
| [5] | Deng, J.C., Gao, P., Mu, X.M., et al., 2017. Impacts and advice of the Grain for Green Project to ecological environment on the Loess Plateau. Research of Soil and Water Conservation. 24(5), 63-68 (in Chinese). |
| [6] | Dong, Y., Yin, D.Q., Li, Y., et al., 2020. Spatio-temporal patterns of vegetation change and driving forces in the Loess Plateau. Journal of China Agricultural University. 25(8), 120-131 (in Chinese). |
| [7] | Fan, X.G., Ma, Z.G., Yang, Q., et al., 2015. Land use/land cover changes and regional climate over the Loess Plateau during 2001-2009. Part I: observational evidence. Clim. Change. 129(3-4), 427-440. |
| [8] | Feng, X.M., Fu, B.J., Piao, S., et al., 2016. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Change. 6(11), 1019-1022. |
| [9] | Gao, H.D., Pang, G.W., Li, Z.B., et al., 2017. Evaluating the potential of vegetation restoration in the Loess Plateau. Acta Geographica Sinica. 5, 863-874 (in Chinese). |
| [10] |
Gao, X.R., Sun, M., Luan, Q.H., et al., 2020. The spatial and temporal evolution of the actual evapotranspiration based on the remote sensing method in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 708, 135111.
pmid: 31810704 |
| [11] | Guo, R., Li, F.M., He, W.Y., et al., 2011. Spatial and temporal variability of annual precipitation during 1958-2007 in Loess Plateau, China. Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture. 2, 551-560. |
| [12] |
Javed, T., Yao, N., Chen, X., et al., 2020. Drought evolution indicated by meteorological and remote-sensing drought indices under different land cover types in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 4258-4274.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06629-2 |
| [13] | Koju, U.A., Zhang, J.H., Maharjan, S., et al., 2020. Analysis of spatiotemporal dynamics of forest Net Primary Productivity of Nepal during 2000-2015. Int. J. Remote Sens. 41(11), 4336-4364. |
| [14] |
Lamchin, M., Lee, W.K., Jeon, S.W., et al., 2018. Long-term trend and correlation between vegetation greenness and climate variables in Asia based on satellite data. Sci. Total Environ. 618, 1089-1095.
pmid: 29100696 |
| [15] | Li, B., Zhang, J.T., 2003. Analysis of relationships between vegetation and climate variables in Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 23(1), 84-91 (in Chinese). |
| [16] | Li, J.J., Li, Z., Lv, Z.M., 2016. Analysis of spatiotemporal variations in land use on the Loess Plateau of China during 1986-2010. Environ. Earth Sci. 75(11), 997. |
| [17] | Li, J.J., Peng, S.Z., Li, Z., 2017. Detecting and attributing vegetation changes on China’s Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 247, 260-270. |
| [18] | Li, Z., Zheng, F.L., Liu, W.Z., et al., 2010. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of extreme temperature and precipitation events on the Loess Plateau of China during 1961-2007. Quat. Int. 226(1-2), 92-100. |
| [19] | Liu, J., Wen, Z.M., Gang, C.C., 2020. Normalized difference vegetation index of different vegetation cover types and its responses to climate change in the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 40(2), 678-691 (in Chinese). |
| [20] |
Liu, L.B., Zhang, Y.T., Wu, S.Y., et al., 2018. Water memory effects and their impacts on global vegetation productivity and resilience. Sci Rep. 8, 2962.
pmid: 29440774 |
| [21] |
Lu, Y.H., Fu, B.J., Feng, X.M., et al., 2012. A policy-driven large scale ecological restoration: Quantifying ecosystem services changes in the Loess Plateau of China. PLoS ONE. 7(2), e31782.
pmid: 22359628 |
| [22] | Ma, X.F., Yan, W., Zhao, C.Y., et al, 2019. Snow-cover area and runoff variation under climate change in the West Kunlun Mountains. Water. 11(11), 2246. |
| [23] | Piao, S.L., Mohammat, A., Fang, J.Y., et al., 2006. NDVI-based increase in growth of temperate grasslands and its responses to climate changes in China. Glob Environ Change. 16(4), 340-348. |
| [24] |
Shi, P., Qin, Y.L., Liu, Q., et al., 2020. Soil respiration and response of carbon source changes to vegetation restoration in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 707, 135507.
pmid: 31874400 |
| [25] | Sun, W.Y., Song, X.Y., Mu, X.M., et al., 2015. Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations associated with climate change and ecological restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 209, 87-99. |
| [26] | Sun, Y., Chen, S.H., Su, H.B., 2020. Spatiotemporal variation of NDVI in different ecotypes on the Loess Plateau and its response to climate change. Geographical Research. 39(5), 1200-1214 (in Chinese). |
| [27] | Timilsena, J., Piechota, T., Tootle, G., 2009. Associations of interdecadal/interannual climate variability and long-term colorado river basin streamflow. J. Hydrol. 365(3-4), 289-301. |
| [28] | Wang, J., Rich, P.M., Price, K.P., 2003. Temporal responses of NDVI to precipitation and temperature in the central Great Plains, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 24(11), 2345-2364. |
| [29] | Wang, Q.X., Fan, X.H., Qin, Z.D., et al., 2012. Change trends of temperature and precipitation in the Loess Plateau region of China, 1961-2010. Glob. Planet. Change. 92-93, 138-147. |
| [30] | Wang, Y.Q., Shao, M.A., Zhu, Y.J., et al., 2011. Impacts of land use and plant characteristics on dried soil layers in different climatic regions on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 151(4), 437-448. |
| [31] | Wu, D.H., Zhao, X., Liang, S.L., et al., 2015. Time-lag effects of global vegetation responses to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 21(9), 3520-3531. |
| [32] | Wu, T., Feng, F., Lin, Q., et al., 2019. Advanced method to capture the time-lag effects between annual NDVI and precipitation variation using RNN in the arid and semi-arid Grasslands. Water. 11(9), 1789. |
| [33] | Xiao, J.F., 2014. Satellite evidence for significant biophysical consequences of the “Grain for Green” Program on the Loess Plateau in China. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 119(12), 2261-2275. |
| [34] | Xin, Z.B., Xu, J.X., Zheng, W., 2007. Impact of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover in Loess Plateau. Scientia Sinica. 37(11), 1504-1511 (in Chinese). |
| [35] | Xin, Z.B., Xu, J.X., Ma, Y.X., 2009. Spatio-temporal variation of erosive precipitation in Loess Plateau during past 50 years. Scientia Geographica Sinica. 29(3), 98-104 (in Chinese). |
| [36] | Yu, B., Shang, S.H., 2017. Multi-year mapping of maize and sunflower in Hetao irrigation district of China with high spatial and temporal resolution vegetation index series. Remote Sens. 9(8), 855. |
| [37] |
Yu, X., Zhou, W.J., Chen, Y.P., et al., 2020. Spatial variation of soil properties and carbon under different land use types on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 703, 134946.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135585 pmid: 31767326 |
| [38] | Zhang, H.Y., Fang, N.F., Shi, Z.H., 2016. Spatio-temporal patterns for the NDVI and its responses to climatic factors in the Loess Plateau, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 36(13), 3960-3968 (in Chinese). |
| [39] |
Zhang, J.Y., Ding, J.L., Wu, P.F., et al., 2020. Assessing arid inland lake watershed area and vegetation response to multiple temporal scales of drought across the Ebinur Lake Watershed. Sci Rep. 10(1), 1354.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57898-8 pmid: 31992731 |
| [40] |
Zhang, S.L., Wang, X.R., Xiao, Z.L., et al., 2020. Quantitative studies of gully slope erosion and soil physiochemical properties during freeze-thaw cycling in a Mollisol region. Sci. Total Environ. 707, 136191.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136078 pmid: 31874400 |
| [41] | Zhang, X.C., Liu, W.Z., 2005. Simulating potential response of hydrology, soil erosion, and crop productivity to climate change in Changwu tableland region on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 131(3-4), 127-142. |
| [42] |
Zheng, K., Wei, J.Z., Pei, J.Y., et al., 2019. Impacts of climate change and human activities on grassland vegetation variation in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 660, 236-244.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.022 pmid: 30640092 |
| [43] | Zhou, S.Y., Chang, J., Hu, T.H., et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal variations of land use and landscape ecological risk in a resource-based city, from rapid development to recession. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 29(1), 475-490. |
| [44] |
Zhuang, Q.W., Wu, S.X., Feng, X.Y., et al., 2020. Analysis and prediction of vegetation dynamics under the background of climate change in Xinjiang, China. PeerJ. 8, e8282.
pmid: 33391872 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号