Regional Sustainability ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 100158.doi: 10.1016/j.regsus.2024.100158cstr: 32279.14.j.regsus.2024.100158
• Full Length Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-11-06
Revised:2024-04-28
Accepted:2024-08-21
Published:2024-09-30
Online:2024-09-25
Contact:
GONG Qunxi
E-mail:gongqunxi@cqjtu.edu.cn
GONG Qunxi. Green transformation paths of resource-based cities in China from the configuration perspective[J]. Regional Sustainability, 2024, 5(3): 100158.
Table 1
Details of the selected 113 resource-based cities (RBCs) in China."
| Region | Number of cities | City |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern region | 19 | Zhangjiakou, Chengde, Tangshan, Xingtai, Handan, Xuzhou, Suqian, Huzhou, Nanping, Sanming, Longyan, Dongying, Zibo, Linyi, Zaozhuang, Jining, Tai’an, Shaoguan, and Yunfu cities |
| Central region | 37 | Datong, Shuozhou, Yangquan, Changzhi, Jincheng, Xinzhou, Jinzhong, Linfen, Yuncheng, Lvliang, Suzhou, Huaibei, Bozhou, Huainan, Chuzhou, Ma’anshan, Tongling, Chizhou, Xuancheng, Jingdezhen, Xinyu, Pingxiang, Ganzhou, Yichun, Sanmenxia, Luoyang, Jiaozuo, Hebi, Puyang, Pingdingshan, Nanyang, Ezhou, Huangshi, Hengyang, Chenzhou, Shaoyang, and Loudi cities |
| Western region | 38 | Baotou, Wuhai, Chifeng, Hulun Buir, Ordos, Baise, Hechi, Hezhou, Guangyuan, Nanchong, Guang’an, Zigong, Luzhou, Panzhihua, Dazhou, Ya’an, Liupanshui, Bijie, Anshun, Qujing, Baoshan, Zhaotong, Lijiang, Lincang, Yan’an, Tongchuan, Weinan, Xianyang, Baoji, Yulin, Baiyin, Wuwei, Zhangye, Qingyang, Pingliang, Longnan, Shizuishan, and Karamay cities |
| Northeastern region | 19 | Fuxin, Fushun, Benxi, Anshan, Panjin, Huludao, Songyuan, Jilin, Liaoyuan, Tonghua, Baishan, Heihe, Daqing, Yichun, Hegang, Shuangyashan, Qitaihe, Jixi, and Mudanjiang cities. |
Table 2
Descriptive statistics and variable calibration points."
| Year | Variable | Mean | Standard deviation | Max | Min | Full membership | Cross-over point | Full nonmembership |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | GTE | 0.6668 | 0.2562 | 1.5008 | 0.3429 | 1.0000 | 0.5849 | 0.4775 |
| EE | 44,310 | 38,660 | 256,877 | 8816 | 52,515 | 31,183 | 23,129 | |
| TI | 0.1633 | 0.1468 | 0.8608 | 0.0055 | 0.1854 | 0.1214 | 0.0725 | |
| GS | 0.2928 | 0.1489 | 0.9760 | 0.0001 | 0.3627 | 0.2619 | 0.1840 | |
| ME | 0.3738 | 0.1162 | 0.6684 | 0.1158 | 0.4436 | 0.3779 | 0.2866 | |
| IS | 0.6602 | 0.1670 | 0.9944 | 0.1511 | 0.7973 | 0.6665 | 0.5226 | |
| ES | 0.3966 | 0.0992 | 0.7153 | 0.1019 | 0.4537 | 0.4063 | 0.3377 | |
| URS | 0.5517 | 0.1574 | 0.9758 | 0.1228 | 0.6649 | 0.5639 | 0.4736 | |
| 2016 | GTE | 0.6757 | 0.2930 | 1.5166 | 0.2599 | 1.0000 | 0.5536 | 0.4417 |
| EE | 47,034 | 29,906 | 215,488 | 13,805 | 56,410 | 40,059 | 27,102 | |
| TI | 0.1239 | 0.1480 | 0.5926 | 0.0018 | 0.1471 | 0.0629 | 0.0224 | |
| GS | 0.3187 | 0.1506 | 1.0001 | 0.0540 | 0.4049 | 0.2937 | 0.2106 | |
| ME | 0.3640 | 0.1186 | 0.6922 | 0.1001 | 0.4277 | 0.3754 | 0.2861 | |
| IS | 0.6348 | 0.1785 | 0.9771 | 0.1948 | 0.7774 | 0.6473 | 0.5019 | |
| ES | 0.4140 | 0.1007 | 0.6337 | 0.1458 | 0.4761 | 0.4146 | 0.3621 | |
| URS | 0.4591 | 0.1644 | 0.9164 | 0.0601 | 0.5691 | 0.4684 | 0.3489 | |
| 2019 | GTE | 0.8290 | 0.2179 | 1.2834 | 0.4256 | 1.0000 | 0.7733 | 0.6360 |
| EE | 52,531 | 28,722 | 188,857 | 16,868 | 59,552 | 43,213 | 34,481 | |
| TI | 0.1374 | 0.1543 | 0.6108 | 0.0024 | 0.1748 | 0.0721 | 0.0259 | |
| GS | 0.3166 | 0.1493 | 0.9303 | 0.0254 | 0.3945 | 0.3152 | 0.2029 | |
| ME | 0.3191 | 0.1021 | 0.6317 | 0.0775 | 0.3702 | 0.3156 | 0.2626 | |
| IS | 0.6195 | 0.1746 | 0.9783 | 0.2097 | 0.7686 | 0.6163 | 0.4928 | |
| ES | 0.4370 | 0.0919 | 0.7250 | 0.0795 | 0.4903 | 0.4330 | 0.3944 | |
| URS | 0.4305 | 0.1676 | 0.9189 | 0.0361 | 0.5425 | 0.4408 | 0.3191 |
Table 3
Results of necessary conditions analysis."
| Condition | Consistency | Coverage | Condition | Consistency | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | 0.5322 | 0.5701 | ~ME | 0.5906 | 0.6193 |
| ~EE | 0.5437 | 0.5549 | IS | 0.5262 | 0.5491 |
| TI | 0.5157 | 0.5546 | ~IS | 0.5621 | 0.5887 |
| ~TI | 0.5676 | 0.5771 | ES | 0.5044 | 0.5309 |
| GS | 0.5073 | 0.5222 | ~ES | 0.5852 | 0.6075 |
| ~GS | 0.5584 | 0.5928 | URS | 0.5215 | 0.5447 |
| ME | 0.4937 | 0.5145 | ~URS | 0.5589 | 0.5847 |
Table 4
Conditional configuration analysis of green transformation."
| Variable | Configuration | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | 2b | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| System environment | EE | ● | ● | $\otimes$ | ||||
| TI | ● | ● | ● | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | |||
| GS | - | ● | ● | $\otimes$ | ||||
| ME | - | ● | ● | $\otimes$ | ||||
| System structure | IS | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | ● |
| ES | - | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | ● | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | ||
| URS | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | $\otimes$ | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Consistency | 0.8159 | 0.9157 | 0.8881 | 0.8433 | 0.8100 | 0.8220 | 0.8956 | |
| Raw coverage | 0.0818 | 0.0975 | 0.1021 | 0.0428 | 0.0713 | 0.0571 | 0.0726 | |
| Unique coverage | 0.0252 | 0.0154 | 0.0215 | 0.0266 | 0.0398 | 0.0422 | 0.0562 | |
| Overall solution consistency | 0.8870 | |||||||
| Overall solution coverage | 0.3322 | |||||||
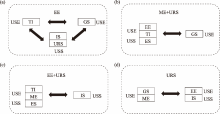
Fig. 2.
Alternative relationship of condition combinations. (a), alternative relationships for configurations 1, 3, and 6; (b), alternative relationships for configurations 4 and 5; (c), alternative relationships for configurations 4 and 6; (d), alternative relationships for configurations 5 and 6. USE, urban system environment; USS, urban system structure."
| [1] | Amara N., Rhaiem M., Halilem N., 2020. Assessing the research efficiency of Canadian scholars in the management field: Evidence from the DEA and fsQCA. J. Bus. Res. 115, 296-306. |
| [2] | Bacon E., Williams M., Davies G., 2020. Coopetition in innovation ecosystems: A comparative analysis of knowledge transfer configurations. J. Bus. Res. 115, 307-316. |
| [3] | Chang H.S., Man C.Y., Su Q., 2021. Research on the site selection of watershed public facilities as multi-use detention basin: An environmental efficiency perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 38649-38663. |
| [4] | Cheng M.L., Wang J.B., Yang S.L., et al., 2024. The driving effect of technological innovation on green development: From the perspective of efficiency. Energ. Policy. 188, 114089, doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2024.114089. |
| [5] | Chuah S.H.W., Tseng M.L., Wu K.J., et al., 2021. Factors influencing the adoption of sharing economy in B2B context in China: Findings from PLS-SEM and fsQCA. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 175, 105892, doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105892. |
| [6] | Dong F., Li Y.F., Qin C., et al., 2021. How industrial convergence affects regional green development efficiency: A spatial conditional process analysis. J. Environ. Manage. 300, 113738, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113738. |
| [7] | Du X.L., Wang Y., Chen F.X., 2024. Evaluation of coal-resource-based cities transformation based on CRITIC-TOPSIS model. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 103, 105271, doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2024.105271. |
| [8] | Du Y.Z., Liu Q.C., Cheng J.Q., 2020. What kind of ecosystem for doing business will contribute to city-level high entrepreneurial activity? A research based on institutional configurations. Journal of Management World. 36, 141-155 (in Chinese). |
| [9] | Du Y.Z., Li J.X., Liu Q.C., et al., 2021. Configurational theory and QCA method from a complex dynamic perspective: Research progress and future directions. Journal of Management World. 37(3), 180-197 (in Chinese). |
| [10] | Duygan M., Fischer M., Pärli R., et al., 2022. Where do smart cities grow? The spatial and socio-economic configurations of smart city development. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 77, 103578, doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103578. |
| [11] | Fan G.G., Wang X.L., Ma G.R., 2011. The contribution of marketization to China’s economic growth. Economic Research Journal. 46, 4-16 (in Chinese). |
| [12] | Fan X.Y., Liu B., Wang K., et al., 2023. Research on the spatiotemporal characteristics of RECC in resource-based cities based on the EWM-CPM: A case study of Sichuan Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 147, 109979, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109979. |
| [13] | Gao J., Wu X.X., Zhang Y., 2020. Research on systematic urban regeneration and implementation way: Based on the complex adaptive system theory. Urban Development Studies. 27(2), 62-68 (in Chinese). |
| [14] | He S.Y., Lee J., Zhou T., et al., 2017. Shrinking cities and resource-based economy: The economic restructuring in China’s mining cities. Cities. 60, 75-83. |
| [15] | He T.T., Song H.P., Chen W.Q., 2023. Recognizing the transformation characteristics of resource-based cities using night-time light remote sensing data: Evidence from 126 cities in China. Resour. Policy. 85, 104013, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.104013. |
| [16] | Hou G.M., 2018. Discussion on the construction of organizational management systematics based on China’s practice in innovational development. China Soft Science. 7, 105-116 (in Chinese). |
| [17] | Hou Y.R., Yang M., Li Y.J., 2024. Coordinated effect of green expansion and carbon reduction: Evidence from sustainable development of resource-based cities in China. J. Environ. Manage. 349, 119534, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119534. |
| [18] |
Hu B.W., Zhou L., Wang Z.H., et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal differentiation of green economic efficiency of resource-based cities in arid area. Resources Science. 42, 383-393 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.02.16 |
| [19] | Jiang C.J., Li J.T., Liu J.L., 2022. Does urbanization affect the gap between urban and rural areas? Evidence from China. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 82, 101271, doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2022.101271. |
| [20] | Jing R., Wang J.P., Shi X., et al., 2020. Influencing factors and models of economic development of China’s resource-based cities from a systematic perspective. Journal of Industrial Technological Economics. 317, 132-142 (in Chinese). |
| [21] | Li B., Dewan H., 2017. Efficiency differences among China’s resource-based cities and their determinants. Resour. Policy. 51, 31-38. |
| [22] | Li J.L., Xu B., 2018. Curse or blessing: How does natural resource abundance affect green economic growth in China? Economic Research Journal. 53(9), 151-167 (in Chinese). |
| [23] | Li M.Y., Yan T.H., 2018. Evaluation of industrial transformation efficiency of China’s resource-based cities based on DEA model and information entropy: Case study of 40 resource-based cities in China. Science and Technology Management Research. 38, 86-93 (in Chinese). |
| [24] | Li Q., Zeng F.E., Liu S., et al., 2020. The effects of China’s sustainable development policy for resource-based cities on local industrial transformation. Resour. Policy. 71, 101940, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101940. |
| [25] | Liao B., Li L., 2022. Spatial division of labor, specialization of green technology innovation process and urban coordinated green development: Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 80, 103778, doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.103778. |
| [26] | Lin J.B., Wang Y.J., Zhang X.H., et al., 2021. Spatial and temporal characteristics and influencing factors of urban resources and environmental efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Journal of Natural Resources. 36(1), 208-222 (in Chinese). |
| [27] | Liu B., Wang J.M., Jing Z.R., et al., 2020. Measurement of sustainable transformation capability of resource-based cities based on fuzzy membership function: A case study of Shanxi Province, China. Resour. Policy. 68, 101739, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101739. |
| [28] | Liu Q., Li F.J., Peng L., et al., 2024. Multiple evaluation framework of sustainability development in resource-based cities: A case study of China. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111338, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111338. |
| [29] | Liu T., Li Y.J., Ren Y.Y., et al., 2019. Economic transformation influencing factors of resources-exhausted cities in China. Resources & Industries. 21(1), 45-53 (in Chinese). |
| [30] | Long R.Y., Li H.F., Wu M.F., et al., 2021. Dynamic evaluation of the green development level of China’s coal-resource-based cities using the TOPSIS method. Resour. Policy. 74, 102415, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102415. |
| [31] | Luo X., Jin Y.Y., Wang C.C., 2017. Research on the green development efficiency of resource-based cities in central China in terms of transformation and upgrading. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University (Social Sciences). 18(6), 77-83 (in Chinese). |
| [32] | Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, 2014. China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2013. Beijing: China Statistics Press (in Chinese). |
| [33] | Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, 2017. China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2016. Beijing: China Statistics Press (in Chinese). |
| [34] | Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, 2020. China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2019. Beijing: China Statistics Press (in Chinese). |
| [35] | Muvingi J., Peer A.A.I., Jablonský J., et al., 2023. Hierarchical groups DEA super-efficiency and group TOPSIS technique: Application on mobile money agents locations. Expert Syst. Appl. 234, 121033, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121033. |
| [36] | National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2014. China Urban Statistical Yearbook 2013. Beijing: China Statistics Press (in Chinese). |
| [37] | National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2017. China Urban Statistical Yearbook 2016. Beijing: China Statistics Press (in Chinese). |
| [38] | National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2020. China Urban Statistical Yearbook 2019. Beijing: China Statistics Press (in Chinese). |
| [39] | Pan M.J., Zhao X., Lv K.J., et al., 2023. Internet development and carbon emission-reduction in the era of digitalization: Where will resource-based cities go? Resour. Policy. 81, 103345, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103345. |
| [40] | Qiu F.D., Yuan H., Zhu C.G., et al., 2018. The industrial transformation effects and influencing factors of regenerative resource-based cities in China. Economic Geography. 38(11), 68-77 (in Chinese). |
| [41] | Ragin C.C., Strand S.I., 2008. Using qualitative comparative analysis to study causal order: Comment on Caren and Panofsky. Sociol. Method. Res. 36(4), 431-441. |
| [42] | Ruan F.L., Yan L., Wang D., 2020. The complexity for the resource-based cities in China on creating sustainable development. Cities. 97, 102571, doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2019.102571. |
| [43] | Ruan F.L., Yan L., Wang D., 2021. Policy effects on the sustainable development of resource-based cities in China: A case study of Yichun City. Resour. Policy. 72, 102145, doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102145. |
| [44] | Ruhlandt R.W.S., Levitt R., Jain R., et al., 2020. One approach does not fit all (smart) cities: Causal recipes for cities’ use of “data and analytics”. Cities. 104, 102800, doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2020.102800. |
| [45] | Schneider C., Wagemann C., 2012. Set-Theoretic Methods for the Social Sciences:A Guide to Qualitative Comparative Analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [46] | Stokke O.S., 2007. Qualitative comparative analysis, shaming, and international regime effectiveness. J. Bus. Res. 60(5), 501-511. |
| [47] | Su Q., 2020. Long-term flood risk assessment of watersheds under climate change based on the game cross-efficiency DEA. Nat. Hazards. 104, 2213-2237. |
| [48] | Sun C.Z., Jiang K., Zhao L.S., 2017. Measurement of green efficiency of water utilization and its spatial pattern in China. Journal of Natural Resources. 32(12), 1999-2011 (in Chinese). |
| [49] | Tao K.T., Zhang S.D., Zhao Y.H., 2021. What does determine performance of government public health governance? A study on co-movement effect based on QCA. Journal of Management World. 37(5), 128-138, 156 (in Chinese). |
| [50] | Tian X.S., Ning Y.C., 2014. The countermeasures research into industries transformation and upgrading approaches of maturing resource-based city: Take the case of Jixi. China Mining Magazine. 23(12), 33-36 (in Chinese). |
| [51] |
Wang X.N., Sun W., 2020. Transformation efficiency of resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin and its influencing factors. Progress in Geography. 39(10), 1643-1655 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.004 |
| [52] | Wang Y.Q., Li Y.Y., Zhu Z.W., et al., 2021. Evaluation of green growth efficiency of oil and gas resource-based cities in China. Clean Technol. Envir. 23, 1785-1795. |
| [53] | Wang Y.J., Chen H., Long R.Y., et al., 2022. Has the sustainable development planning policy promoted the green transformation in China’s resource-based cities? Resour. Conserv. Recy. 180, 106181, doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106181. |
| [54] | Wang Y.J., Chen H., Long R.Y., et al., 2023a. How does population aging affect urban green transition development in China? An empirical analysis based on spatial econometric model. Environ. Impact Asses. 99, 107027, doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2022.107027. |
| [55] | Wang Z.R., Fu H.Q, Zhou L., 2023b. Multiple urban resilience evaluation of resource-based cities’ sustainable transformation effect. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 191, 106912, doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.106912. |
| [56] |
Wen Q., Hou K.Y., Zheng D.Y., et al., 2022. Evaluation of industrial transformation capability and optimization path of growing resource-based cities: A case study of Yulin, China. Scientia Geographica Sinica. 42(4), 682-691 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2022.04.013 |
| [57] | Wu J.X., Nie X., Wang H., 2023. Curse to blessing: The carbon emissions trading system and resource-based cities’ carbon mitigation. Energ. Policy. 183, 113796, doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2023.113796. |
| [58] | Xu J.W., Xu X.Y., Chen X.P., et al., 2013. Evaluation on urban efficiencies of Gansu Province based on DEA-Cross Model. Journal of Natural Resources. 28(4), 618-624 (in Chinese). |
| [59] | Yang Y.Y., Guo H.X., Chen L.F., et al., 2019. Regional analysis of the green development level differences in Chinese mineral resource-based cities. Resour. Policy. 61, 261-272. |
| [60] | Yu J.Y., 2014. Qian Xuesen system scientific thought and system science system. Scientific Decision Making. 12, 2-22 (in Chinese). |
| [61] | Yuan H., Zhu C.L., 2018. Do national high-tech zones promote the transformation and upgrading of China’s industrial structure. China Industrial Economics. 8, 60-77 (in Chinese). |
| [62] | Zhai B., Nie H., 2010. Study on the coordinated urban-rural development in the transformation of resource-based cities-Take Baiyin of Gansu Province as an example. Urban Stud. 17, 68-90. |
| [63] | Zhai X.Q., An Y.F., 2021. The relationship between technological innovation and green transformation efficiency in China: An empirical analysis using spatial panel data. Technol. Soc. 64, 101498, doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101498. |
| [64] | Zhang M., Yan T.H., Ren Q.Z., 2022. Does innovative development drive green economic growth in resource-based cities? Evidence from China. Front. Env. Sci. 9, 745498, doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2021.745498. |
| [65] | Zhao X.C., Long L.C., Yin S., et al., 2023. How technological innovation influences carbon emission efficiency for sustainable development? Evidence from China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 14, 100135, doi: 10.1016/j.resenv.2023.100135. |
| [66] | Zhou J.T., Yu X.W., Chen X., 2023. How does environmental legislation guide urban green transition development? Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manage. 345, 118813, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118813. |
| [67] | Zhou L., Che L., Zhou C.H., et al., 2020. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban green development efficiency in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 30, 724-742. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 REGSUS Wechat
REGSUS Wechat
 新公网安备 65010402001202号
新公网安备 65010402001202号
