Regional Sustainability ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (3): 208-222.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2022.09.001cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2022.09.001
• Full Length Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Chena,b, WANG Hongweia,b,*( ), XIE Linga,b, YI Suyana,b, TAN Boa,b
), XIE Linga,b, YI Suyana,b, TAN Boa,b
Received:2022-04-08
Revised:2022-07-18
Accepted:2022-09-12
Published:2022-10-17
Online:2022-11-29
Contact:
WANG Hongwei
E-mail:wanghw_777@163.com
MA Chen, WANG Hongwei, XIE Ling, YI Suyan, TAN Bo. Regional characteristics and spatiotemporal differentiation of the prevalence of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Xinjiang, China[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2022, 3(3): 208-222.
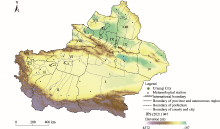
Fig. 1.
Overview of the study area. Note that the figure is based on the standard map (新S(2021)047) of the Map Service System (https://xinjiang.tianditu.gov.cn/main/bzdt.html) marked by the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Platform for Common Geospatial Information Services, and the standard map has not been modified. I, Bayingol Mongolian Autonomous Prefecture; II, Hotan Prefecture; III, Kashgar Prefecture; IV, Hami Prefecture; V, Turpan City; VI, Aksu Prefecture; VII, Kizilsu Kirgiz Autonomous Prefecture; VIII, Ili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture; IX, Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture; X, Bortala Mongolian Autonomous Prefecture; XI, Karamay City; XII, Tacheng Prefecture; XIII, Altay Prefecture."
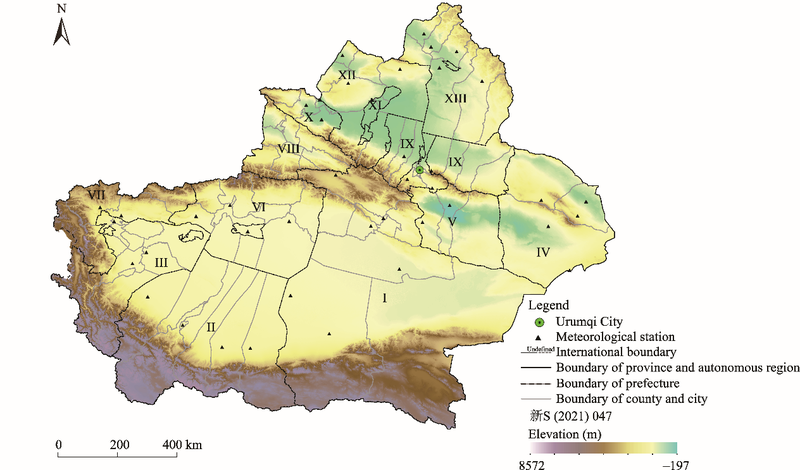

Fig. 4.
Interannual variation of HFMD from 2009 to 2018 in northern (a) and southern (b) Xinjiang; the box plot analysis of the interannual (c) and monthly (d) variations of HFMD from 2009 to 2018 in northern and southern Xinjiang; and monthly variation of HFMD from 2009 to 2018 in northern (e) and southern (f) Xinjiang."

Table 1
Detection results of factors influencing HFMD epidemics in Xinjiang in 2009, 2012, 2015, and 2018."
| 2009 | 2012 | 2015 | 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influencing factor ranking | q value | Influencing factor ranking | q value | Influencing factor ranking | q value | Influencing factor ranking | q value |
| X5 | 0.26 | X6 | 0.36 | X6 | 0.32 | X8 | 0.32 |
| X11 | 0.13 | X11 | 0.30 | X12 | 0.22 | X7 | 0.26 |
| X13 | 0.13 | X5 | 0.27 | X7 | 0.15 | X10 | 0.22 |
| X3 | 0.12 | X3 | 0.17 | X3 | 0.14 | X3 | 0.22 |
| X10 | 0.11 | X9 | 0.16 | X10 | 0.12 | X6 | 0.20 |
| X6 | 0.10 | X13 | 0.11 | X5 | 0.10 | X5 | 0.17 |
| X7 | 0.10 | X10 | 0.10 | X8 | 0.10 | X11 | 0.16 |
| 2009 | 2012 | 2015 | 2018 | ||||
| Interaction factors | q value | Interaction factors | q value | Interaction factors | q value | Interaction factors | q value |
| X3∩X5 | 0.75 | X6∩X8# | 0.67 | X6∩X10 | 0.73 | X8∩X12 | 0.69 |
| X3∩X13 | 0.71 | X5∩X11 | 0.64 | X3∩X6 | 0.66 | X10∩X12 | 0.67 |
| X9∩X13 | 0.61 | X6∩X11# | 0.62 | X3∩X10 | 0.62 | X4∩X7 | 0.57 |
| X5∩X8 | 0.55 | X4∩X8 | 0.58 | X11∩X12 | 0.60 | X2∩X10 | 0.57 |
| X10∩X13 | 0.54 | X2∩X11 | 0.57 | X4∩X6 | 0.58 | X8∩X10 | 0.56 |
| X4∩X5 | 0.52 | X5∩X8 | 0.57 | X9∩X10# | 0.57 | X2∩X12 | 0.54 |
| X5∩X13# | 0.55 | X6∩X7 | 0.57 | X7∩X12 | 0.54 | X8∩X3 | 0.54 |

Fig. 8.
Detection results and evolution characteristics of factors influencing HFMD epidemics in northern (a) and southern (b) Xinjiang in 2009, 2012, 2015, and 2018. X1, population density; X2, birth rate; X3, urbanization rate; X4, industrialization rate; X5, regional GDP; X6, per capita GDP; X7, temperature; X8, relative humidity; X9, sunshine hours; X10, precipitation; X11, dryness; X12, per capita residential land area; X13, per capita industrial land area."
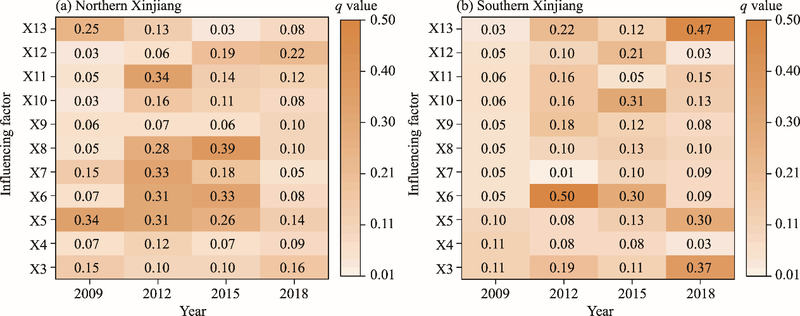
Table 2
Detection results of factors influencing HFMD epidemics in northern and southern Xinjiang in 2009, 2012, 2015, and 2018."
| 2009 | 2012 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Xinjiang | Southern Xinjiang | Northern Xinjiang | Southern Xinjiang | ||||
| Interaction factor | q value | Interaction factor | q value | Interaction factor | q value | Interaction factor | q value |
| X5∩X3 | 0.76 | X9∩X4 | 0.57 | X11∩X5 | 0.85 | X7∩X6 | 0.95 |
| X13∩X3 | 0.71 | X9∩X4 | 0.57 | X8∩X5 | 0.78 | X11∩X4 | 0.68 |
| X13∩X4 | 0.55 | X11∩X3 | 0.45 | X8∩X6 | 0.74 | X12∩X6 | 0.67 |
| X8∩X5 | 0.55 | X4∩X3 | 0.44 | X8∩X4 | 0.69 | X12∩X9 | 0.66 |
| X13∩X10 | 0.54 | X9∩X3 | 0.43 | X11∩X6# | 0.66 | X6∩X4 | 0.64 |
| X5∩X4 | 0.52 | X11∩X4 | 0.42 | X12∩X7 | 0.64 | X6∩X3 | 0.64 |
| 2015 | 2018 | ||||||
| Northern Xinjiang | Southern Xinjiang | Northern Xinjiang | Southern Xinjiang | ||||
| Interaction factor | q value | Interaction factor | q value | Interaction factor | q value | Interaction factor | q value |
| X12∩X7 | 0.72 | X12∩X7 | 0.72 | X11∩X13 | 0.71 | X4∩X6 | 0.90 |
| X12∩X6 | 0.81 | X8∩X4 | 0.71 | X9∩X13 | 0.61 | X4∩X14 | 0.88 |
| X10∩X6 | 0.75 | X10∩X9# | 0.71 | X12∩X13 | 0.61 | X3∩X12 | 0.87 |
| X10∩X2 | 0.73 | X12∩X4 | 0.70 | X13∩X14 | 0.59 | X3∩X10 | 0.86 |
| X9∩X6 | 0.71 | X10∩X6 | 0.68 | X6∩X13 | 0.59 | X11∩X12 | 0.86 |
| X10∩X7 | 0.71 | X6∩X3 | 0.63 | X5∩X13 | 0.58 | X12∩X14 | 0.84 |
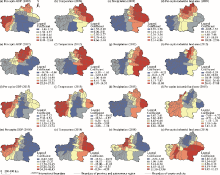
Fig. 9.
Spatial distribution of the regression coefficients of dominant factors (per capita GDP, temperature, precipitation, and per capita industrial land area) influencing HFMD epidemics in Xinjiang in 2009 (a, b, c, and d), 2012 (e, f, g, and h), 2015 (i, j, k, and l), and 2018 (m, n, o, and p)."

| [1] |
Alirol, E., Getaz, L., Stoll, B., et al., 2011. Urbanisation and infectious diseases in a globalised world. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 11(2), 131-141.
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70223-1 |
| [2] |
Bie, Q.Q., Qiu, D.S., Hu, H., et al., 2010. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of hand-foot-mouth disease in China. Journal of Geo-information Science. 12(3), 380-384. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2010.00380 |
| [3] |
Chen, C., Lin, H.L., Li, X.Q., 2014. Short-term effects of meteorological factors on children hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangzhou, China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 58, 1605-1614.
doi: 10.1007/s00484-013-0764-6 pmid: 24258319 |
| [4] | Cao, C.X., Li, G.H., Sheng, Z., et al., 2012. Research on the environmental impact factors of hand-foot-mouth disease in Shenzhen, China using RS and GIS technologies. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Munich, Germany. |
| [5] | Department of Housing and Construction of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, 2010-2018. Annual report on urban construction statistics in Xinjiang. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese) |
| [6] |
Fan, C.N., Liu, F.F., Zhao, X., et al., 2020. An alternative comprehensive index to quantify the interactive effect of temperature and relative humidity on hand, foot and mouth disease: A two-stage time series study including 143 cities in mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 740, 140106, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140106.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140106 |
| [7] |
Gong, S.S., Wang, W.W., Chen, H.Y., et al., 2020. Geographical characteristics and influencing factors of the prevalence of hand, foot and mouth disease in Hubei Province. Scientia Geographica Sinica. 40, 999-1009. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.06.016 |
| [8] | Hong, Z.M., Hao, H., Li, C.Y., et al., 2018. Exploration of potential risks of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China using geographically weighted regression model. Sci Rep. 8(1), 1-10. |
| [9] | Hu, M.G., Li, Z.J., Wang, J.F, et al., 2012. Determinants of the incidence of hand, foot and mouth disease in China using geographically weighted regression models. PloS one. 7, 1-8. |
| [10] |
Huang, R.F., Wei, J.T., Li, Z.W., et al., 2021. Spatial-temporal mapping and risk factors for hand foot and mouth disease in northwestern inland China. Plos Neglect. Trop. Dis. 15(3), e0009210, doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009210.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009210 |
| [11] |
Lin, H.L., Zou, H., Wang, Q.Z., et al., 2013. Short-term effect of El Nino-Southern oscillation on pediatric hand, foot and mouth disease in Shenzhen, China. PloS one. 8(7), e65585, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065585.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065585 |
| [12] |
Li, T., Yang, Z., Di, B., et al., 2014. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease and weather factors in Guangzhou, southern China. Epidemiol. Infect. 142(8), 1741-1750.
doi: 10.1017/S0950268813002938 pmid: 24267476 |
| [13] |
Liao, Y.L., Ouyang, R.B., Wang, J.F., et al., 2015. A study of spatiotemporal delay in hand, foot and mouth disease in response to weather variations based on SVD: A case study in Shan-dong Province, China. BMC Public Health. 15(1), 1-10.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-15-1 |
| [14] | Liao, J., Qin, Z., Zuo, Z., et al., 2016. Spatial-temporal mapping of hand foot and mouth disease and the long-term effects associated with climate and socio-economic variables in Sichuan Province, China from 2009 to 2013. Sci. Total Environ. 563, 152-159. |
| [15] | Liao, J.Q., Qin, Z.J., Zuo, Z.L., et al., 2016. Spatial-temporal mapping of hand foot and mouth disease and the long-term effects associated with climate and socio-economic variables in Sichuan Province, China from 2009 to 2013. Sci. Total Environ. 563, 152-159. |
| [16] | Li, Y.C., Li, Y., Zhu, G.G., 2018. A new definition method of climate-sensitive region and its prediction. Acta Geographica Sinica. 73(3), 1283-1295. (in Chinese) |
| [17] |
Li, H., Zhang, M.X., Wang, R., 2019. The effects of regional geographical factors on children's respiratory diseases in Jingyuan, Ningxia. Geographical Research. 38(12), 2889-2898. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020181236 |
| [18] |
Mao, Q., Wang, Y., Bian, L., et al., 2016. EV71 vaccine, a new tool to control outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD). Expert Rev. Vaccines. 15(5), 599-606.
doi: 10.1586/14760584.2016.1138862 |
| [19] | National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, 2018. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of hand foot mouth disease (2018 Edition). Infectious disease information. 31(3), 193-198. (in Chinese) |
| [20] |
Nguyen, H.X., Chu, C., Tran, Q.D., et al., 2019. Temporal relationships between climate variables and hand-foot-mouth disease: a multi-province study in the Mekong Delta Region, Vietnam. Int. J. Biometeorol. 64(3), 389-396.
doi: 10.1007/s00484-019-01824-9 |
| [21] | Niu, W.K., 2012. Epidemiological characteristic and death risk factors of hand, foot and mouth disease in Shandong Province, 2007-2011. MSc Thesis. Jinan: Shandong University. (in Chinese) |
| [22] |
Onozuka, D., Hashizume, M., 2011. The influence of temperature and humidity on the incidence of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 410-411, 119-125.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.09.055 |
| [23] | Qiu, W.Y., Li, L.F., Zhang, J.H., et al., 2017. A bayesian network method considering spatial cluster to evaluate health risk of hand, foot and mouth disease. Journal of Geo-information Science. 19(6), 1036-1048. (in Chinese) |
| [24] |
Qi, H.C., Li, Y., Zhang, J., et al., 2020. Quantifying the risk of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) attributable to meteorological factors in East China: A time series modelling study. Sci. Total Environ. 728(3), 138548, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138548.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138548 |
| [25] |
Shi, N.N., Han, Y., Wang, Q., et al., 2021. Risk assessment of sandstorm diffusion and landscape pattern optimization in southern Xinjiang. Acta Geographica Sinica. 76(1), 73-86. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202101006 |
| [26] |
Song, C., Shi, X., Bo, Y.C., et al., 2019. Exploring spatiotemporal nonstationary effects of climate factors on hand, foot, and mouth disease using Bayesian Spatiotemporally Varying Coefficients (STVC) model in Sichuan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 648, 550-560.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.114 |
| [27] | Stanaway, J.D., 2013. Insights from disease ecology:Focus on hand, foot and mouth disease in China. PhD Dissertation. Washington: University of Washington. |
| [28] |
Wang, H., Du, Z.H., Wang, X.J., et al., 2015. Detecting the association between meteorological factors and hand, foot, and mouth disease using spatial panel data models. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 34, 66-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.03.007 pmid: 25770912 |
| [29] |
Wang, J.F., Li, X.H., Christakos, G., et al., 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 24(1), 107-127.
doi: 10.1080/13658810802443457 |
| [30] |
Wang, J.F, Guo, Y.S., Christakos, G., et al., 2011. Hand, foot and mouth disease: spatiotemporal transmission and climate. Int. J. Health Geogr. 10(1), 1-10.
doi: 10.1186/1476-072X-10-1 |
| [31] |
Wang, J.F., Zhang, T.L., Fu, B.J., 2016. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 67, 250-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.02.052 |
| [32] |
Wang, J.F., Xu, C.D., 2017. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geographica Sinica. 72(1), 116-134. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701010 |
| [33] | Wang, Q., Zhai, P.M., Qin, D.H., 2020. New perspectives on ‘warming-wetting’ trend in Xinjiang, China. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 11(3), 252-260. |
| [34] |
Wang, Y., Feng, Z.J., Yang, Y., 2011. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in china: Patterns of spread and transmissibility. Epidemiology. 22(6), 781-792.
doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e318231d67a pmid: 21968769 |
| [35] |
Wang, Y.J., Lai, Y.S., Du, Z.C., et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in Guangdong Province, China and Potential Predictors, 2009-2012. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 16(7), 1191, doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071191.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071191 |
| [36] | Wu, B.P., Yang, D., Wang, J.F., et al., 2016. Space-time variability and determinants of hand, foot and mouth in Shandong province: a bayesian spatio-temporal modeling approach. Journal of Geo-information Science. 18(12), 1645-1652. (in Chinese) |
| [37] | Xie, L., Wang, H.W., Liu, S.H., et al., 2021. Study on spatiotemporal evolution of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) in China under the influence of meteorological factors. Journal of Geo-information Science. 23(3), 431-442. (in Chinese) |
| [38] | Statistical Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, 2010-2019. Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese) |
| [39] |
Xing, W.J., Liao, Q.H., Viboud, C., 2014. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in China, 2008 moutan epidemiological study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 14(4), 308-318.
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70342-6 |
| [40] | Xu, Y.L., Li, D., 2010. Relationship between Climatic Factors and HFMD in Zhangdian District of Zibo. J. Trop. Med. 10(10), 1237-1239. |
| [41] |
Xu, Z., Hu, W., Jiao, K., et al., 2019a. The effect of temperature on childhood hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangdong Province, China, 2010-2013: a multicity study. BMC Infect. Dis. 19(1), 969-979.
doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4594-y |
| [42] |
Xu, C.D., Zhang, X.X., Xiao, G.X., 2019b. Spatiotemporal decomposition and risk determinants of hand, foot and mouth disease in Henan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 657, 509-516.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.039 |
| [43] |
Yang, Z., Lei, J., Duan, Z.L., et al., 2016. Spatial distribution of population in Xinjiang. Geographical Research. 35(12), 2333-2346. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11821/dlyj201612012 |
| [44] |
Yang, S.Q., Xing, X.Y., Dong, W.H., et al., 2018. The spatio-temporal response of influenza A (H1N1) to meteorological factors in Beijing. Acta Geographica Sinica. 73(3), 460-473. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201803006 |
| [45] |
Yao, J.Q., Chen, Y.N., Guan, X.F., et al., 2022. Recent climate and hydrological changes in a mountain-basin system in Xinjiang, China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 226, 103957, doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103957.
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103957 |
| [46] | Zhang, K.J., 2018. Spatial-temporal distribution and risk prediction research on HFMD in Xi’an, China. MSc Thesis. Xi’an: Fourth Military Medical University. (in Chinese) |
| [47] | Zhang, X.X., 2019. Spatiotemporal patterns and determinants of potential impact factors to hand, foot and mouth disease in Henan province, China. MSc Thesis. Xi’an: Chang’an University. (in Chinese) |
| [48] | Zhang, X.X., Wang, L., Yin, L.C., et al., 2019. Spatial-temporal variation analysis and risk determinants of hand, foot and mouth disease in Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan, China. Journal of Geo-information Science. 21, 398-406. (in Chinese) |
| [49] |
Zhang, X.X., Xu, C.D., Xiao, G.X., 2020. Spatial heterogeneity of the association between temperature and hand, foot, and mouth disease risk in metropolitan and other areas. Sci. Total Environ. 713, 136623, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136623.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136623 |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号